
A cactus is a member of the plant family Cactaceae, a family comprising about 127 genera with some 1750 known species of the order Caryophyllales. The word "cactus" derives, through Latin, from the Ancient Greek κάκτος, kaktos, a name originally used by Theophrastus for a spiny plant whose identity is now not certain. Cacti occur in a wide range of shapes and sizes. Most cacti live in habitats subject to at least some drought. Many live in extremely dry environments, even being found in the Atacama Desert, one of the driest places on earth. Cacti show many adaptations to conserve water. Almost all cacti are succulents, meaning they have thickened, fleshy parts adapted to store water. Unlike many other succulents, the stem is the only part of most cacti where this vital process takes place. Most species of cacti have lost true leaves, retaining only spines, which are highly modified leaves. As well as defending against herbivores, spines help prevent water loss by reducing air flow close to the cactus and providing some shade. In the absence of leaves, enlarged stems carry out photosynthesis. Cacti are native to the Americas, ranging from Patagonia in the south to parts of western Canada in the north—except for Rhipsalis baccifera, which also grows in Africa and Sri Lanka.

Nopal is a common name in Spanish for Opuntia cacti, as well as for its pads.

Opuntia microdasys is a species of flowering plant in the cactus family Cactaceae, native and endemic to central and northern Mexico.

Opuntia ficus-indica, the prickly pear, is a species of cactus that has long been a domesticated crop plant grown in agricultural economies throughout arid and semiarid parts of the world. Likely having originated in Mexico, O. ficus-indica is the most widespread and most commercially important cactus.

Cylindropuntia is a genus of cacti, containing species commonly known as chollas, native to northern Mexico and the Southwestern United States. They are known for their barbed spines that tenaciously attach to skin, fur, and clothing. Stands of cholla are called cholla gardens. Individuals within these colonies often exhibit the same DNA, as they were formerly tubercles of an original plant.

Amphisbaena fuliginosa, also known as the black-and-white worm lizard, speckled worm lizard or spotted worm lizard, is a species of amphisbaenian in the genus Amphisbaena. The ecology of A. fuliginosa is poorly known due to its fossorial habits. However, this species can be easily distinguished from others because of its characteristic white and black mosaic pattern that covers both the dorsal and ventral side.

The sooty grassquit is a small bird. It is recognized as a tanager closely related to Darwins finches.
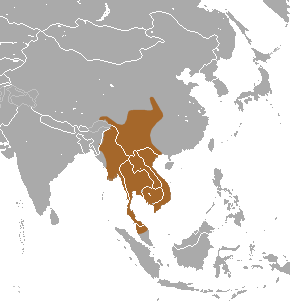
The Southeast Asian shrew is a species of mammal in the family Soricidae. It is found in Cambodia, India, China, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, Thailand, and Vietnam.

Macropidia fuliginosa, the sole species of genus Macropidia, is a perennial rhizomatous flowering plant. Commonly known as the black kangaroo paw, it is endemic to Southwest Australia, specifically from Perth to Geraldton in the north of the region.

Opuntia basilaris, the beavertail cactus or beavertail pricklypear, is a cactus species found in the southwest United States. It occurs mostly in the Mojave, Anza-Borrego, and Colorado Deserts, as well as in the Colorado Plateau and northwest Mexico. It is also found throughout the Grand Canyon and Colorado River region as well as into southern Utah and Nevada, and in the western Arizona regions along the Lower Colorado River Valley.

Opuntia humifusa, commonly known as the devil's-tongue, Eastern prickly pear or Indian fig, is a cactus of the genus Opuntia present in parts of eastern North America.

Phragmatobia fuliginosa, the ruby tiger, is a moth of the family Erebidae.

Opuntia, commonly called prickly pear, is a genus of flowering plants in the cactus family Cactaceae. Prickly pears are also known as tuna (fruit), sabra, nopal from the Nahuatl word nōpalli for the pads, or nostle, from the Nahuatl word nōchtli for the fruit; or paddle cactus. The genus is named for the Ancient Greek city of Opus, where, according to Theophrastus, an edible plant grew and could be propagated by rooting its leaves. The most common culinary species is the Indian fig opuntia.

Opuntia littoralis is a species of prickly pear cactus known by the common name coastal pricklypear. It is sometimes called the sprawling prickly pear due to its short stems and habit of growing close to the ground. "Littoral" means "pertaining to the seashore".
Caladenia fuliginosa is a plant in the orchid family Orchidaceae and is endemic to the Yorke Peninsula in South Australia. It is a ground orchid with a single hairy leaf and a single relatively large, creamy-yellow flower, sometimes with reddish lines. The flowers have a smell resembling hot metal.

Synchita fuliginosa is a species of cylindrical bark beetle in the family Zopheridae. It is found in North America.

Opuntia elata is a species of cactus found in Bolivia, Paraguay, southern Brazil, northern Argentina, and Uruguay.

Opuntia stenopetala is a species of columnar cactus found in Mexico.

Opuntia quitensis is a species of columnar cactus found in Peru and Ecuador.

Opuntia nemoralis is a species of cactus (Cactaceae) native to the United States. It is found in the South-Central region, in the states of Arkansas, Louisiana, Texas, and with a single specimen tentatively identified from Missouri. Its natural habitat is in sandy prairies, saline and sodic barrens, and rock outcrops.




















