Protein kinase C and casein kinase substrate in neurons protein 1 also known as syndapin I [5] [6] is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PACSIN1 gene. [7]
Protein kinase C and casein kinase substrate in neurons protein 1 also known as syndapin I [5] [6] is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PACSIN1 gene. [7]
PACSIN1 has been shown to interact with GTPases of the Dynamin family (Dynamin 1, 2 and 3). Based on this interaction, its localization and functional role the protein was named syndapin I (synaptic dynamin-associated protein I).
A variety of interactions have been published:

Huntingtin(Htt) is the protein coded for in humans by the HTT gene, also known as the IT15 ("interesting transcript 15") gene. Mutated HTT is the cause of Huntington's disease (HD), and has been investigated for this role and also for its involvement in long-term memory storage.
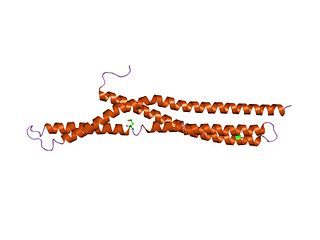
In molecular biology, BAR domains are highly conserved protein dimerisation domains that occur in many proteins involved in membrane dynamics in a cell. The BAR domain is banana-shaped and binds to membrane via its concave face. It is capable of sensing membrane curvature by binding preferentially to curved membranes. BAR domains are named after three proteins that they are found in: Bin, Amphiphysin and Rvs.

Amphiphysin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AMPH gene.

Growth Associated Protein 43 (GAP43) is a protein encoded by the GAP43 gene in humans.
Dynamin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DNM2 gene.

Casein kinase II subunit beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CSNK2B gene. It is a ubiquitous protein kinase which regulates metabolic pathways, signal transduction, transcription, translation, and replication. The enzyme localizes to the endoplasmic reticulum and the Golgi apparatus.

Dynamin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DNM1 gene.

Endophilin-A1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SH3GL2 gene.

AP-3 complex subunit beta-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the AP3B1 gene.

SH3 and multiple ankyrin repeat domains protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SHANK2 gene. Two alternative splice variants, encoding distinct isoforms, are reported. Additional splice variants exist but their full-length nature has not been determined.

Inositol-trisphosphate 3-kinase A is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ITPKA gene.

Dynamin-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DNM3 gene. The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the dynamin family which possess mechanochemical properties involved in actin-membrane processes, predominantly in membrane budding. DNM3 is upregulated in Sézary's syndrome.

Protein kinase C and casein kinase substrate in neurons protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PACSIN2 gene. Pacsin 2 is involved in the formation of caveolae.

DnaJ homolog subfamily C member 5, also known as cysteine string protein or CSP is a protein, that in humans encoded by the DNAJC5 gene. It was first described in 1990.

Protein kinase C and casein kinase substrate in neurons protein 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PACSIN3 gene.

Palmitoyltransferase ZDHHC17 is an enzyme that contains a DHHC domain that in humans is encoded by the ZDHHC17 gene.

Coiled-coil domain-containing protein 113 also known as HSPC065, GC16Pof6842 and GC16P044152, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCDC113 gene. The human CCDC113 gene is located on chromosome 16q21 and encodes 5,304 base pairs of mRNA and 377 amino acids.

Activity-regulated cytoskeleton-associated protein is a plasticity protein that in humans is encoded by the ARC gene. The gene is believed to derive from a retrotransposon. The protein is found in the neurons of tetrapods and other animals where it can form virus-like capsids that transport RNA between neurons.
Bulk endocytosis refers to a form of endocytosis of synaptic vesicles at nerve terminals. In bulk endocytosis, compared to clathrin-mediated endocytosis, a larger area of presynaptic plasma membrane is internalised as cisternae or endosomes from which multiple synaptic vesicles can subsequently bud off. Bulk endocytosis is activated specifically during intense stimulation, such as during high-frequency trains of action potentials or in response to membrane depolarization by high extracellular concentrations of potassium.
Casein kinase I isoform epsilon or CK1ε, is an enzyme that is encoded by the CSNK1E gene in humans. It is the mammalian homolog of doubletime. CK1ε is a serine/threonine protein kinase and is very highly conserved; therefore, this kinase is very similar to other members of the casein kinase 1 family, of which there are seven mammalian isoforms. CK1ε is most similar to CK1δ in structure and function as the two enzymes maintain a high sequence similarity on their regulatory C-terminal and catalytic domains. This gene is a major component of the mammalian oscillator which controls cellular circadian rhythms. CK1ε has also been implicated in modulating various human health issues such as cancer, neurodegenerative diseases, and diabetes.