Turkmenistan is a landlocked country in Central Asia, bordering the Caspian Sea to the west, Iran and Afghanistan to the south, Uzbekistan to the north-east, and Kazakhstan to the north-west. It is the southernmost republic of the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the loose federation created at the end of 1991 by most of the Post-Soviet states.
Turkmenistan has a state-controlled press and monitored communication systems. Turkmenistan's telecommunications services are considered to be the least developed of all the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) countries. Overall, the telecom market in this predominantly rural country is relatively small but has been trying boldly to expand in recent years. The state-owned Turkmen Telecom has been the primary provider of public telephone, email and internet services, and through a subsidiary has been operating a GSM mobile network in competition with a private mobile operator, BCTI.

Iran has a long paved road system linking most of its towns and all of its cities. In 2011 the country had 173,000 kilometres (107,000 mi) of roads, of which 73% were paved. In 2008 there were nearly 100 passenger cars for every 1,000 inhabitants.

The Karakum Desert, also spelled Kara-Kum and Gara-Gum, is a desert in Central Asia. The name refers to the shale-rich sand beneath the surface. It occupies about 70 percent, or roughly 350,000 km2 (140,000 sq mi), of Turkmenistan.

The Moskva is a river that flows through western Russia. It rises about 140 km (90 mi) west of Moscow and flows roughly east through the Smolensk and Moscow Oblasts, passing through central Moscow. About 110 km (70 mi) southeast of Moscow, at the city of Kolomna, it flows into the Oka, itself a tributary of the Volga, which ultimately flows into the Caspian Sea.

Balkan Region is the westernmost of the five regions of Turkmenistan. Clockwise from north it borders Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan (north); two provinces of Turkmenistan (east), Iran (south), and the Caspian Sea (west). The capital city is Balkanabat, formerly known as Nebit Dag. The region's boundaries are identical to those of the former Krasnovodsk Oblast', a Soviet-era province of the Turkmen Soviet Socialist Republic with its capital in the city of Krasnovodsk. This oblast was liquidated and restored repeatedly in the 20th century, concluding with its abolition in 1988. However, the administrative boundaries of the region were restored in 1991 when Balkan Region was established with its capital being moved to Nebit Dag which was later renamed Balkanabat.

Türkmenbaşy, formerly known as Krasnovodsk, Kyzyl-Su, and Shagadam, is a city in Balkan Province in western Turkmenistan, on the Türkmenbaşy Gulf of the Caspian Sea. It sits at an elevation of 27 metres. The population was 86,800, mostly ethnic Turkmens but also Russian, Armenian and Azeri minorities. As the terminus of the Trans-Caspian Railway and site of a major seaport on the Caspian, it is an important transportation center. The city is also the site of Turkmenistan's largest oil refining complex.

Balkanabat, formerly Nebit-Dag and Neftedag, is the administrative centre of Balkan Province, the largest province in Turkmenistan. It lies at the foot of the Balkan Daglary mountain range. Balkanabat is about 450 km west of Ashgabat and 160 km east of the seaport city of Türkmenbaşy. The city layout is a grid of apartment blocks called kvartal (quarters). The main streets are Magtymguly, Pervomayskiy and Gurbansoltan eje şaýoly.

The Sarygamysh Lake, also Sarykamysh or Sary-Kamysh, is a lake in Central Asia. It is about midway between the Caspian Sea and the (former) Aral Sea. It is the largest lake in Turkmenistan, in which three quarters of the entire lake's area is located. The Sarykamysh basin and the Sarykamysh delta of the Amu Darya river are physical and geographical nature regions of the Dashoguz Region of Turkmenistan.

Pirallahi Island or Pirallakhi Island is an island in the Caspian Sea. The island is part of Azerbaijan and lies off the north-eastern shore of the Apsheron Peninsula, 43 kilometres (27 mi) to the east-north-east of Baku.

The Trans-Caspian Gas Pipeline is a proposed subsea pipeline between Türkmenbaşy in Turkmenistan, and Baku in Azerbaijan. According to some proposals it would also include a connection between the Tengiz Field in Kazakhstan, the Sangachal Terminal in Baku, and Türkmenbaşy. The Trans-Caspian Gas Pipeline project would transport natural gas from Turkmenistan and Kazakhstan to European Union member countries, circumventing both Russia and Iran. It would do this by feeding the Southern Gas Corridor. This project attracts significant interest since it would connect vast Turkmen gas resources to major consumers Turkey and Europe.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Turkmenistan:
Tyuleny Island is an uninhabited island in the Caspian Sea. It belongs to the Dagestan Republic, a federal subject of the Russian Federation.

Chechen Island is a coastal island on the western shore of the Caspian Sea. It is located 20 km east of Krainovka right off the headland on the northern tip of the Agrakhan Peninsula. This island belongs to the Republic of Dagestan, a federal subject of the Russian Federation.

The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake and sometimes referred to as a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia: east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia, south of the fertile plains of Southern Russia in Eastern Europe, and north of the mountainous Iranian Plateau. It covers a surface area of 371,000 km2 (143,000 sq mi), an area approximately equal to that of Japan, with a volume of 78,200 km3 (19,000 cu mi). It has a salinity of approximately 1.2%, about a third of the salinity of average seawater. It is bounded by Kazakhstan to the northeast, Russia to the northwest, Azerbaijan to the southwest, Iran to the south, and Turkmenistan to the southeast.

Bereket, formerly Gazanjyk or Kazandzhik, is a city in Balkan Province in western Turkmenistan. Bereket is the administrative centre of Bereket District.
Protected areas of Turkmenistan include nine nature reserves (zapovednik) and 13 sanctuaries (zakaznik) with a total area of 19,750 km2 or more than 4% of Turkmenistan's territory.

Hazar Nature Reserve is a nature reserve (zapovednik) of Turkmenistan.

The fishing industry in Turkmenistan has been of benefit to the economy of Turkmenistan and food supply, particularly on the Caspian Sea for centuries. The fishing industry took off around 1910 in Turkmenistan but declined between 1950 and 1990, with the banning of sturgeon catching in Turkmen waters. Today, the fishing industry is developing rapidly, due to technological modernization and renewal schemes and the growth of aquaculture. Under the command of the Turkmen president, fishing facilities in the country have been reconstructed and constructed with modern industry infrastructure, particularly in the Caspian Sea 610 km coastline of western Turkmenistan in Balkan Province.

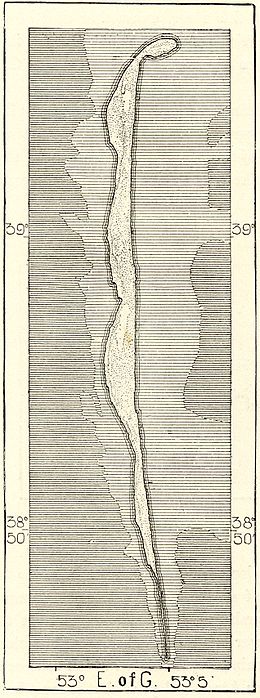
The Cheleken Peninsula is a peninsula located in western Turkmenistan, in the eastern shores of the Caspian Sea.