
Flavonoids are a class of polyphenolic secondary metabolites found in plants, and thus commonly consumed in the diets of humans.

Catechin is a flavan-3-ol, a type of secondary metabolite providing antioxidant roles in plants. It belongs to the subgroup of polyphenols called flavonoids.

Myb genes are part of a large gene family of transcription factors found in animals and plants. In humans, it includes Myb proto-oncogene like 1 and Myb-related protein B in addition to MYB proper. Members of the extended SANT/Myb family also include the SANT domain and other similar all-helical homeobox-like domains.

Anthocyanins, also called anthocyans, are water-soluble vacuolar pigments that, depending on their pH, may appear red, purple, blue, or black. In 1835, the German pharmacist Ludwig Clamor Marquart named a chemical compound that gives flowers a blue color, Anthokyan, in his treatise "Die Farben der Blüthen". Food plants rich in anthocyanins include the blueberry, raspberry, black rice, and black soybean, among many others that are red, blue, purple, or black. Some of the colors of autumn leaves are derived from anthocyanins.
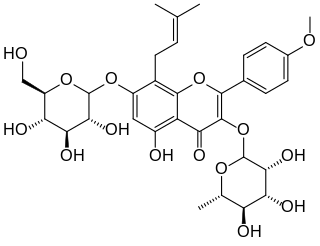
Icariin is a chemical compound classified as a prenylated flavonol glycoside, a type of flavonoid. It is the 8-prenyl derivative of kaempferol 3,7-O-diglucoside. The compound has been isolated from several species of plant belonging to the genus Epimedium which are commonly known as horny goat weed, Yin Yang Huo, and Herba epimedii. Extracts from these plants produce aphrodisiac effects, and are used in traditional Chinese medicine to enhance erectile function. However, clinical trial data are lacking to support these claims.

Baicalein (5,6,7-trihydroxyflavone) is a flavone, a type of flavonoid, originally isolated from the roots of Scutellaria baicalensis and Scutellaria lateriflora. It is also a constituent of Oroxylum indicum and thyme. It is the aglycone of baicalin.

Fisetin (7,3′,4′-flavon-3-ol) is a plant flavonol from the flavonoid group of polyphenols. It can be found in many plants, where it serves as a yellow/ochre colouring agent. It is also found in many fruits and vegetables, such as strawberries, apples, persimmons, onions and cucumbers. Its chemical formula was first described by Austrian chemist Josef Herzig in 1891.

Galangin is a flavonol, a type of flavonoid.

Ononin is an isoflavone glycoside, the 7-O-β-D-glucopyranoside of formononetin, which in turn is the 4'-O-methoxy derivative of the parent isoflavone daidzein.

Luteolinidin is a member of the 3-deoxyanthocyanidins. It is a cation with ill-defined anions. This orange species that can be found in Sorghum bicolor.

Fisetinidin is an anthocyanidin. It has been obtained from the heartwood of Acacia mearnsii, from the bark of Rhizophora apiculata and can also be synthesized. Fisetinidin is very similar in structure to fisetin, which itself differs in structure from quercetin only by an additional hydroxyl group on the latter.
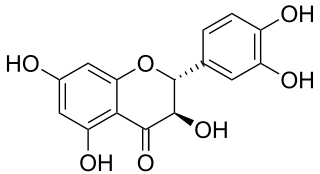
Taxifolin (5,7,3',4'-flavan-on-ol), also known as dihydroquercetin, belongs to the subclass flavanonols in the flavonoids, which in turn is a class of polyphenols. It is extracted from plants such as Siberian larch and milk thistle.

Butin is a flavanone, a type of flavonoid. The compound can be found in the seeds of Vernonia anthelmintica (Asteraceae) and in the wood of Dalbergia odorifera (Fabaceae).

The 3-Deoxyanthocyanidins and their glycosides are molecules with an anthocyanidins backbone lacking an hydroxyl group at position 3 on the C-ring. This nomenclature is the inverse of that which is commonly used in flavonoids, where the hydroxy-group is assumed absent if it is not specified, e. g. flavan-3-ol, flavan-4-ol, flavan-3,4-ol and flavonol.

3-Hydroxyflavone is a chemical compound. It is the backbone of all flavonols, a type of flavonoid. It is a synthetic compound, which is not found naturally in plants. It serves as a model molecule as it possesses an excited-state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT) effect to serve as a fluorescent probe to study membranes for example or intermembrane proteins. The green tautomer emission and blue-violet normal emission originate from two different ground state populations of 3HF molecules. The phenomenon also exists in natural flavonols. Although 3-hydroxyflavone is almost insoluble in water, its aqueous solubility can be increased by encapsulation in cyclodextrin cavities.
The O-methylated flavonoids or methoxyflavonoids are flavonoids with methylations on hydroxyl groups. O-methylation has an effect on the solubility of flavonoids.

Prenylated flavonoids or prenylflavonoids are a sub-class of flavonoids. They are widely distributed throughout the plant kingdom. Some are known to have phytoestrogenic or antioxidant properties. They are given in the list of adaptogens in herbalism. Chemically they have a prenyl group attached to their flavonoid backbone. It is usually assumed that the addition of hydrophobic prenyl groups facilitate attachment to cell membranes. Prenylation may increase the potential activity of its original flavonoid.

Xanthohumol is a natural product found in the female inflorescences of Humulus lupulus, also known as hops. This compound is also found in beer and belongs to a class of compounds that contribute to the bitterness and flavor of hops. Xanthohumol is a prenylated chalconoid, biosynthesized by a type III polyketide synthase (PKS) and subsequent modifying enzymes.

Senegalia afra, also known as hook-thorn or Acacia afra, is a tree that occurs commonly in southern Africa. Though it is cultivated, it often occurs naturally in Gauteng suburban gardens, together with Acacia karroo and Acacia robusta.
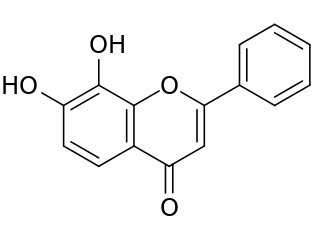
Tropoflavin, also known as 7,8-dihydroxyflavone, is a naturally occurring flavone found in Godmania aesculifolia, Tridax procumbens, and primula tree leaves. It has been found to act as a potent and selective small-molecule agonist of the tropomyosin receptor kinase B (TrkB), the main signaling receptor of the neurotrophin brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF). Tropoflavin is both orally bioavailable and able to penetrate the blood–brain barrier. A prodrug of tropoflavin with greatly improved potency and pharmacokinetics, R13, is under development for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease.



















