
Orbiting Vehicle or OV, originally designated SATAR, comprised five disparate series of standardized American satellites operated by the US Air Force, launched between 1965 and 1971. Forty seven satellites were built, of which forty three were launched and thirty seven reached orbit. With the exception of the OV3 series and OV4-3, they were launched as secondary payloads, using excess space on other missions. This resulted in extremely low launch costs and short proposal-to-orbit times. Typically, OV satellites carried scientific and/or technological experiments, 184 being successfully orbited through the lifespan of the program.

Orbiting Vehicle 2-1, the first satellite of the second series of the United States Air Force's Orbiting Vehicle program, was an American life science research satellite. Its purpose was to determine the extent of the threat posed to astronauts by the Van Allen radiation belts. Launched 15 October 1965, the mission resulted in failure when the upper stage of OV2-1's Titan IIIC booster broke up.

Orbiting Vehicle 1-1, was the first satellite in the OV1 series of the United States Air Force's Orbiting Vehicle program. OV1-1 was an American Earth science research satellite designed to measure radiation, micrometeoroid density, and magnetic fields in orbit. Launched 21 January 1965, the mission resulted in failure when, after a successful launch of its Atlas booster, OV1-1's onboard Altair motor failed to fire.

Orbiting Vehicle 1-3, was the second satellite in the OV1 series of the United States Air Force's Orbiting Vehicle program. OV1-3 was an American life science research satellite designed to measure the effects of orbital radiation on the human body. Launched 28 May 1965, the mission resulted in failure when its Atlas booster exploded two minutes after launch.

Orbiting Vehicle 1-2, launched 5 October 1965, was the third, and first successful, satellite in the OV1 series of the United States Air Force's Orbiting Vehicle program. A radiation measuring satellite designed to conduct research for the planned Manned Orbital Laboratory project, OV1-2 was the first American spacecraft to be placed into orbit on a western trajectory. The satellite stopped functioning in April 1967 after a series of technical problems starting two months after launch.

Orbiting Vehicle 2-3, the second satellite of the second series of the United States Air Force's Orbiting Vehicle program, was an American solar astronomy, geomagnetic and particle science research satellite. Launched 22 December 1965 along with three other satellites, the mission resulted in failure when the spacecraft failed to separate from the upper stage of its Titan IIIC.

Orbiting Vehicle 1-4, launched 30 Mar 1966, was the fourth, and second successful, satellite in the OV1 series of the United States Air Force's Orbiting Vehicle program. OV1-4 was a long-term bioscience and materials science satellite, designed to return data relevant to long-term human presence in space. Its launch marked the first time two satellites were placed into orbit side by side with each other.

Orbiting Vehicle 1-5 was launched 30 Mar 1966, and was the fifth satellite in the OV1 series of the United States Air Force's Orbiting Vehicle program. OV1-5 conducted optical experiments, surveying the Earth in the infrared spectrum to see if water, land, mountains and deserts could be distinguished by their thermal gradients. It was launched concurrently with OV1-4 in the first ever side-by-side satellite orbital deployment.
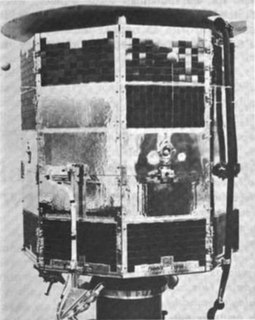
Orbiting Vehicle 3-1, launched 22 April 1966, was the first satellite in the OV3 series of the United States Air Force's Orbiting Vehicle program. The satellite measured radiation above the Earth, returning useful data for over a year. It is still in orbit as of 1 April 2021.

Orbiting Vehicle 3-4, launched 10 June 1966, was the second satellite to be launched in the OV3 series of the United States Air Force's Orbiting Vehicle program. The satellite measured radiation above the Earth, helping to determine the hazard posed to human spaceflight at typically traveled altitudes. OV3-4 is still in orbit as of 6 June 2021.

Orbiting Vehicle 1-7, launched 14 July 1966, was the sixth satellite launched in the OV1 series of the United States Air Force's Orbiting Vehicle program. OV1-7 was a sky science satellite, designed to return data on charged particles in orbit as well as measurements of solar X-rays and nightglow. Co-launched with OV1-8, the satellite was lost when it failed to detach from its launch rocket.

Orbiting Vehicle 1-8, launched 14 July 1966, was the seventh satellite launched in the OV1 series of the United States Air Force's Orbiting Vehicle program. OV1-8 was designed to test the passive communications utility of an aluminum grid sphere versus a balloon satellite.

Orbiting Vehicle 3-3, launched 4 August 1966, was the third satellite to be launched in the OV3 series of the United States Air Force's Orbiting Vehicle program. The satellite measured charged particles in orbit so that their danger to space-based payloads could be assessed. OV3-3 is still in orbit as of 29 July 2021.

Orbiting Vehicle 3-2, launched 28 October 1966, was the fourth satellite to be launched in the OV3 series of the United States Air Force's Orbiting Vehicle program. The satellite measured charged particles in orbit, mapping irregularities in the ionosphere, particularly the auroral zone. OV3-2 reentered the Earth's atmosphere on 29 September 1971.

Orbiting Vehicle 1-6 was launched via Titan IIIC rocket into orbit 2 November 1966 along with two other satellites in the United States Air Force's Orbiting Vehicle series on the first and only Manned Orbiting Laboratory test flight. The eighth satellite in the OV1 series to be launched, OV1-6 was designed to release a number of inflatable spheres, which would then be used in classified tracking experiments conducted on the ground. It is uncertain whether or not the satellite successfully released any of its spheres. OV1-6 reentered the Earth's atmosphere on 31 December 1966.

Orbiting Vehicle 1-9, launched 11 December 1966 along with OV1-10, was the ninth satellite in the OV1 series of the United States Air Force's Orbiting Vehicle program. OV1-9 recorded low frequency radio emissions and particle radiation in Earth's exosphere; the satellite also collected data on the impact of long-term radiation on biological samples and tissue equivalents. OV1-9 returned the first proof that Earth has an electric field.

Orbiting Vehicle 1-10, launched 11 December 1966 along with OV1-9, was the tenth satellite in the OV1 series of the United States Air Force's Orbiting Vehicle program. Designed to observe atmospheric airglow, X-ray and cosmic radiation, OV1-10 returned significant data on the Sun as well as on geophysical phenomena in Earth's magnetic field. OV1-10 reentered Earth's atmosphere on 30 November 2002.
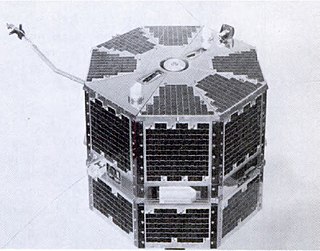
Orbiting Vehicle 3-5, launched 31 January 1967, was the fifth satellite to be launched in the OV3 series of the United States Air Force's Orbiting Vehicle program.

Orbiting Vehicle 1-86 was a satellite launched 27 July 1967 to measure the temperature radiation properties of different types of terrain. Part of the OV1 series of USAF satellites, using standardized designs and sent to orbit on decommissioned Atlas ICBMs to reduce development and launching costs, OV1-86 was launched with two other satellites in the series, OV1-11 and OV1-12, in the first triple launch of the program. It was the only OV1 satellite to be cobbled together from two of its sister satellites, utilizing the unused body on OV1-8 and the unused propulsion module on OV1-6. OV1-86's was only partially successful due to the failure of its Vertistat gravity-gradient_stabilization system. The satellite reentered the Earth's atmosphere on 22 February 1972.

Orbiting Vehicle 1–12 was a satellite launched 27 July 1967 to measure the radiation hazard posed by solar flares. Part of the OV1 series of USAF satellites, using standardized designs and sent to orbit on decommissioned Atlas ICBMs to reduce development and launching costs, OV1-12 was launched with two other satellites in the series, OV1-11 and OV1-86, in the first triple launch of the program. Only partially successful due to an inability to remain stable in orbit, the satellite reentered the Earth's atmosphere on 22 July 1980.














