The Opiliones are an order of arachnids colloquially known as harvestmen, harvesters, or daddy longlegs. As of April 2017, over 6,650 species of harvestmen have been discovered worldwide, although the total number of extant species may exceed 10,000. The order Opiliones includes five suborders: Cyphophthalmi, Eupnoi, Dyspnoi, Laniatores, and Tetrophthalmi, which were named in 2014.

Laniatores is the largest suborder of the arachnid order Opiliones with over 4,000 described species worldwide. The majority of the species are highly dependent on humid environments and usually correlated with tropical and temperate forest habitats.

Cosmetidae is a family of harvestmen in the suborder Laniatores. With over 700 species, it is one of the largest families in Opiliones. They are distributed from Argentina to the southern USA with the highest diversity in northern South America, Central America and Mexico. This Nearctic-Neotropical family comprises Opiliones with elaborate white/yellow/green/orange/red stripes and spots on the dorsal scutum and peculiar pedipalps strongly compressed and applied on the chelicerae.

The Eupnoi are a suborder of harvestmen, with more than 200 genera, and about 1,700 described species.

Cyphophthalmi is a suborder of harvestmen, colloquially known as mite harvestmen. Cyphophthalmi comprises 36 genera, and more than two hundred described species. The six families are currently grouped into three infraorders: the Boreophthalmi, Scopulophthalmi, and Sternophthalmi.

The Phalangiidae are a family of harvestmen with about 380 known species. The best known is Phalangium opilio. Dicranopalpus ramosus is an invasive species in Europe.

Megabunus diadema is a species of harvestman distributed in Western Europe, where it has been found in Iceland, Faroe Islands, Western Norway, Great Britain, Western France, Belgium and Northern Spain.
An ozophore is an elevated cone present in the harvestman suborder Cyphophthalmi. It carries the openings, called ozopores, of the defensive glands that are present in many harvestmen.
Nemastomoides is an extinct genus of harvestmen known from the Carboniferous fossil record. The genus is the only member of the family Nemastomoididae and contains three described species. Nemastomoides elaveris was found in the Coal Measures of Commentry in northern France, together with Eotrogulus fayoli.
The Stygnidae are a family of neotropical harvestmen within the suborder Laniatores.
Agoristenidae are a neotropical harvestman family of the Suborder Laniatores, in the superfamily Gonyleptoidea.

The Cranaidae are a family of neotropical harvestmen within the suborder Laniatores.
The Icaleptidae are a small family of neotropical harvestmen within the suborder Laniatores. Although only two species have been described, many more are probably to be discovered.
The Fissiphalliidae are a small neotropical family of harvestmen within the suborder Laniatores.
The Travuniidae are a small family of harvestman with little more than ten described species, within the suborder Laniatores.

The Cladonychiidae are a small family of harvestman with about 33 described species, within the suborder Laniatores.
Stomotheca is the term applied to the feeding apparatus in front of the mouth of harvestmen, and sometimes the related scorpions. Usually it consists of the epistome (labrum), two pairs of coxapophyses and often a labium.

Opiliones are an order of arachnids and share many common characteristics with other arachnids. However, several differences separate harvestmen from other arachnid orders such as spiders. The bodies of opiliones are divided into two tagmata : the abdomen (opisthosoma) and the cephalothorax (prosoma). Unlike spiders, the juncture between the abdomen and cephalothorax is often poorly defined. Harvestmen have chelicerae, pedipalps and four pairs of legs. Most harvestmen have two eyes, although there are eyeless species.
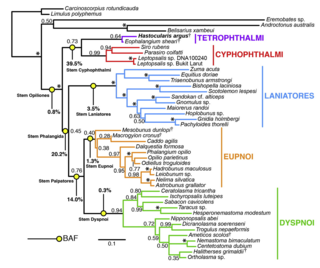
Harvestmen (Opiliones) are an order of arachnids often confused with spiders, though the two orders are not closely related. Research on harvestman phylogeny is in a state of flux. While some families are clearly monophyletic, that is share a common ancestor, others are not, and the relationships between families are often not well understood.

Tetrophthalmi is an extinct suborder of Opiliones that had both median and lateral eyes. First described in 2014, it is known from two extinct species. Phylogenetic analysis suggests that this eye arrangement is the ancestral condition for harvestmen, placing Tetrophthalmi and Cyphophthalmi in a basal position within Opiliones.