
Nymphaea is a genus of hardy and tender aquatic plants in the family Nymphaeaceae. The genus has a cosmopolitan distribution. Many species are cultivated as ornamental plants, and many cultivars have been bred. Some taxa occur as introduced species where they are not native, and some are weeds. Plants of the genus are known commonly as water lilies, or waterlilies in the United Kingdom. The genus name is from the Greek νυμφαία, nymphaia and the Latin nymphaea, which means "water lily" and were inspired by the nymphs of Greek and Latin mythology.

Nymphaea alba, the white waterlily, European white water lily or white nenuphar, is an aquatic flowering plant in the family Nymphaeaceae. It is native to North Africa, temperate Asia, Europe and tropical Asia.

Nuphar lutea, the yellow water-lily, brandy-bottle, or spadderdock, is an aquatic plant of the family Nymphaeaceae, native to northern temperate and some subtropical regions of Europe, northwest Africa, and western Asia. This species was used as a food source and in medicinal practices from prehistoric times with potential research and medical applications going forward.

Nymphaea odorata subsp. tuberosa is a subspecies of Nymphaea odorata native to the region spanning from Central and Eastern Canada, extending to North Central and Northeastern United States.

Nymphaea leibergii, also known as the dwarf waterlily and Leiberg's waterlily, is a perennial emergent aquatic plant belonging to the genus Nymphaea. It can be found across northern North America in ponds and slow moving streams. Populations of this plant are infrequent throughout its range, and it is protected as a state threatened plant in Maine, Michigan, and Minnesota.

Nymphaea nouchali, often known by its synonym Nymphaea stellata, or by common names blue lotus, star lotus, red water lily, dwarf aquarium lily, blue water lily, blue star water lily or manel flower, is a water lily of genus Nymphaea. It is native to southern and eastern parts of Asia, and is the national flower of Bangladesh and Sri Lanka. In Sanskrit it is called utpala. This species is usually considered to include the blue Egyptian lotus N. nouchali var. caerulea. In the past, taxonomic confusion has occurred, with the name Nymphaea nouchali incorrectly applied to Nymphaea pubescens.

Nymphaea thermarum, also known as Pygmy Rwandan water lily, is a species of water lily that is endemic to Rwanda. Once thought to be extinct in the wild, all wild plants were believed to be lost due to destruction of its native habitat, but it was thought to be saved from extinction when it was grown from seed at the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew in 2009. A previously-unknown wild population was discovered in 2023.

Nymphaea gigantea, commonly known as the giant waterlily or blue waterlily, is a perennial, herbaceous plant in the family Nymphaeaceae which is native to parts of northern and eastern Australia, and it has been widely cultivated elsewhere. It is an aquatic plant whose natural habitat is permanent and semi-permanent still water bodies
Nymphaea divaricata is a species of waterlily native to Angola, Zambia, and the Democratic Republic of the Congo.

Nymphaea heudelotii is a species of waterlily native to the region spanning from tropical West Africa to Uganda and Botswana.

Nymphaea vaporalis is a species of waterlily endemic to Queensland, Australia.

Nymphaea gracilis is a species of waterlily endemic to Mexico. It is the only species of its genus which is endemic to Mexico.

Nymphaea immutabilis is a species of waterlily native to Western Australia, the Northern Territory, and Queensland, Australia.

Nymphaea jacobsii is a species of waterlily endemic to Queensland, Australia.

Nymphaea kakaduensis is a species of waterlily endemic to the Northern Territory, Australia.

Nymphaea loriana is a species of waterlily endemic to Manitoba, and Saskatchewan, Canada.

Nymphaea lukei is a species of waterlily endemic to Western Australia.

Nymphaea rubra is a species of waterlily native to the region spanning from Sri Lanka and northeastern India to western and central Malesia. Additionally, it has been introduced to regions such as Southeast China, Cuba, Guyana, Hungary, and Suriname.
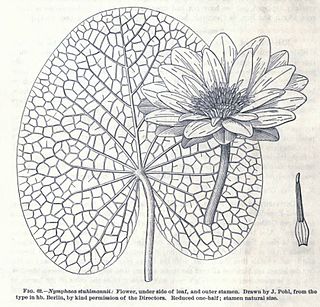
Nymphaea stuhlmannii is a species of waterlily endemic to Tanzania.
Nymphaea nouchali var. ovalifolia is a variety of the water lily species Nymphaea nouchali Burm.f. native to the region spanning from West Tanzania to South Africa.

















