Related Research Articles

Biology – The natural science that studies life. Areas of focus include structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy.
Complexity characterises the behaviour of a system or model whose components interact in multiple ways and follow local rules, leading to non-linearity, randomness, collective dynamics, hierarchy, and emergence.
Systems theory is the transdisciplinary study of systems, i.e. cohesive groups of interrelated, interdependent components that can be natural or artificial. Every system has causal boundaries, is influenced by its context, defined by its structure, function and role, and expressed through its relations with other systems. A system is "more than the sum of its parts" by expressing synergy or emergent behavior.

In philosophy, systems theory, science, and art, emergence occurs when a complex entity has properties or behaviors that its parts do not have on their own, and emerge only when they interact in a wider whole.

Biomechanics is the study of the structure, function and motion of the mechanical aspects of biological systems, at any level from whole organisms to organs, cells and cell organelles, using the methods of mechanics. Biomechanics is a branch of biophysics.

A superorganism, or supraorganism, is a group of synergetically-interacting organisms of the same species. A community of synergetically-interacting organisms of different species is called a holobiont.
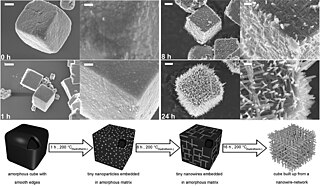
Self-organization, also called spontaneous order in the social sciences, is a process where some form of overall order arises from local interactions between parts of an initially disordered system. The process can be spontaneous when sufficient energy is available, not needing control by any external agent. It is often triggered by seemingly random fluctuations, amplified by positive feedback. The resulting organization is wholly decentralized, distributed over all the components of the system. As such, the organization is typically robust and able to survive or self-repair substantial perturbation. Chaos theory discusses self-organization in terms of islands of predictability in a sea of chaotic unpredictability.
An organizational structure defines how activities such as task allocation, coordination, and supervision are directed toward the achievement of organizational aims.

Bionics or biologically inspired engineering is the application of biological methods and systems found in nature to the study and design engineering systems and modern technology.
Holism in science, holistic science, or methodological holism is an approach to research that emphasizes the study of complex systems. Systems are approached as coherent wholes whose component parts are best understood in context and in relation to both each other and to the whole. Holism typically stands in contrast with reductionism, which describes systems by dividing them into smaller components in order to understand them through their elemental properties.
A complex adaptive system is a system that is complex in that it is a dynamic network of interactions, but the behavior of the ensemble may not be predictable according to the behavior of the components. It is adaptive in that the individual and collective behavior mutate and self-organize corresponding to the change-initiating micro-event or collection of events. It is a "complex macroscopic collection" of relatively "similar and partially connected micro-structures" formed in order to adapt to the changing environment and increase their survivability as a macro-structure. The Complex Adaptive Systems approach builds on replicator dynamics.

Ceramic engineering is the science and technology of creating objects from inorganic, non-metallic materials. This is done either by the action of heat, or at lower temperatures using precipitation reactions from high-purity chemical solutions. The term includes the purification of raw materials, the study and production of the chemical compounds concerned, their formation into components and the study of their structure, composition and properties.
Nanotechnology is impacting the field of consumer goods, several products that incorporate nanomaterials are already in a variety of items; many of which people do not even realize contain nanoparticles, products with novel functions ranging from easy-to-clean to scratch-resistant. Examples of that car bumpers are made lighter, clothing is more stain repellant, sunscreen is more radiation resistant, synthetic bones are stronger, cell phone screens are lighter weight, glass packaging for drinks leads to a longer shelf-life, and balls for various sports are made more durable. Using nanotech, in the mid-term modern textiles will become "smart", through embedded "wearable electronics", such novel products have also a promising potential especially in the field of cosmetics, and has numerous potential applications in heavy industry. Nanotechnology is predicted to be a main driver of technology and business in this century and holds the promise of higher performance materials, intelligent systems and new production methods with significant impact for all aspects of society.

A system is a group of interacting or interrelated elements that act according to a set of rules to form a unified whole. A system, surrounded and influenced by its environment, is described by its boundaries, structure and purpose and is expressed in its functioning. Systems are the subjects of study of systems theory and other systems sciences.

The global brain is a neuroscience-inspired and futurological vision of the planetary information and communications technology network that interconnects all humans and their technological artifacts. As this network stores ever more information, takes over ever more functions of coordination and communication from traditional organizations, and becomes increasingly intelligent, it increasingly plays the role of a brain for the planet Earth. In the philosophy of mind, global brain finds an analog in Averroes's theory of the unity of the intellect

In mechanical engineering, a compliant mechanism is a flexible mechanism that achieves force and motion transmission through elastic body deformation. It gains some or all of its motion from the relative flexibility of its members rather than from rigid-body joints alone. These may be monolithic (single-piece) or jointless structures. Some common devices that use compliant mechanisms are backpack latches and paper clips. One of the oldest examples of using compliant structures is the bow and arrow.
A social-ecological system consists of 'a bio-geo-physical' unit and its associated social actors and institutions. Social-ecological systems are complex and adaptive and delimited by spatial or functional boundaries surrounding particular ecosystems and their context problems.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to applied science:

Artificial life is a field of study wherein researchers examine systems related to natural life, its processes, and its evolution, through the use of simulations with computer models, robotics, and biochemistry. The discipline was named by Christopher Langton, an American theoretical biologist, in 1986. In 1987 Langton organized the first conference on the field, in Los Alamos, New Mexico. There are three main kinds of alife, named for their approaches: soft, from software; hard, from hardware; and wet, from biochemistry. Artificial life researchers study traditional biology by trying to recreate aspects of biological phenomena.
Biomimetic architecture is a branch of the new science of biomimicry defined and popularized by Janine Benyus in her 1997 book. Biomimicry refers to innovations inspired by nature as one which studies nature and then imitates or takes inspiration from its designs and processes to solve human problems. The book suggests looking at nature as a Model, Measure, and Mentor", suggesting that the main aim of biomimicry is sustainability.
References
- ↑ Barbieri, Marcello (2003). The Organic Codes: An Introduction to Semantic Biology. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-53100-9.
- ↑ "Organic unity: literature". Encyclopedia Britannica. Retrieved 8 February 2019.
- ↑ Schmitthenner, Heinrich (1951). Studien Über Carl Ritter. Frankfurt a.M.: Verlag Dr. Waldemar Kramer. pp. 40–71.