
Scorpions are predatory arachnids of the order Scorpiones. They have eight legs, and are easily recognized by a pair of grasping pincers and a narrow, segmented tail, often carried in a characteristic forward curve over the back and always ending with a stinger. The evolutionary history of scorpions goes back 435 million years. They mainly live in deserts but have adapted to a wide range of environmental conditions, and can be found on all continents except Antarctica. There are over 2,500 described species, with 22 extant (living) families recognized to date. Their taxonomy is being revised to account for 21st-century genomic studies.

A pseudoscorpion, also known as a false scorpion or book scorpion, is an arachnid belonging to the order Pseudoscorpiones, also known as Pseudoscorpionida or Chelonethida.

Palpigrades, commonly known as microwhip scorpions, are arachnids belonging to the order Palpigradi.

Thelyphonida is an arachnid order comprising invertebrates commonly known as whip scorpions or vinegaroons. They are often called uropygids in the scientific community based on an alternative name for the order, Uropygi. The name "whip scorpion" refers to their resemblance to true scorpions and possession of a whiplike tail, and "vinegaroon" refers to their ability when attacked to discharge an offensive, vinegar-smelling liquid, which contains acetic acid.

Solifugae is an order of animals in the class Arachnida known variously as camel spiders, wind scorpions, sun spiders, or solifuges. The order includes more than 1,000 described species in about 153 genera. Despite the common names, they are neither true scorpions nor true spiders. Most species of Solifugae live in dry climates and feed opportunistically on ground-dwelling arthropods and other small animals. The largest species grow to a length of 12–15 cm (5–6 in), including legs. A number of urban legends exaggerate the size and speed of the Solifugae, and their potential danger to humans, which is negligible.

The emperor scorpion, Pandinus imperator, is a species of scorpion native to rainforests and savannas in West Africa. It is one of the largest scorpions in the world and lives for 6–8 years. Its body is black, but like other scorpions it glows pastel green or blue under ultraviolet light. It is a popular species in the pet trade, and is protected by CITES.

A gravel road is a type of unpaved road surfaced with gravel that has been brought to the site from a quarry or stream bed. They are common in less-developed nations, and also in the rural areas of developed nations such as Canada and the United States. In New Zealand, and other Commonwealth countries, they may be known as metal roads. They may be referred to as "dirt roads" in common speech, but that term is used more for unimproved roads with no surface material added. If well constructed and maintained, a gravel road is an all-weather road.

Hadrurus arizonensis, the giant desert hairy scorpion, giant hairy scorpion, or Arizona Desert hairy scorpion is the largest scorpion in North America, and one of the 8–9 species of Hadrurus in the United States, attaining a length of 14 cm (5.5 in). Its large size allows it to feed easily on other scorpions and a variety of other prey, including lizards and snakes. They have also been known to take down or fight with the Giant Desert Centipedes of Arizona. This species is usually yellow with a dark top and has crab-like pincers. It gets its common names from the brown hairs that cover its body. These hairs help it to detect vibration in the soil. A similar species is the Hadrurus spadix.

Parabuthus transvaalicus is a species of venomous scorpion from semi-arid parts of southern Africa.

Opistophthalmus is a genus of scorpions known commonly as burrowing scorpions, tricolored scorpions, serkets, or hissing scorpions. They are found predominantly in southern Africa. They are known for making deep and elaborate burrows.

Scorpio maurus is a species of North African and Middle Eastern scorpion, also known as the large-clawed scorpion or Israeli gold scorpion.

Broomistega is an extinct genus of temnospondyl amphibian in the family Rhinesuchidae. It is known from one species, Broomistega putterilli, which was named in 2000. Fossils are known from the Early Triassic Lystrosaurus Assemblage Zone of the Beaufort Group in the Karoo Basin of present-day South Africa, a region that had been an enclave of Gondwana. Specimens of B. putterilli were once thought to represent young individuals of another larger rhinesuchid such as Uranocentrodon, but the species is now regarded as a paedomorphic taxon, possessing the features of juvenile rhinesuchids into adulthood.
Buthacus is a genus of scorpion of the family Buthidae. It is distributed across northern and western Africa, Israel, Palestine, Jordan, Syria, the Arabian Peninsula, Iraq, Iran, Afghanistan, and Pakistan.

Androctonus australis is a hardy desert scorpion from North Africa, Somaliland, the Middle East, Pakistan and India. A. australis, along with A. amoreuxi and Pandinus imperator, is the most commonly available scorpions found in the exotic animal trade.

Parabuthus is a genus of large and highly venomous Afrotropical scorpions, that show a preference for areas of low rainfall. Their stings are medically important and human fatalities have been recorded.

The robust burrowing scorpion is a widespread species of scorpion in the drier regions of southern Africa. It is a burrowing scorpion, which often places its burrow beside a large rock. Compared to others of its genus, it has a particularly sturdy body with large pinchers.

Urodacus yaschenkoi, commonly known as the inland robust scorpion, is a species of scorpion belonging to the subfamily Urodacinae. It is native to central Australia.

Parabuthus granulatus, commonly known as the granulated thick-tailed scorpion, a large species of scorpion from the drier parts of southern Africa. It measures some 11.5 cm, and is dark yellow to brown in colour. It has a relatively small vesicle, but is one of the more venomous scorpion species of the region. Of all scorpion species, it causes most of the serious cases of envenomation in South Africa, and a few people die each year from their sting.
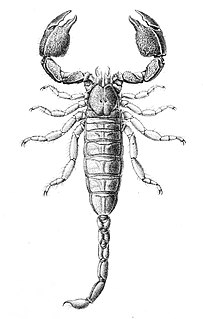
Cheloctonus jonesii is a species of scorpion in the family Hemiscorpiidae (Liochelidae) native to southern Africa.

Chelostoma florisomne, the large scissor-bee, is a species of hymenopteran in the family Megachilidae.




















