
The giant catfish, also known as the giant sea catfish, giant salmon catfish, giant marine-catfish, or the khagga, is a species of catfish in the family Ariidae. It was described by Eduard Rüppell in 1837, originally under the genus Bagrus. It inhabits estuaries and occasionally freshwater bodies, in Japan, Australia, Polynesia, southern Vietnam in the Mekong Delta, the Red Sea and the northwestern Indian Ocean. It dwells at a depth range of 10 to 195 m. It reaches a maximum total length of 185 cm (73 in), but usually reaches a TL of 70 cm (28 in).
Occella is a genus of poachers native to the northern Pacific Ocean.
Anatoly Petrovich Andriyashev was a Soviet and Russian ichthyologist, marine biologist, and zoogeographist, notable for his studies of marine fauna of the Arctic and the Northern Pacific.
Gnathophis nystromi is an eel in the family Congridae. It was described by David Starr Jordan and John Otterbein Snyder in 1901, originally under the genus Leptocephalus. It contains two subspecies, Gnathophis nystromi nystromi, and Gnathophis nystromi ginanago, which was described by Hirotoshi Asano in 1958, originally under the genus Rhynchocymba.
Serrivomer sector, known commonly as the sawtooth eel, the saw-tooth snipe or the deep-sea eel, is an eel in the family Serrivomeridae. It was described by Samuel Garman in 1899. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the eastern and western Pacific Ocean, including Japan, Chile, and California, USA. It dwells at a depth range of 0 to 3,243 metres, most often around 305 metres (1,001 ft). Males can reach a maximum total length of 76 centimetres (30 in).
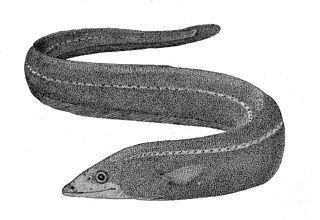
The shortdorsal cutthroat eel is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by Albert Günther in 1887. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the Indo-Pacific and western central Atlantic Ocean, including Zanzibar, Maldives, Australia, Japan, Suriname, and the Gulf of Mexico. It dwells at a depth range of 900 to 3,000 metres, most often between 1,000 to 2,500 metres, and leads a benthic lifestyle, inhabiting the continental slope. Males can reach a maximum total length of 111 centimetres (44 in).
The Kaup's arrowtooth eel is an eel in the family Synaphobranchidae. It was described by James Yate Johnson in 1862. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling eel which is known from the Indo-Western Pacific and eastern and western Atlantic Ocean, including the Faroe Islands, Iceland, Cape Verde, the Western Sahara, Nigeria, Namibia, South Africa, Greenland, France, Saint Pierre and Miquelon, the United Kingdom, Ireland, the Philippines, Portugal, Spain, the Bahamas, Brazil, Canada, Cuba, Japan, Australia, Mauritania, Morocco, and Hawaii. It dwells at a depth range of 120 to 4,800 metres, most often between 400 to 2,200 metres, and inhabits the upper abyssal zone on the continental slope. It is intolerant of the temperatures of higher waters. Males can reach a maximum total length of 100 centimetres (39 in).
The northern spearnose poacher is a fish in the family Agonidae. It was described by David Starr Jordan and Charles Henry Gilbert in 1880, originally under the genus Agonus. It is a marine, temperate water-dwelling fish which is known from the eastern Pacific Ocean, including southeastern Alaska to southern California, USA. It dwells at a depth range of 0 to 163 metres. Males can reach a maximum total length of 20 centimetres (7.9 in).
The sturgeon poacher is a fish in the family Agonidae. It was described by Wilhelm Gottlieb Tilesius von Tilenau in 1813. It is a marine, temperate water-dwelling fish which is known from the northern Pacific Ocean, including the western Bering Sea, Cape Navarin, the Commander Islands, the Sea of Okhotsk, the Aleutian Islands, and northern California, USA. It dwells at a depth range of 2 to 710 metres, and inhabits soft benthic sediments. Males can reach a maximum total length of 30.5 centimetres (12.0 in).
The sawback poacher is a species of fish in the family Agonidae. It was described by Charles Henry Gilbert in 1896, originally under the genus Odontopyxis. It is a marine, temperate water-dwelling fish which is known from the northern Pacific Ocean, including Japan, the Gulf of Anadyr, the Bering Sea, the Aleutian chain, and British Columbia, Canada. It dwells at a depth range of 18 to 975 metres, and inhabits soft sediments. Males can reach a maximum total length of 27 centimetres (11 in).
Sarritor knipowitschi is a poacher fish in the family Agonidae. It was described by Georgii Ustinovich Lindberg and Anatoly Petrovich Andriyashev in 1937, originally as a subspecies of Sarritor leptorhynchus. It is a marine, temperate water-dwelling fish which is known from the Okhotsk Sea and the Sea of Japan, in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. It is known to dwell at a depth range of 30 to 190 metres. Males can reach a maximum standard length of 14.4 centimetres (5.7 in).
The longnose poacher is a fish in the family Agonidae. It was described by Charles Henry Gilbert in 1896, originally under the genus Odontopyxis. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling fish which is known from the northern Pacific Ocean, including the Bering Sea, southeastern Alaska, northern Japan, the Sea of Japan and the Sea of Okhotsk. It dwells at a depth range of 20 to 460 metres. Males can reach a maximum total length of 25 centimetres (9.8 in).
The Bering poacher is a fish in the family Agonidae. It was described by Wilhelm Gottlieb Tilesius von Tilenau in 1813, originally in the genus Agonus. It is a marine, temperate water-dwelling fish which is known from the northern Pacific Ocean, including Kotzebue Sound, the northern Sea of Japan, the Sea of Okhotsk, Akun Island, and the Gulf of Alaska. It dwells at a depth range of 0–325 metres. Males can reach a maximum standard length of 21.6 centimetres.
Occella iburia is a fish in the family Agonidae. It was described by David Starr Jordan and Edwin Chapin Starks in 1904, originally in the genus Occa.
Occella kasawae is a fish in the family Agonidae. It was described by David Starr Jordan and Carl Leavitt Hubbs, originally in the genus Iburiella. It is a marine, temperate water-dwelling fish which is known from the northwestern Pacific Ocean, including the southern Okhotsk Sea and Hokkaido, Japan. It dwells at a depth range of 12–140 metres.

Agonomalus jordani is a fish in the family Agonidae. It was described by David Starr Jordan and Edwin Chapin Starks in 1904.

Agonomalus proboscidalis is a fish in the family Agonidae. It was described by Achille Valenciennes in 1858, originally under the genus Aspidophorus. It is a marine, polar water-dwelling fish which is known from the northwestern Pacific Ocean, including northern Japan, the Sea of Japan, and the Sea of Okhotsk. It is known to dwell at a depth range of 20 to 102 metres. Males can reach a maximum total length of 20 centimetres (7.9 in).

The fourhorn poacher is a fish in the family Agonidae. It was described by Achille Valenciennes in 1829, originally under the genus Aspidophorus. It is a marine, temperate water-dwelling fish which is known from the northern Pacific Ocean, including the Sea of Okhotsk, the Sea of Japan, the Bering Sea, the Kuril Islands, and Washington, USA. It is non-migratory, and dwells at a depth range of 0 to 452 metres, most often at around 100 to 150 metres. It inhabits sediments of sand and gravel. Males can reach a maximum total length of 12 centimetres (4.7 in), but more commonly reach a TL of 10 centimetres (3.9 in). The maximum recorded weight is 24 grams (0.053 lb), and the maximum recorded age is 7 years.

The dragon poacher is a fish in the family Agonidae. It was described by Peter Simon Pallas in 1769, originally under the genus Cottus. It is a marine, deep water-dwelling fish which is known from the northern Pacific Ocean, including the Sea of Japan, the Sea of Okhotsk, and the Bering Sea. It dwells at a depth range of 19 to 750 metres, and inhabits gravel, sand and mud sediments. Males can reach a maximum total length of 42 centimetres (17 in).
The crucifix sea catfish — also known as the Christfish, the crucifix/crucifex catfish, the crucifixfish, or the gillbacker, — is a species of catfish in the family Ariidae.




