Related Research Articles
"Algivirga pacifica" is a Gram-negative and aerobic bacterium from the genus "Algivirga" which has been isolated from seawater from Micronesia.
Aliiglaciecola is a genus from the family of Alteromonadaceae.
Hoeflea olei is a Gram-negative and rod-shaped bacteria from the genus of Hoeflea which has been isolated from water in Kerala in India. Hoeflea olei has the ability to degrade diesel oil.
Oricola is a genus of bacteria from the family of Phyllobacteriaceae.
Thalassocola ureilytica is a Gram-negative, aerobic and rod-shaped bacterium from the genus of Thalassocola which has been isolated from seawater from the South China Sea.
Camelimonas fluminis is a Gram-negative, aerobic, short rod-shaped and non-spore-forming bacteria from the genus of Camelimonas which has been isolated from water from the Hanjiang River in Wuhan in China. Camelimonas fluminis has the ability to degrade cyhalothrin.
Sphingobacterium cibie is a Gram-negative, aerobic, rod-shaped and non-motile bacterium from the genus of Sphingobacterium which has been isolated from food-waste compost.
Acetivibrio clariflavus is an anaerobic bacterium from the genus Acetivibrio which has been isolated from sludge from a cellulose-degrading bioreactor in Japan.
Noviherbaspirillum is a genus of bacteria in the family of Oxalobacteraceae.

Noviherbaspirillum malthae is a Gram-negative, aerobic and rod-shaped bacterium from the genus Noviherbaspirillum which has been isolated from Kaohsiung County in Taiwan.
Cellulomonas iranensis is a cellulolytic and mesophilic bacterium from the genus Cellulomonas which has been isolated from forest soil from Iran.
Cellulomonas persica is a mesophilic and cellulolytic bacterium from the genus Cellulomonas which has been isolated from forest soil in Iran.
Actibacterium ureilyticum is a Gram-negative, aerobic and rod-shaped bacterium from the genus of Actibacterium with a polar flagella which has been isolated from seawater from the South China Sea in Taiwan.
Cribrihabitans neustonicus is a Gram-negative, non-spore-forming, strictly aerobic and motile bacterium from the genus of Cribrihabitans which has been isolated from seawater from Hualien in Taiwan.
Ammoniphilus resinae is a Gram-variable, endospore-forming and facultatively anaerobic bacteria from the genus of Ammoniphilus which has been isolated from aged resin from a tropical rainforest in Indonesia.
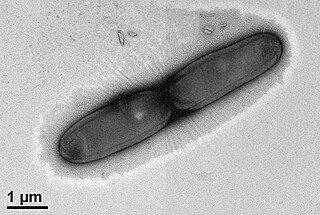
Castellaniella fermenti is a Gram-negative and aerobic bacterium from the genus Castellaniella which has been isolated from fermented food from Taiwan.
Idiomarina tyrosinivorans is a Gram-negative, strictly aerobic, non-spore-forming, curved-rod-shaped, tyrosine-metabolizing and motile bacterium from the genus Idiomarina which has been isolated from water off the river Pingtung in Taiwan.
Aequorivita echinoideorum is a Gram-negative, rod-shaped and aerobic bacterium from the genus of Aequorivita which has been isolated from a sea urchin from Penghu Island in Taiwan.
Filimonas aquilariae is a Gram-negative, aerobic and rod-shaped bacterium from the genus of Filimonas which has been isolated from agarwood chips.
Lutibacter oricola is a Gram-negative, aerobic, rod-shaped and non-motile bacterium from the genus of Lutibacter which has been isolated from seawater from Seo-do from the Liancourt Rocks.
References
- 1 2 Parte, A.C. "Oricola". LPSN .
- 1 2 "Oricola cellulosilytica". www.uniprot.org.
- ↑ Parker, Charles Thomas; Garrity, George M (2015). Parker, Charles Thomas; Garrity, George M (eds.). "Nomenclature Abstract for Oricola cellulosilytica Hameed et al. 2015". The NamesforLife Abstracts. doi:10.1601/nm.26694.
- ↑ Hameed, Asif; Shahina, Mariyam; Lai, Wei-An; Lin, Shih-Yao; Young, Li-Sen; Liu, You-Cheng; Hsu, Yi-Han; Young, Chiu-Chung (8 January 2015). "Oricola cellulosilytica gen. nov., sp. nov., a cellulose-degrading bacterium of the family Phyllobacteriaceae isolated from surface seashore water, and emended descriptions of Mesorhizobium loti and Phyllobacterium myrsinacearum". Antonie van Leeuwenhoek. 107 (3): 759–771. doi:10.1007/s10482-014-0370-6. PMID 25566955. S2CID 15204152.