
Chlorine is a chemical element with the symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine is a yellow-green gas at room temperature. It is an extremely reactive element and a strong oxidising agent: among the elements, it has the highest electron affinity and the third-highest electronegativity on the revised Pauling scale, behind only oxygen and fluorine. On several scales other than the revised Pauling scale, nitrogen's electronegativity is also listed as greater than chlorine's, such as on the Allen, Allred-Rochow, Martynov-Batsanov, Mulliken-Jaffe, Nagle, and Noorizadeh-Shakerzadeh electronegativity scales.
Fluoride is an inorganic, monatomic anion of fluorine, with the chemical formula F−
, whose salts are typically white or colorless. Fluoride salts typically have distinctive bitter tastes, and are odorless. Its salts and minerals are important chemical reagents and industrial chemicals, mainly used in the production of hydrogen fluoride for fluorocarbons. Fluoride is classified as a weak base since it only partially associates in solution, but concentrated fluoride is corrosive and can attack the skin.
The Swern oxidation, named after Daniel Swern, is a chemical reaction whereby a primary or secondary alcohol is oxidized to an aldehyde or ketone using oxalyl chloride, dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) and an organic base, such as triethylamine. It is one of the many oxidation reactions commonly referred to as 'activated DMSO' oxidations. The reaction is known for its mild character and wide tolerance of functional groups.

Hydrofluoric acid is a solution of hydrogen fluoride (HF) in water. Solutions of HF are colourless, acidic and highly corrosive. It is used to make most fluorine-containing compounds; examples include the commonly used pharmaceutical antidepressant medication fluoxetine (Prozac) and the material PTFE (Teflon). Elemental fluorine is produced from it. It is commonly used to etch glass and silicon wafers.

Iron(III) chloride is the inorganic compound with the formula FeCl3. Also called ferric chloride, it is a common compound of iron in the +3 oxidation state. The anhydrous compound is a crystalline solid with a melting point of 307.6 °C. The color depends on the viewing angle: by reflected light the crystals appear dark green, but by transmitted light they appear purple-red.

Sodium fluoride (NaF) is an inorganic compound with the formula NaF. It is used in trace amounts in the fluoridation of drinking water, in toothpaste, in metallurgy, and as a flux, and is also used in pesticides and rat poison. It is a colorless or white solid that is readily soluble in water. It is a common source of fluoride in the production of pharmaceuticals and is used to prevent dental cavities.

Caesium fluoride or cesium fluoride is an inorganic compound with the formula CsF and it is a hygroscopic white salt. Caesium fluoride can be used in organic synthesis as a source of the fluoride anion. Caesium also has the highest electropositivity of all non-radioactive elements and fluorine has the highest electronegativity of all known elements.
Chlorine trifluoride is an interhalogen compound with the formula ClF3. This colorless, poisonous, corrosive, and extremely reactive gas condenses to a pale-greenish yellow liquid, the form in which it is most often sold (pressurized at room temperature). The compound is primarily of interest in plasmaless cleaning and etching operations in the semiconductor industry, in nuclear reactor fuel processing, as a component in rocket fuels, and other industrial operations.

Oxalyl chloride is an organic chemical compound with the formula (COCl)2. This colorless, sharp-smelling liquid, the diacyl chloride of oxalic acid, is a useful reagent in organic synthesis.

Nickel(II) fluoride is the chemical compound with the formula NiF2. It is an ionic compound of nickel and fluorine and forms yellowish to green tetragonal crystals. Unlike many fluorides, NiF2 is stable in air.

Cobalt(III) fluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula CoF3. Hydrates are also known. The anhydrous compound is a hygroscopic brown solid. It is used to synthesize organofluorine compounds.

Xenon difluoride is a powerful fluorinating agent with the chemical formula XeF
2, and one of the most stable xenon compounds. Like most covalent inorganic fluorides it is moisture-sensitive. It decomposes on contact with water vapor, but is otherwise stable in storage. Xenon difluoride is a dense, colourless crystalline solid.
Organofluorine chemistry describes the chemistry of the organofluorines, organic compounds that contain the carbon–fluorine bond. Organofluorine compounds find diverse applications ranging from oil and water repellents to pharmaceuticals, refrigerants, and reagents in catalysis. In addition to these applications, some organofluorine compounds are pollutants because of their contributions to ozone depletion, global warming, bioaccumulation, and toxicity. The area of organofluorine chemistry often requires special techniques associated with the handling of fluorinating agents.
Sulfonyl halide groups occur when a sulfonyl functional group is singly bonded to a halogen atom. They have the general formula RSO2X where X is a halogen. The stability of sulfonyl halides decreases in the order fluorides > chlorides > bromides > iodides, all four types being well known. The sulfonyl chlorides and fluorides are of dominant importance in this series.
Formyl fluoride is the organic compound with the formula HC(O)F.

Cyanuric fluoride or 2,4,6-trifluoro-1,3,5-triazine is a chemical compound with the formula (CNF)3. It is a colourless, pungent liquid. It has been used as a precursor for fibre-reactive dyes, as a specific reagent for tyrosine residues in enzymes, and as a fluorinating agent.
Selectfluor, a trademark of Air Products and Chemicals, is a reagent in chemistry that is used as a fluorine donor. This compound is a derivative of the nucleophillic base DABCO. It is a colourless salt that tolerates air and even water. It has been commercialized for use for electrophilic fluorination.

Fluorine is a chemical element with the symbol F and atomic number 9. It is the lightest halogen and exists at standard conditions as a highly toxic, pale yellow diatomic gas. As the most electronegative element, it is extremely reactive, as it reacts with all other elements except for argon, neon, and helium.
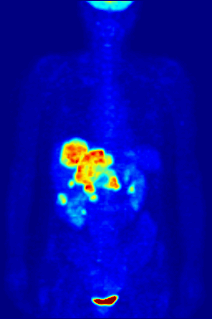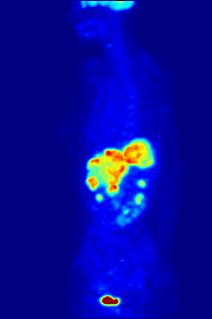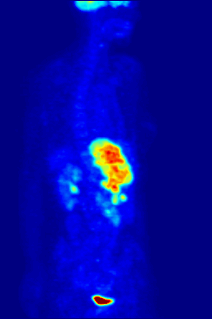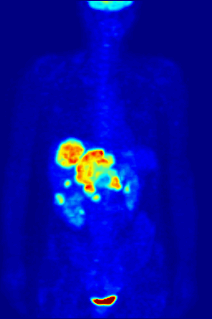
Fluorine may interact with biological systems in the form of fluorine-containing compounds. Though elemental fluorine (F2) is very rare in everyday life, fluorine-containing compounds such as fluorite occur naturally as minerals. Naturally occurring organofluorine compounds are extremely rare. Man-made fluoride compounds are common and are used in medicines, pesticides, and materials. Twenty percent of all commercialized pharmaceuticals contain fluorine, including Lipitor and Prozac. In many contexts, fluorine-containing compounds are harmless or even beneficial to living organisms; in others, they are toxic.
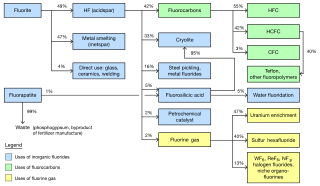
The global market for chemicals from fluorine was about US$16 billion per year as of 2006. The industry was predicted to reach 2.6 million metric tons per year by 2015. The largest market is the United States. Western Europe is the second largest. Asia Pacific is the fastest growing region of production. China in particular has experienced significant growth as a fluorochemical market and is becoming a producer of them as well. Fluorite mining was estimated in 2003 to be a $550 million industry, extracting 4.5 million tons per year.














