
The Battle of Bình Giã was conducted by the Viet Cong (VC) and People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN) from December 28, 1964, to January 1, 1965, during the Vietnam War in Bình Giã, Phước Tuy province, South Vietnam.

The Battle of Ba Gia was a major battle that marked the beginning of the Viet Cong's (VC) Summer Offensive of 1965, during the early phases of the Vietnam War. The battle took place in Quảng Ngãi Province, South Vietnam, between May 28–31, 1965.

The Republic of Vietnam Marine Division was part of the armed forces of South Vietnam. It was established by Ngo Dinh Diem in 1954 when he was Prime Minister of the State of Vietnam, which became the Republic of Vietnam in 1955. The longest-serving commander was Lieutenant General Le Nguyen Khang. In 1969, the VNMC had a strength of 9,300, 15,000 by 1973, and 20,000 by 1975.

The Seventh Division was part of the Army of the Republic of Vietnam (ARVN), the army of the nation state of South Vietnam that existed from 1955 to 1975. It was part of the IV Corps, which oversaw the Mekong Delta region of the country.

The Fifth Division of the Army of the Republic of Vietnam (ARVN)—the army of the nation state of South Vietnam that existed from 1955 to 1975—was part of the III Corps that oversaw the region of the country surrounding the capital, Saigon.

The 2nd Division was a division of the Army of the Republic of Vietnam (ARVN)—the army of the nation state of South Vietnam that existed from 1955 to 1975. It was part of I Corps that oversaw the northernmost region of South Vietnam.

Operation Truong Cong Dinh, was a United States and Army of the Republic of Vietnam (ARVN) security operation to reestablish South Vietnamese control over the northern Mekong Delta in the aftermath of the Tet Offensive. The operation aimed to root out Viet Cong (VC) forces in the area, and to stop them from attacking traffic on the nearby Highway 4.
Operation Coronado IV was the fourth of the Operation Coronado series of riverine military operations conducted by the U.S. Mobile Riverine Force (MRF), designed to shut down Viet Cong (VC) strongholds in the Mekong Delta. It ran from 19 August to 9 September 1967. It took place in Long An, Gò Công and Kiến Hòa Provinces.
Operation Coronado V was a riverine military operation conducted by the U.S. Mobile Riverine Force (MRF) and elements of the Army of the Republic of Vietnam from 12 September to 5 October 1967 in an attempt to shut down Viet Cong (VC) strongholds in the Mekong Delta. The first part of the operation took place in Định Tường Province. After receiving intelligence that the VC 263rd Main Force battalion had been seen in the region, three Allied battalions were brought in on 12 September by helicopters and boats. Immediately there was heavy contact, and although the Allies reported killing 134, the majority of the VC escaped. Sweeps of the area resulted in another major confrontation with the VC on 15 September. During the four-day period, U.S. and ARVN reported 213 VC killed. The Allied forces then moved into adjoining Kiến Hòa Province. From 5–7 October another encounter with the VC 263rd Battalion resulted and the Allies reported 163 VC killed while losing seven.

Operation Coronado IX was a riverine military operation conducted by the Mobile Riverine Force (MRF) of the United States and elements of the Army of the Republic of Vietnam (ARVN) from November 1967 to January 1968 in an attempt to destroy Viet Cong (VC) strongholds in the Mekong Delta. In the middle of November, clashes resulted in the capture of VC supplies and hideouts. During this period, the VC lost 178 men but killed only 26. For the next few weeks there was little contact, although some abandoned VC bunkers were destroyed and supplies captured. On 4 December, a large engagement occurred when a VC battalion encountered the South Vietnamese 5th Marine Battalion. 266 VC were killed, mostly by the Marines. The Marines lost 40 killed, while the Americans suffered 9 dead. Over the next month and the Christmas period, there was only sporadic skirmishes, but at the start of the new year, there were some medium size battles in which the Americans killed a few dozen VC. After this there was little contact.

Operation Coronado XI was the eleventh of the Operation Coronado series of riverine military operations conducted by the U.S. Mobile Riverine Force (MRF) and units of the Army of the Republic of Vietnam (ARVN), designed to secure Cần Thơ in the aftermath of the Tet Offensive. It ran from 12 February to 3 March 1968.

The Hue–Da Nang Campaign was a series of military actions conducted by the People's Army of Vietnam (PAVN) against the Army of the Republic of Vietnam (ARVN) during the Vietnam War, also known in Vietnam as the American War. The campaign was centred on the cities of Huế and Da Nang, with secondary fronts in the provinces of Quảng Trị and Quảng Ngãi. The campaign began on March 5 and concluded on April 2, 1975.

Đồng Tâm Base Camp is a former U.S. Army, U.S. Navy, and Army of the Republic of Vietnam (ARVN) base west of Mỹ Tho in the Mekong Delta, southern Vietnam.
Operation Kien Giang 9-1 was a joint U.S. and Army of the Republic of Vietnam (ARVN) operation in Dinh Tuong Province from 16–19 November 1967.
Operation Quyet Thang, was a United States Army and Army of the Republic of Vietnam (ARVN) security operation to reestablish South Vietnamese control over the areas immediately around Saigon in the aftermath of the Tet Offensive. The operation started on 11 March 1968 and ended on 7 April 1968.
Operation Enterprise was a U.S. Army pacification and security operation that took place in Long An Province, lasting from 13 February 1967 to 11 March 1968.

The battle of Cholon and Phú Thọ Racetrack began during the early hours of 31 January 1968 and continued until 11 February 1968. The attacks by Vietcong (VC) forces were one of several major attacks around Saigon in the first days of the Tet offensive. The attacks were repulsed with the VC suffering heavy losses and substantial damage to the densely populated area of Cholon.
The War of the flags was a phase of fighting throughout South Vietnam lasting from 23 January to 3 February 1973 as the forces of North and South Vietnam each sought to maximize the territory under their control before the ceasefire in place agreed by the Paris Peace Accords came into effect on 27 January 1973. The fighting continued past the ceasefire date and into early February. South Vietnamese forces made greater territorial gains and inflicted significant losses on the North Vietnamese forces.
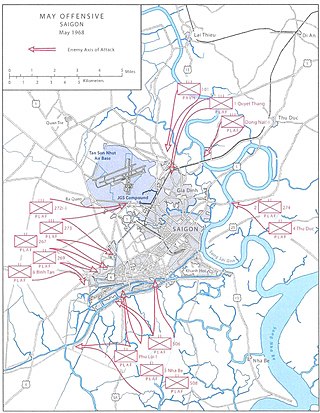
The Battle of West Saigon took place from 5–12 May 1968 during the May Offensive of the Vietnam War as South Vietnamese and United States forces countered the main thrust of the offensive against the western suburbs of Saigon.
Operation Coronado X was the tenth of the Operation Coronado series of riverine military operations conducted by the U.S. Mobile Riverine Force (MRF) and units of the Army of the Republic of Vietnam (ARVN), originally planned as a sweep of western Dinh Tuong Province and eastern Kien Phong Province, however with the outbreak of the Tet Offensive on 31 January 1968 it instead became the MRF reaction to eject Vietcong (VC) forces from Mỹ Tho and Vĩnh Long. It ran from 23 January to 12 February 1968 and resulted in 269 VC killed for the loss of 12 U.S. killed.












