
Lipid signaling, broadly defined, refers to any biological cell signaling event involving a lipid messenger that binds a protein target, such as a receptor, kinase or phosphatase, which in turn mediate the effects of these lipids on specific cellular responses. Lipid signaling is thought to be qualitatively different from other classical signaling paradigms because lipids can freely diffuse through membranes. One consequence of this is that lipid messengers cannot be stored in vesicles prior to release and so are often biosynthesized "on demand" at their intended site of action. As such, many lipid signaling molecules cannot circulate freely in solution but, rather, exist bound to special carrier proteins in serum.

Hippocalcin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HPCA gene.

Caspase-10 is an enzyme that, in humans, is encoded by the CASP10 gene.

Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type IV is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CAMK4 gene.

5'-AMP-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha-1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRKAA1 gene.
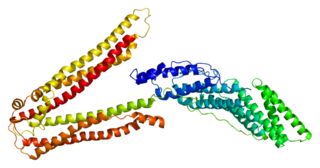
Programmed cell death 6-interacting protein also known as ALIX is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PDCD6IP gene.

PITSLRE serine/threonine-protein kinase CDC2L1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CDK11B gene.
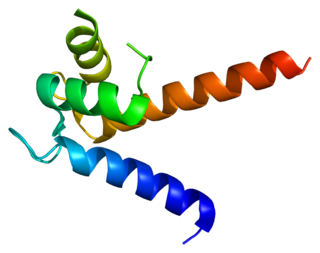
S100 calcium-binding protein P (S100P) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the S100P gene.
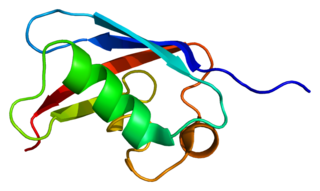
FAS-associated factor 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FAF1 gene.

Annexin A7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ANXA7 gene.

Annexin A11 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ANXA11 gene.

Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MAP3K4 gene.

Sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticulum calcium ATPase 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ATP2A3 gene.

S100 calcium-binding protein A3 (S100A3) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the S100A3 gene.

Triadin, also known as TRDN, is a human gene associated with the release of calcium ions from the sarcoplasmic reticulum triggering muscular contraction through calcium-induced calcium release. Triadin is a multiprotein family, arising from different processing of the TRDN gene on chromosome 6. It is a transmembrane protein on the sarcoplasmic reticulum due to a well defined hydrophobic section and it forms a quaternary complex with the cardiac ryanodine receptor (RYR2), calsequestrin (CASQ2) and junctin proteins. The luminal (inner compartment of the sarcoplasmic reticulum) section of Triadin has areas of highly charged amino acid residues that act as luminal Ca2+ receptors. Triadin is also able to sense luminal Ca2+ concentrations by mediating interactions between RYR2 and CASQ2. Triadin has several different forms; Trisk 95 and Trisk 51, which are expressed in skeletal muscle, and Trisk 32 (CT1), which is mainly expressed in cardiac muscle.

Protein unc-13 homolog B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UNC13B gene.

Alpha-1,3/1,6-mannosyltransferase ALG2 is an enzyme that is encoded by the ALG2 gene. Mutations in the human gene are associated with congenital defects in glycosylation The protein encoded by the ALG2 gene belongs to two classes of enzymes: GDP-Man:Man1GlcNAc2-PP-dolichol alpha-1,3-mannosyltransferase and GDP-Man:Man2GlcNAc2-PP-dolichol alpha-1,6-mannosyltransferase.

Kv channel-interacting protein 1 also known as KChIP1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KCNIP1 gene.

Grancalcin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GCA gene.

Peflin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PEF1 gene.





















