
Antoine Laurent de Jussieu was a French botanist, notable as the first to publish a natural classification of flowering plants; much of his system remains in use today. His classification was based on an extended unpublished work by his uncle, the botanist Bernard de Jussieu.

The Monimiaceae is a family of flowering plants in the magnoliid order Laurales. It is closely related to the families Hernandiaceae and Lauraceae. It consists of shrubs, small trees, and a few lianas of the tropics and subtropics, mostly in the southern hemisphere. The largest center of diversity is New Guinea, with about 75 species. Lesser centres of diversity are Madagascar, Australia, and the neotropics. Africa has one species, Xymalos monospora, as does Southern Chile. Several species are distributed through Malesia and the southwest Pacific.

Southwest Australia is a biogeographic region in Western Australia. It includes the Mediterranean-climate area of southwestern Australia, which is home to a diverse and distinctive flora and fauna.

Jacques-Julien Houtou de Labillardière was a French biologist noted for his descriptions of the flora of Australia. Labillardière was a member of a voyage in search of the La Pérouse expedition. He published a popular account of his journey and produced the first Flora on the region.

Banksia ser. Dryandra is a series of 94 species of shrub to small tree in the plant genus Banksia. It was considered a separate genus named Dryandra until early 2007, when it was merged into Banksia on the basis of extensive molecular and morphological evidence that Banksia was paraphyletic with respect to Dryandra.

Banksia nivea, commonly known as honeypot dryandra, is a species of rounded shrub that is endemic to Western Australia. The Noongar peoples know the plant as bulgalla. It has linear, pinnatipartite leaves with triangular lobes, heads of cream-coloured and orange or red flowers and glabrous, egg-shaped follicles.

Louis René Étienne Tulasne, a.k.a. Edmond Tulasne was a French botanist and mycologist born in Azay-le-Rideau.

The flora of Western Australia comprises 10,842 published native vascular plant species and a further 1,030 unpublished species. They occur within 1,543 genera from 211 families; there are also 1,335 naturalised alien or invasive plant species more commonly known as weeds. There are an estimated 150,000 cryptogam species or nonvascular plants which include lichens, and fungi although only 1,786 species have been published, with 948 algae and 672 lichen the majority.

Hibbertia cuneiformis, commonly known as cut-leaf hibbertia, is species of erect or sprawling shrub that is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It grows to between 1 and 2 m tall and has yellow flowers which appear from January to March or from June to November in the species' native range.

Seringia hermanniifolia, commonly known as crinkle-leaved firebush, is a species of flowering plant in the mallow family and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is a low-growing or prostrate, suckering shrub with hairy new growth, hairy, wavy, oblong to egg-shaped leaves and mauve to bluish flowers arranged in groups of 3 to 8.
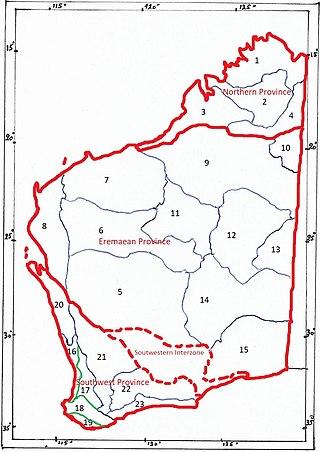
The botanical provinces of Western Australia (or Beard's Provinces) delineate "natural" phytogeographic regions of WA, based on climate and types of vegetation. John Stanley Beard, in "Plant Life of Western Australia" (p. 29-37) gives a short history of the various mappings.

The Pilbara shrublands is a deserts and xeric shrublands ecoregion in Western Australia. It is coterminous with the Pilbara IBRA region. For other definitions and uses of "Pilbara region" see Pilbara.

Opercularia echinocephala is a species of plant within the genus Opercularia, in the family Rubiaceae. It is endemic to the southwest of Western Australia.

Billardiera fusiformis, commonly known as Australian bluebell, is a species of flowering plant in the family Pittosporaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is a sturdy, shrubby climber that has linear to narrowly elliptic leaves and blue, white or pink, nodding flowers arranged singly or in groups of up to four.
Dendrobium affine, commonly known as the white butterfly orchid, malakmalak or matngala in Australian Aboriginal languages is an epiphytic orchid in the family Orchidaceae. It has cylindrical pseudobulbs, each with up to ten leaves and flowering stems with up to twenty white flowers with yellow or purple markings on the labellum. It occurs in northern Australia, New Guinea and Timor, where it grows on the bark of trees.

Hibbertia subvaginata is a species of flowering plant in the family Dilleniaceae and is endemic to Western Australia. It is a small shrub that has yellow flowers with stamens arranged around three or four carpels.

Opercularia apiciflora is a plant in the Rubiaceae family. It was first described in 1804 by Jacques Labillardière. There are no synonyms.

Hibbertia vaginata is a species of flowering plant in the family Dilleniaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is an erect, spreading shrub that typically grows to a height of 20–75 cm (7.9–29.5 in).

Thomasia discolor is a species of flowering plant in the family Malvaceae and is endemic to the south-west of Western Australia. It is a multi-stemmed shrub with densely hairy branchlets, coarsely serrated, egg-shaped leaves with a heart-shaped base, and many small pink, cream-coloured or white flowers.

Garuga floribunda, commonly known as garuga, is a plant in the frankincense and myrrh family Burseraceae, with a broad distribution from northeastern India through southeast Asia and northern Australia to the southwestern Pacific. It is a tree up to 36 m (118 ft) tall and a trunk diameter up to 90 cm (35 in). The compound leaves are about 38 cm (15 in) long, arranged spirally and clustered near the tips of the branches. The leaflets are odd in number, with dentate margins, and measure up to 10 cm (3.9 in) long by 5 cm (2.0 in) wide.





















