
Catechin is a flavan-3-ol, a type of secondary metabolite providing antioxidant roles in plants. It belongs to the subgroup of polyphenols called flavonoids.

In enzymology, a shikimate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.25) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a dihydrokaempferol 4-reductase (EC 1.1.1.219) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a retinol dehydrogenase (RDH) (EC 1.1.1.105) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, an UDP-N-acetylmuramate dehydrogenase (EC 1.3.1.98) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 2'-hydroxydaidzein reductase (EC 1.3.1.51) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a cis-2-enoyl-CoA reductase (NADPH) (EC 1.3.1.37) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a Delta14-sterol reductase (EC 1.3.1.70) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an enoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase (NADPH, A-specific) (EC 1.3.1.39) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an enoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] reductase (NADPH, B-specific) (EC 1.3.1.10) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a trans-2-enoyl-CoA reductase (NADPH) (EC 1.3.1.38) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a leucocyanidin oxygenase (EC 1.14.11.19) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a trans-cinnamate 4-monooxygenase (EC 1.14.14.91) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, an aspartate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase is an enzyme that is very important in the biosynthesis of amino acids in prokaryotes, fungi, and some higher plants. It forms an early branch point in the metabolic pathway forming lysine, methionine, leucine and isoleucine from aspartate. This pathway also produces diaminopimelate which plays an essential role in bacterial cell wall formation. There is particular interest in ASADH as disabling this enzyme proves fatal to the organism giving rise to the possibility of a new class of antibiotics, fungicides, and herbicides aimed at inhibiting it.

In enzymology, a saccharopine dehydrogenase (NADP+, L-glutamate-forming) (EC 1.5.1.10) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a saccharopine dehydrogenase (NADP+, L-lysine-forming) (EC 1.5.1.8) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Aromadendrin is a flavanonol, a type of flavonoid. It can be found in the wood of Pinus sibirica.
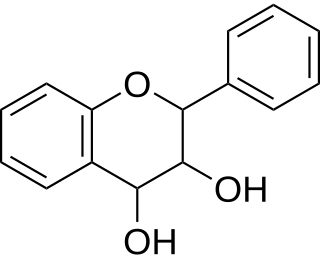
Leucoanthocyanidin (flavan-3,4-diols) are colorless chemical compounds related to anthocyanidins and anthocyanins. Leucoanthocyanins can be found in Anadenanthera peregrina and in several species of Nepenthes including N. burbidgeae, N. muluensis, N. rajah, N. tentaculata, and N. × alisaputrana.

Leucocyanidin is a colorless chemical compound that is a member of the class of natural products known as leucoanthocyanidins.
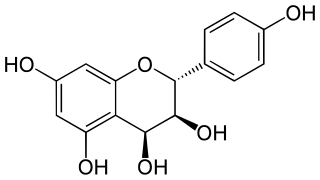
Leucopelargonidin is a colorless chemical compound related to leucoanthocyanins. It can be found in Albizia lebbeck, in the fruit of Anacardium occidentale (Cashew), in the fruit of Areca catechu, in the fruit of Hydnocarpus wightiana, in the rhizome of Rumex hymenosepalus, in Zea mays (Corn) and in Ziziphus jujuba.









