Lava Beds National Monument is located in northeastern California, in Siskiyou and Modoc counties. The monument lies on the northeastern flank of Medicine Lake Volcano and has the largest total area covered by a volcano in the Cascade Range.

Schonchin Butte is a cinder cone on the northern flank of Medicine Lake Volcano in the Cascade Range in northern California. Frothy lava, cooled in the air, created the large cinder cones throughout Lava Beds National Monument. It is named for Old Schonchin, a chief of the Modoc people during the late nineteenth century. Erupting more than 30,000 years ago, the volcano spewed ash and cinders into the air much like a can of soda when shaken. A lava spatter rampart is at the very top.

Volcanic cones are among the simplest volcanic landforms. They are built by ejecta from a volcanic vent, piling up around the vent in the shape of a cone with a central crater. Volcanic cones are of different types, depending upon the nature and size of the fragments ejected during the eruption. Types of volcanic cones include stratocones, spatter cones, tuff cones, and cinder cones.

Craters of the Moon National Monument and Preserve is a U.S. National Monument and national preserve in the Snake River Plain in central Idaho. It is along US 20, between the small towns of Arco and Carey, at an average elevation of 5,900 feet (1,800 m) above sea level. The protected area's features are volcanic and represent one of the best-preserved flood basalt areas in the continental United States.

Sunset Crater is a cinder cone located north of Flagstaff in U.S. State of Arizona. The crater is within the Sunset Crater Volcano National Monument.
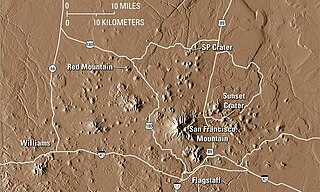
The San Francisco volcanic field is an area of volcanoes in northern Arizona, north of Flagstaff, USA. The field covers 1,800 square miles (4,700 km²) of the southern boundary of the Colorado Plateau. The field contains 600 volcanoes ranging in age from nearly 6 million years old to less than 1,000 years, of which Sunset Crater is the youngest. The highest peak in the field is Humphreys Peak, at Flagstaff's northern perimeter: the peak is Arizona's highest at 12,633 feet and is a part of the San Francisco Peaks, an extinct stratovolcano complex.

Pisgah Crater, or Pisgah Volcano, is a young volcanic cinder cone rising above a lava plain in the Mojave Desert, between Barstow and Needles, California in San Bernardino County, California. The volcanic peak is around 2.5 miles (4.0 km) south of historic U.S. Route 66-National Old Trails Highway and of Interstate 40, and west of the town of Ludlow. The volcano had a historic elevation of 2,638 feet (804 m), but has been reduced to 2,545 feet (776 m) due to mining.

The Coconino National Forest is a 1.856-million acre United States National Forest located in northern Arizona in the vicinity of Flagstaff. Originally established in 1898 as the "San Francisco Mountains National Forest Reserve", the area was designated a U.S. National Forest in 1908 when the San Francisco Mountains National Forest Reserve was merged with lands from other surrounding forest reserves to create the Coconino National Forest. Today, the Coconino National Forest contains diverse landscapes, including deserts, ponderosa pine forests, flatlands, mesas, alpine tundra, and ancient volcanic peaks. The forest surrounds the towns of Sedona and Flagstaff and borders four other national forests; the Kaibab National Forest to the west and northwest, the Prescott National Forest to the southwest, the Tonto National Forest to the south, and the Apache-Sitgreaves National Forest to the southeast. The forest contains all or parts of ten designated wilderness areas, including the Kachina Peaks Wilderness, which includes the summit of the San Francisco Peaks. The headquarters are in Flagstaff. There are local ranger district offices in Flagstaff, Happy Jack, and Sedona.

Lava Butte is a cinder cone in central Oregon, United States, just west of U.S. Route 97 between the towns of Bend, Oregon, and Sunriver, Oregon. It is part of a system of small cinder cones on the northwest flank of Newberry Volcano, a massive shield volcano which rises to the southeast. The cinder cone is capped by a crater which extends about 60 feet (20 m) deep beneath its south rim, and 160 feet (50 m) deep from the 5,020-foot (1,530 m) summit on its north side. Lava Butte is part of the Newberry National Volcanic Monument.

Mount Elden or Elden Mountain is located in central Coconino County northeast of Flagstaff, Arizona. It takes its name from one of the region's earliest Anglo settlers, John Elden, who, along with his family, established a homestead on the mountain's lower slopes and grazed sheep on the open grasslands below during the late 19th century.

The Cima Dome & Volcanic Field National Natural Landmark, or Cinder Cones National Natural Landmark, includes the Cima Dome, Cima Volcanic Field, and Cima Volcanic Range, and is in the Mojave Desert within San Bernardino County, California, United States.

S P Crater is a cinder cone volcano in the San Francisco volcanic field, 25 miles (40 km) north of Flagstaff, Arizona. It is surrounded by several other cinder cones which are older and more eroded. It is a striking feature on the local landscape, with a well-defined lava flow that extends for 4.3 miles (7 km) to the north.
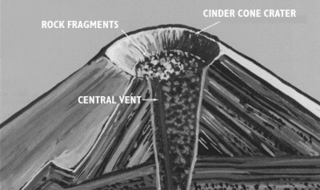
A cinder cone is a steep conical hill of loose pyroclastic fragments, such as either volcanic clinkers, volcanic ash, or cinder that has been built around a volcanic vent. The pyroclastic fragments are formed by explosive eruptions or lava fountains from a single, typically cylindrical, vent. As the gas-charged lava is blown violently into the air, it breaks into small fragments that solidify and fall as either cinders, clinkers, or scoria around the vent to form a cone that often is symmetrical; with slopes between 30–40°; and a nearly circular ground plan. Most cinder cones have a bowl-shaped crater at the summit.

Vulcan's Throne is a cinder cone volcano and a prominent landmark on the North Rim of the Grand Canyon in Arizona, United States. Vulcan's Throne, about a mile (1.7 km) west of Toroweap overlook, is part of the Uinkaret volcanic field. The journals of traveler George Corning Fraser record a trip to the summit of Vulcan's Throne in 1914. At the time, the surrounding area was used for sheep grazing, and a small reservoir had been constructed at the base of the volcano. Fraser wrote that
Vulcan's Throne is a pure cinder cone covered with scoriae, cinders, clinkers and peperino lying loose on the surface, with a slope, as near as I could measure, from 28° to 31°. A little sage, many cacti and perhaps some other similar low plants grow on it, but otherwise nothing. Climbing it was like ascending a sand-dune. Every step forward involved slipping half way back and boots were soon filled with painful bits of stone.

Mount Baldy is a mountain in eastern Arizona in the United States. It is the highest point in the White Mountains and Apache County. It is the fifth-highest point in the state, and the highest outside the San Francisco Peaks in the Flagstaff area. With a summit elevation of 11,409 feet (3,477 m), the peak of Mount Baldy rises above the tree line and is left largely bare of vegetation, lending the mountain its current name.

Roden Crater is a cinder cone type of volcanic cone from an extinct volcano, with a remaining interior volcanic crater. It is located northeast of the city of Flagstaff in northern Arizona, United States.

Red Mountain is a volcanic cinder cone located in the Coconino National Forest of northern Arizona, United States, 25 miles northwest of Flagstaff. It rises 1,000 feet (300 m) above the surroundings terrain and is shaped like the letter "U", with its opening towards the west. Geological Survey (USGS) and Northern Arizona University scientists suggest that Red Mountain was formed in eruptions nearly 740,000 years ago.

Strawberry Crater is a cinder cone volcano, more than 1,000 feet (300 m) high, in the San Francisco volcanic field, 20 miles (32 km) north of Flagstaff, Arizona. It is along Forest Road 545 between the Wupatki National Monument and Sunset Crater National Monument in the Strawberry Crater Wilderness. The crater lies in a volcanic field at a base elevation of about 5,500 feet (1,700 m), and prominence heights of about 6,526 feet (1,989 m). The northwestern end of the crater is covered with lava flows, while the southern end is filled with low cinder cones. Several of the surrounding cones include the better known, taller and younger Sunset Crater in the adjacent Sunset Crater National Monument.
Lenox Crater is a cinder cone located in the San Francisco Volcanic Field in Coconino County, Arizona, an area known for volcanic activity. The volcano erupted approximately 1,000 years ago, filling a small depression with ash and volcanic cinders. The lava flow from the eruption flowed near the base of Sunset Crater. The elevation of the highest point on the rim of Lenox Crater is 7,243 ft, with a topographical prominence of 181 ft. A small trail leads to the top, giving great views of Sunset Crater and the surrounding mountains.