Related Research Articles

Mir was a space station that operated in low Earth orbit from 1986 to 2001, operated by the Soviet Union and later by Russia. Mir was the first modular space station and was assembled in orbit from 1986 to 1996. It had a greater mass than any previous spacecraft. At the time it was the largest artificial satellite in orbit, succeeded by the International Space Station (ISS) after Mir's orbit decayed. The station served as a microgravity research laboratory in which crews conducted experiments in biology, human biology, physics, astronomy, meteorology, and spacecraft systems with a goal of developing technologies required for permanent occupation of space.

The Salyut programme was the first space station programme, undertaken by the Soviet Union. It involved a series of four crewed scientific research space stations and two crewed military reconnaissance space stations over a period of 15 years, from 1971 to 1986. Two other Salyut launches failed. In one respect, Salyut had the task of carrying out long-term research into the problems of living in space and a variety of astronomical, biological and Earth-resources experiments, and on the other hand the USSR used this civilian programme as a cover for the highly secretive military Almaz stations, which flew under the Salyut designation. Salyut 1, the first station in the programme, became the world's first crewed space station.
Human spaceflight programs have been conducted, started, or planned by multiple countries and companies. Until the 21st century, human spaceflight programs were sponsored exclusively by governments, through either the military or civilian space agencies. With the launch of the privately funded SpaceShipOne in 2004, a new category of human spaceflight programs – commercial human spaceflight – arrived. By the end of 2022, three countries and one private company (SpaceX) had successfully launched humans to Earth orbit, and two private companies had launched humans on a suborbital trajectory. The criteria for what constitutes human spaceflight vary. The Fédération Aéronautique Internationale defines spaceflight as any flight over 100 kilometers (62 mi). In the United States professional, military, and commercial astronauts who travel above an altitude of 80 kilometers (50 mi) are awarded the United States Astronaut Badge. This article follows the FAI definition of spaceflight.

Salyut 1 (DOS-1) was the world's first space station launched into low Earth orbit by the Soviet Union on April 19, 1971. The Salyut program followed this with five more successful launches of seven more stations. The final module of the program, Zvezda (DOS-8), became the core of the Russian segment of the International Space Station and remains in orbit.

Salyut 2 (OPS-1) was a Soviet space station which was launched in 1973 as part of the Salyut programme. It was the first Almaz military space station to fly. Within two weeks of its launch, the station had lost attitude control and depressurized, leaving it unusable. Its orbit decayed and it re-entered the atmosphere on 28 May 1973, without any crews having visited it.

Salyut 3 was a Soviet space station launched on 25 June 1974. It was the second Almaz military space station, and the first such station to be launched successfully. It was included in the Salyut program to disguise its true military nature. Due to the military nature of the station, the Soviet Union was reluctant to release information about its design, and about the missions relating to the station.

Salyut 5, also known as OPS-3, was a Soviet space station. Launched in 1976 as part of the Salyut programme, it was the third and last Almaz space station to be launched for the Soviet military. Two Soyuz missions visited the station, each manned by two cosmonauts. A third Soyuz mission attempted to visit the station, but failed to dock, whilst a fourth mission was planned but never launched.

Salyut 6, DOS-5, was a Soviet orbital space station, the eighth station of the Salyut programme. It was launched on 29 September 1977 by a Proton rocket. Salyut 6 was the first space station to receive large numbers of crewed and uncrewed spacecraft for human habitation, crew transfer, international participation and resupply, establishing precedents for station life and operations which were enhanced on Mir and the International Space Station.

Salyut 7 was a space station in low Earth orbit from April 1982 to February 1991. It was first crewed in May 1982 with two crew via Soyuz T-5, and last visited in June 1986, by Soyuz T-15. Various crew and modules were used over its lifetime, including 12 crewed and 15 uncrewed launches in total. Supporting spacecraft included the Soyuz T, Progress, and TKS spacecraft.

The Almaz program was a highly secret Soviet military space station program, begun in the early 1960s.

Soyuz T-15 was a crewed mission to the Mir and Salyut 7 space stations and was part of the Soyuz programme. It marked the final flight of the Soyuz-T spacecraft, the third generation Soyuz spacecraft, which had been in service for seven years from 1979 to 1986. This mission marked the first time that a spacecraft visited, and docked with, two space stations in the same mission.
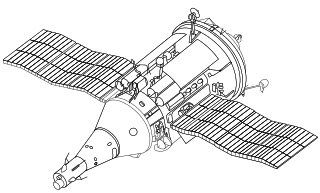
The TKS spacecraft was a Soviet spacecraft conceived in the late 1960s for resupply flights to the military Almaz space station.

Vladimir Nikolayevich Chelomey or Chelomei was a Soviet engineer and designer in missile program of the former Soviet Union. He invented the first Soviet pulse jet engine and was responsible for the development of the world's first anti-ship cruise missiles and ICBM program of Soviet Union such as the UR-100, UR-200, UR-500 and UR-700.

The Vozvraschaemyi Apparat, or VA spacecraft, was a Soviet crew capsule, intended to serve as a crewed launch and reentry vehicle. Initially designed for the LK-1 human lunar flyby spacecraft for one of the Soviet crewed lunar programs, then the LK-700 redesign, it was later repurposed for the Almaz military space station program. The VA capsule on display at the Smithsonian National Air and Space Museum was labeled as Merkur, following a mistranslation of the original documentation – while incorrect, the name is being used in the West for the VA spacecraft and capsule.
Excalibur Almaz was a private spaceflight company which planned to provide a variety of deep space crewed exploration missions, micro-gravity science, and payload delivery. EA also aimed to offer Low Earth Orbit cargo and crew delivery and return.

Kvant-1 (37KE) was the first module to be attached in 1987 to the Mir Core Module, which formed the core of the Soviet space station Mir. It remained attached to Mir until the entire space station was deorbited in 2001.
Kosmos 1686, also known as TKS-4, was a heavily modified TKS spacecraft which docked unmanned to the Soviet space station Salyut 7 as part of tests to attach scientific expansion modules to stations in Earth orbit. The module which docked to the station was the FGB component of a TKS vehicle launched on September 27, 1985, and was designed to test systems planned for use on the Mir Core Module. The spacecraft docked with Salyut 7 on October 2, 1985, during the long-duration stay of the cosmonauts of its fifth principal expedition, which arrived on Soyuz T-14. It was the last flown TKS spacecraft.

The Functional Cargo Block or FGB was part of the Soviet TKS spacecraft. The TKS spacecraft was intended to be used as a resupply craft for Almaz space stations and saw some test flights in the Salyut space station program. The TKS spacecraft was formed by mating a FGB with a VA spacecraft, with both the VA and the FGB being capable of independent operation.

Orel or Oryol, formerly Federation, and PPPTS, is a project by Roscosmos to develop a new-generation, partially reusable crewed spacecraft.
Soyuz 7K-TK was a proposed Soviet spacecraft, which was designed for delivering cosmonauts to Soyuz R piloted military stations. This Soyuz version was equipped with both rendezvous and docking equipment was the basis for the Soyuz 7K-OKS space station ferry which flew two crewed flights in 1971.