Child sex tourism (CST) is tourism for the purpose of engaging in the prostitution of children, which is commercially facilitated child sexual abuse. The definition of child in the United Nations Convention on the Rights of the Child is "every human being below the age of 18 years". Child sex tourism results in both mental and physical consequences for the exploited children, which may include sexually transmitted infections, "drug addiction, pregnancy, malnutrition, social ostracism, and death", according to the State Department of the United States. Child sex tourism, part of the multibillion-dollar global sex tourism industry, is a form of child prostitution within the wider issue of commercial sexual exploitation of children. Child sex tourism victimizes approximately 2 million children around the world. The children who perform as prostitutes in the child sex tourism trade often have been lured or abducted into sexual slavery.
Operation Ore was a British police operation that commenced in 1999 following information received from US law enforcement, which was intended to prosecute thousands of users of a website reportedly featuring child pornography. It was the United Kingdom's biggest ever computer crime investigation, leading to 7,250 suspects identified, 4,283 homes searched, 3,744 arrests, 1,848 charged, 1,451 convictions, 493 cautioned and 140 children removed from suspected dangerous situations and an estimated 33 suicides. Operation Ore identified and prosecuted some sex offenders, but the validity of the police procedures was later questioned, as errors in the investigations resulted in many false arrests.
Operation Avalanche was a major United States investigation of child pornography on the Internet launched in 1999 after the arrest and conviction of Thomas and Janice Reedy, who operated an Internet pornography business called Landslide Productions in Fort Worth, Texas. It was made public in early August 2001, at the end of Operation Avalanche, that 100 arrests were made out of 144 suspects. It was followed by Operation Ore in the United Kingdom, Operation Snowball in Canada, Operation Pecunia in Germany, Operation Amethyst in Ireland, and Operation Genesis in Switzerland.

Europol, officially the European Union Agency for Law Enforcement Cooperation, is the law enforcement agency of the European Union (EU). Established in 1998, it is based in The Hague, Netherlands, and serves as the central hub for coordinating criminal intelligence and supporting the EU's member states in their efforts to combat various forms of serious and organized crime, as well as terrorism.
Definitions and restrictions on pornography vary across jurisdictions. The production, distribution, and possession of pornographic films, photographs, and similar material are activities that are legal in many but not all countries, providing that any specific people featured in the material have consented to being included and are above a certain age. Various other restrictions often apply as well. The minimum age requirement for performers is most typically 18 years.
Operation Auxin was an Australian Federal Police operation in September 2004, leading to the arrest of almost 200 people on charges of child pornography. These people were all accused of purchasing child pornography over the Internet, using their credit cards, from Belarusian crime syndicates; the credit card payments had been processed by a company named Landslide.com in Fort Lauderdale, Florida. Among the accused were people holding positions of trust in the community, such as police officers, members of the military, teachers, and ministers of religion. Several of the suspects committed suicide. It was the follow-up to the U.S. FBI operation Operation Avalanche. And has been associated with Operation FALCON.
Operation Cathedral was a police operation that broke up a major international child pornography ring called The Wonderland Club operating over the Internet. It was led by the British National Crime Squad in cooperation with 1,500 officers from 13 other police forces around the world, who simultaneously arrested 104 suspects in 13 countries on 2 September 1998. The case received widespread international attention due to the highly organised nature of the ring, leading to public concerns of online child sexual abuse and legislative changes in the UK.
The 2004 Ukrainian child pornography raids occurred a few months before the First Orange Revolution, when police in Ukraine raided a softcore child pornography ring operating in the cities of Kyiv, Kharkiv, and Simferopol. The ring had operated since 2001 and used a modeling agency as a front.

Christopher Paul Neil, better known as Mr. Swirl Face or Vico, is a Canadian convicted child molester. He was the subject of a highly publicized Interpol investigation of the child sexual abuse of at least 12 young boys in Vietnam, Cambodia, and Thailand, primarily owing to the Internet release of pornographic images depicting the abuse. He was arrested by Royal Thai Police in October 2007.
Task Force Argos is a branch of the Queensland Police Service, responsible for the investigation of online child exploitation and abuse. Founded in 1997, the unit's original charter was to investigate institutional child abuse allegations arising from the Forde Inquiry.
Legal frameworks around fictional pornography depicting minors vary depending on country and nature of the material involved. Laws against production, distribution, and consumption of child pornography generally separate images into three categories: real, pseudo, and virtual. Pseudo-photographic child pornography is produced by digitally manipulating non-sexual images of real minors to make pornographic material. Virtual child pornography depicts purely fictional characters. "Fictional pornography depicting minors," as covered in this article, includes these latter two categories, whose legalities vary by jurisdiction, and often differ with each other and with the legality of real child pornography.
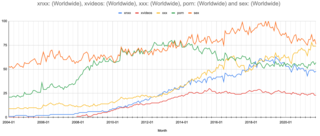
Internet pornography is any pornography that is accessible over the Internet; primarily via websites, FTP connections, peer-to-peer file sharing, or Usenet newsgroups. The greater accessibility of the World Wide Web from the late 1990s led to an incremental growth of Internet pornography, the use of which among adolescents and adults has since become increasingly popular.
The Australian law prohibits all sexual depictions of children under an age set by state and territory legislation. The relevant ages are under 16 in the Australian Capital Territory, New South Wales, Queensland and Western Australia, under 17 in South Australia, and under 18 in the other jurisdictions and under federal law. The laws covering child pornography are differently defined in the various Australian jurisdictions, as are the penalties. The laws also cover depictions of sexual acts involving people over the threshold age who are simulating or otherwise alluding to being underage, even if all those involved are of a legal age. People have been successfully prosecuted after describing acts of abuse via MMS.
Child pornography is illegal in most countries, but there is substantial variation in definitions, categories, penalties, and interpretations of laws. Differences include the definition of "child" under the laws, which can vary with the age of sexual consent; the definition of "child pornography" itself, for example on the basis of medium or degree of reality; and which actions are criminal. Laws surrounding fictional child pornography are a major source of variation between jurisdictions; some maintain distinctions in legality between real and fictive pornography depicting minors, while others regulate fictive material under general laws against child pornography.
Child pornography is erotic material that depicts persons under the designated age of majority. The precise characteristics of what constitutes child pornography varies by criminal jurisdiction.
In the Netherlands, child pornography is illegal, making it one of the 103 out of 193 UN member states where it is illegal.
Operation Delego was a major international child pornography investigation, launched in 2009, which dismantled an international pedophile ring that operated an invitation-only Internet site named Dreamboard which featured incentives for images of the violent sexual abuse of young children under twelve, including infants. Only 72 charges were filed against the approximately 600 members of Dreamboard due to the extensive encryption involved. Members were required to upload new material at least every 50 days to maintain their access and remain in good standing.
Project Spade, an international police investigation into child pornography, began in October 2010 in Toronto, Canada. The investigation started when Toronto Police Service officers made on-line contact with a man who was alleged to have been sharing pornographic videos via the Internet and by mail. The investigation eventually covered over 50 countries. 348 people were arrested internationally, and 386 children were said to have been rescued. The primary producers were Igor Rusanov and Andrey Ivanov in Crimea, Ukraine, Markus Roth in Romania, and Paul Kruger in Germany.
Cybersex trafficking, live streaming sexual abuse, webcam sex tourism/abuse or ICTs -facilitated sexual exploitation is a cybercrime involving sex trafficking and the live streaming of coerced sexual acts and/or rape on webcam.
Operation Lobos, also known as Operation Wolves, was a Brazilian-centered 12-country multinational operation to target the operations of a TOR onion service known as Baby Heart. Additional objectives and targets of the joint operation were the deanonymization of the TOR host servers, TOR administrators, and TOR users associated with the target website and several other targeted websites/chat-sites that were alleged to contain or be used to traffic illegal images of child sexual abuse materials (CSAM) and other categories of legal nude and non-nude images of persons under 18. As of February 2024, the complete list of target websites/chat-sites involved in this operation has not been released by any government; however, the primary targets appeared to be the following: Baby Heart, Hurt-meh, Boyvids 4.0, Anjos Prohibidos (BR)/Forbidden Angels, and Loli Lust. Court documents have indicated that there were at least two other websites/chat-sites that were targeted; however, the names of the websites/chat-sites have not been made public.


