
A sled, skid, sledge, or sleigh is a land vehicle that slides across a surface, usually of ice or snow. It is built with either a smooth underside or a separate body supported by two or more smooth, relatively narrow, longitudinal runners similar in principle to skis. This reduces the amount of friction, which helps to carry heavy loads.

A cart or dray is a vehicle designed for transport, using two wheels and normally pulled by one or a pair of draught animals. A handcart is pulled or pushed by one or more people.

A carriage is a private four-wheeled vehicle for people and is most commonly horse-drawn. Second-hand private carriages were common public transport, the equivalent of modern cars used as taxis. Carriage suspensions are by leather strapping and, on those made in recent centuries, steel springs. Two-wheeled carriages are informal and usually owner-driven.

A wagon or waggon is a heavy four-wheeled vehicle pulled by draught animals or on occasion by humans, used for transporting goods, commodities, agricultural materials, supplies and sometimes people.

A draft horse (US), draught horse (UK) or dray horse, less often called a carthorse, work horse or heavy horse, is a large horse bred to be a working animal doing hard tasks such as plowing and other farm labor. There are a number of breeds, with varying characteristics, but all share common traits of strength, patience, and a docile temperament which made them indispensable to generations of pre-industrial farmers.

A pack animal, also known as a sumpter animal or beast of burden, is an individual or type of working animal used by humans as means of transporting materials by attaching them so their weight bears on the animal's back, in contrast to draft animals which pull loads but do not carry them.

Carting is a dog sport or activity in which a dog pulls a dogcart filled with supplies, such as farm goods, camping equipment, groceries or firewood, but sometimes pulling people. Carting as a sport is also known as dryland mushing and is practiced all around the world, often to keep winter sled dogs in competition form during the off-season.

Mode of transport is a term used to distinguish between different ways of transportation or transporting people or goods. The different modes of transport are air, water, and land transport, which includes rails or railways, road and off-road transport. Other modes also exist, including pipelines, cable transport, and space transport. Human-powered transport and animal-powered transport are sometimes regarded as their own mode, but never fall into the other categories. In general, transportation is used for moving of people, animals, and other goods from one place to another. Means of transport, on the other hand, refers to the transport facilities used to carry people or cargo according to the chosen mode. Each mode of transport has a fundamentally different technological solution, and some require a separate environment. Each mode has its own infrastructure, vehicles, transport operators and operations.

A working animal is an animal, usually domesticated, that is kept by humans and trained to perform tasks instead of being slaughtered to harvest animal products. Some are beasts of burden that provide transportation and aid in physical labor, while others are service animals trained to execute certain specialized tasks. They may also be used for milking or herding. Some, at the end of their working lives, may also be used for meat or other products such as leather.

A horse-drawn vehicle is a mechanized piece of equipment pulled by one horse or by a team of horses. These vehicles typically had two or four wheels and were used to carry passengers and/or a load. They were once common worldwide, but they have mostly been replaced by automobiles and other forms of self-propelled transport.
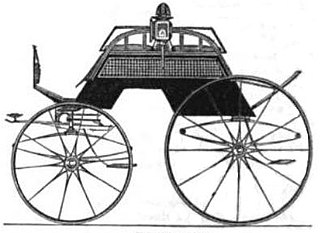
A dogcart is a light horse-drawn vehicle, originally designed for sporting shooters, with a box behind the driver's seat to contain one or more retriever dogs. The dog box could be converted to a second seat. Later variants included :

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to transport:

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to vehicles:

A packhorse, pack horse, or sumpter refers to a horse, mule, donkey, or pony used to carry goods on its back, usually in sidebags or panniers. Typically packhorses are used to cross difficult terrain, where the absence of roads prevents the use of wheeled vehicles. Use of packhorses dates from the neolithic period to the present day. Today, westernized nations primarily use packhorses for recreational pursuits, but they are still an important part of everyday transportation of goods throughout much of the developing world and have some military uses in rugged regions.

Mounted search and rescue (MSAR) is a specialty within search and rescue (SAR), using horses as search partners and for transportation to search for missing persons. SAR responders on horseback are primarily a search resource, but also can provide off-road logistics support and transportation. Mounted SAR responders can in some terrains move faster on the ground than a human on foot, can transport more equipment, and may be physically less exhausted than a SAR responder performing the same task on foot. Mounted SAR responders typically have longer initial response times than groundpounder SAR resources, due to the time required to pick up trailer, horse(s), and perhaps also water, feed, and equipment.

Driving, when applied to horses, ponies, mules, or donkeys, is a broad term for hitching equines to a wagon, carriage, cart, sleigh, or other horse-drawn vehicle by means of a harness and working them in this way. It encompasses a wide range of activities from pleasure driving, to harness racing, to farm work, horse shows, and even international combined driving.

A coach is a large, closed, four-wheeled, passenger-carrying vehicle or carriage usually drawn by two or more horses controlled by a coachman, a postilion, or both. A coach has doors in its sides and a front and a back seat inside. The driver has a raised seat in front of the carriage to allow better vision. It is often called a box, box seat, or coach box. There are many of types of coaches depending on the vehicle's purpose.

Breeching ( "britching") is a strap around the haunches of a draft, pack or riding animal. Both under saddle and in harness, breeching engages when an animal slows down or travels downhill and is used to brake or stabilize a load.

This is a basic glossary of equestrian terms that includes both technical terminology and jargon developed over the centuries for horses and other equidae, as well as various horse-related concepts. Where noted, some terms are used only in American English (US), only in British English (UK), or are regional to a particular part of the world, such as Australia (AU).

Human-powered land vehicles are land vehicles propelled over ground by human power, The main ways to support the weight of a human-powered land vehicle and its contents above the ground are rolling contact; sliding contact; intermittent contact; no contact at all as with anything carried; or some combination of the above. The main methods of using human power to propel a land vehicle are some kind of drivetrain; pushing laterally against the ground with a wheel, skate, or ski that simultaneously moves forward; by pushing against the ground directly with an appendage opposite to the direction of travel; or by propeller. Human-powered land vehicles can be propelled by persons riding in the vehicle or by persons walking or running and not supported by the vehicle.





















