
Hydnoroideae is a subfamily of parasitic flowering plants in the order Piperales. Traditionally, and as recently as the APG III system it given family rank under the name Hydnoraceae. It is now submerged in the Aristolochiaceae. It contains two genera, Hydnora and Prosopanche:
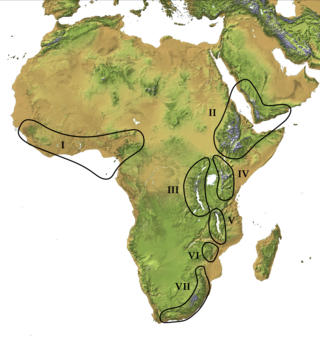
The Afromontane regions are subregions of the Afrotropical realm, one of the Earth's eight biogeographic realms, covering the plant and animal species found in the mountains of Africa and the southern Arabian Peninsula. The Afromontane regions of Africa are discontinuous, separated from each other by lower-lying areas, and are sometimes referred to as the Afromontane archipelago, as their distribution is analogous to a series of sky islands.

Sparrmannia africana, the African hemp or African linden, is a species of flowering plant in the mallow family Malvaceae, native to open woodland in South Africa and Madagascar. It is one of up to seven species in the genus Sparrmannia. The genus name is after Anders Sparrman.

Prunus africana, the African cherry, has a wide distribution in Africa, occurring in montane regions of central and southern Africa and on the islands of Bioko, São-Tomé, Grande Comore, and Madagascar. It can be found at 900–3,400 m (3,000–10,000 ft) above sea level. It is a canopy tree 30–40 m in height, and is the tallest member of Prunus. Large-diameter trees have impressive, spreading crowns. It requires a moist climate, 900–3,400 mm (35–130 in) annual rainfall, and is moderately frost-tolerant. P. africana appears to be a light-demanding, secondary-forest species.

The rufous-naped lark or rufous-naped bush lark is a widespread and conspicuous species of lark in the lightly wooded grasslands, open savannas and farmlands of the Afrotropics. Males attract attention to themselves by a bold and often repeated wing-fluttering display from a prominent perch, which is accompanied by a melodious and far-carrying whistled phrase. This rudimentary display has been proposed as the precursor to the wing-clapping displays of other bush lark species. They have consistently rufous outer wings and a short erectile crest, but the remaining plumage hues and markings are individually and geographically variable. It has a straight lower, and longish, curved upper mandible.

Burkea africana, the wild syringa, is a deciduous, medium-sized, spreading, flat-topped tree which grows in the woodlands and savannas of sub-Saharan Africa. It is the sole species in genus Burkea, which belongs to the subfamily Caesalpinioideae of the family Fabaceae.
P. africana may refer to:
A. africana may refer to:
T. africana may refer to:

Celtis africana, the white stinkwood, is a deciduous tree in the family Cannabaceae. Its habit ranges from a tall tree in forest to a medium-sized tree in bushveld and open country, and a shrub on rocky soil. It occurs in Yemen and Somaliland and over large parts of Africa south of the Sahara. It is a common tree in the south and east of southern Africa, where the odour given off by freshly-cut green timber is similar to that of Ocotea bullata or black stinkwood.

Areas of forest which grow in KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa mostly on south facing slopes in higher rainfall areas, and along the humid coastal areas. Different types of forest can be identified by their species composition which depends mostly on the altitude, latitude and substrate in which they grow. South facing slopes are favourable for the development of forest as they are more shaded, and therefore cooler and retain more moisture than the northern slopes. The extra moisture on the south slopes is not only favoured by forest trees, but also helps to prevent or subdue wildfires. Fires can also be blocked by cliff faces and rocks or boulders on these slopes, and by streams or rivers at the base of the slopes. The coastal regions are conducive to forest formation, because of high rainfall and humidity which are favoured by forest trees and also help to prevent or subdue fires. The rivers of the coastal areas are also broader than further inland, which may often prevent fires from spreading long distances, and fires generally burn uphill and therefore more often away from areas at low altitude.

Myrsine africana, also called Cape myrtle, African boxwood or thakisa, is a species of shrub in the family Primulaceae. It is indigenous to Southern and Eastern Africa, the Azores, the Arabian Peninsula, South Asia and East Asia.

Southern Afrotemperate Forest is a kind of tall, shady, multilayered indigenous South African forest. This is the main forest-type in the south-western part of South Africa, naturally extending from the Cape Peninsula in the west, as far as Port Elizabeth in the east. In this range, it usually occurs in small forest pockets, surrounded by fynbos vegetation.
Zandvlei Estuary Nature Reserve is a 300-hectare (740-acre) nature reserve and recreational area located in Muizenberg near Cape Town, South Africa.
Commiphora africana, commonly called African myrrh, is a small deciduous tree belonging to the Burseraceae, a family akin to the Anacardiaceae, occurring widely over sub-Saharan Africa in Angola, Botswana, Burkina Faso, Chad, Eswatini, Eritrea, Ethiopia, Kenya, Mali, Mauritania, Mozambique, Namibia, Niger, Senegal, Somalia, South Africa, Sudan, Tanzania, Uganda, Zambia and Zimbabwe. On sandy soils this species sometimes forms pure stands, deserving consideration as a plant community or association.

The Free State National Botanical Garden, located just outside Bloemfontein covers 70 hectares, and is home to about 400 species of plants, largely native to Free State and Northern Cape Provinces and Lesotho. Near Bain's Vlei, the garden was established in 1965, around 10 km north of downtown between picturesque dolerite rocks. 140 bird species, 50 mammal species, and 50 reptile species live in the park. A wild olive tree there is probably more than 200 years old. The herbarium preserves 50,000 species. There is also a bird hide, a dam, and wide lawns.

Commelina africana, the common yellow commelina, is a widespread species of flowering plant in the family Commelinaceae. It is native to Sub‑Saharan Africa, Madagascar, Réunion, and the Arabian Peninsula, and has been introduced to India. It is occasionally consumed as a leaf vegetable, and occasionally fed to rabbits and pigs.











