 Chemical structure of Afzelechin (2R,3S) | |
 Chemical structure of Afzelechin (2R,3S) in ball-and-stick format | |
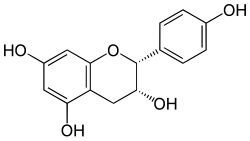 Chemical structure of Epiafzelechin (2R,3R) | |
 Chemical structure of Epiafzelechin (2R,3R) in ball-and-stick format | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name Afzelechin: (2R,3S)-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromene-3,5,7-triol Epiafzelechin: (2R,3R)-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromene-3,5,7-triol | |
| Other names 3,5,7,4′-Tetrahydroxyflavan 3,4′,5,7-Flavantetrol | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol) | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID | |
| UNII |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C15H14O5 | |
| Molar mass | 274.26 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
Afzelechin is a flavan-3-ol, a type of flavonoid. It can be found in Bergenia ligulata (a.k.a.paashaanbhed in Ayurveda traditional Indian medicine). [1] It exists as at least two major epimers (afzelechin and epiafzelechin).