
Proteasomes are protein complexes which degrade unneeded or damaged proteins by proteolysis, a chemical reaction that breaks peptide bonds. Enzymes that help such reactions are called proteases.

Ubiquitin is a small regulatory protein found in most tissues of eukaryotic organisms, i.e., it is found ubiquitously. It was discovered in 1975 by Gideon Goldstein and further characterized throughout the late 1970s and 1980s. Four genes in the human genome code for ubiquitin: UBB, UBC, UBA52 and RPS27A.

A ubiquitin ligase is a protein that recruits an E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme that has been loaded with ubiquitin, recognizes a protein substrate, and assists or directly catalyzes the transfer of ubiquitin from the E2 to the protein substrate. In simple and more general terms, the ligase enables movement of ubiquitin from a ubiquitin carrier to another thing by some mechanism. The ubiquitin, once it reaches its destination, ends up being attached by an isopeptide bond to a lysine residue, which is part of the target protein. E3 ligases interact with both the target protein and the E2 enzyme, and so impart substrate specificity to the E2. Commonly, E3s polyubiquitinate their substrate with Lys48-linked chains of ubiquitin, targeting the substrate for destruction by the proteasome. However, many other types of linkages are possible and alter a protein's activity, interactions, or localization. Ubiquitination by E3 ligases regulates diverse areas such as cell trafficking, DNA repair, and signaling and is of profound importance in cell biology. E3 ligases are also key players in cell cycle control, mediating the degradation of cyclins, as well as cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor proteins. The human genome encodes over 600 putative E3 ligases, allowing for tremendous diversity in substrates.

Ubiquitin-like modifier activating enzyme 1 (UBA1) is an enzyme which in humans is encoded by the UBA1 gene. UBA1 participates in ubiquitination and the NEDD8 pathway for protein folding and degradation, among many other biological processes. This protein has been linked to X-linked spinal muscular atrophy type 2, neurodegenerative diseases, and cancers.

Deubiquitinating enzymes (DUBs), also known as deubiquitinating peptidases, deubiquitinating isopeptidases, deubiquitinases, ubiquitin proteases, ubiquitin hydrolases, ubiquitin isopeptidases, are a large group of proteases that cleave ubiquitin from proteins. Ubiquitin is attached to proteins in order to regulate the degradation of proteins via the proteasome and lysosome; coordinate the cellular localisation of proteins; activate and inactivate proteins; and modulate protein-protein interactions. DUBs can reverse these effects by cleaving the peptide or isopeptide bond between ubiquitin and its substrate protein. In humans there are nearly 100 DUB genes, which can be classified into two main classes: cysteine proteases and metalloproteases. The cysteine proteases comprise ubiquitin-specific proteases (USPs), ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolases (UCHs), Machado-Josephin domain proteases (MJDs) and ovarian tumour proteases (OTU). The metalloprotease group contains only the Jab1/Mov34/Mpr1 Pad1 N-terminal+ (MPN+) (JAMM) domain proteases.
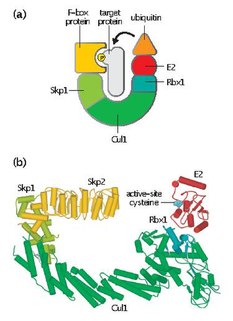
Skp, Cullin, F-box containing complex is a multi-protein E3 ubiquitin ligase complex that catalyzes the ubiquitination of proteins destined for 26S proteasomal degradation. Along with the anaphase-promoting complex, SCF has important roles in the ubiquitination of proteins involved in the cell cycle. The SCF complex also marks various other cellular proteins for destruction.

Ubiquitin-activating enzymes, also known as E1 enzymes, catalyze the first step in the ubiquitination reaction, which can target a protein for degradation via a proteasome. This covalent bond of ubiquitin or ubiquitin-like proteins to targeted proteins is a major mechanism for regulating protein function in eukaryotic organisms. Many processes such as cell division, immune responses and embryonic development are also regulated by post-translational modification by ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like proteins.

S-phase kinase-associated protein 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SKP2 gene.

E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase NEDD4, also known as neural precursor cell expressed developmentally down-regulated protein 4 is an enzyme that is, in humans, encoded by the NEDD4 gene.

Cullin 1, also known as CUL1, is a human protein and gene from cullin family. This protein plays an important role in protein degradation and protein ubiquitination.

NEDD8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NEDD8 gene. This ubiquitin-like (UBL) protein becomes covalently conjugated to a limited number of cellular proteins, in a process called NEDDylation similar to ubiquitination. Human NEDD8 shares 60% amino acid sequence identity to ubiquitin. The primary known substrates of NEDD8 modification are the cullin subunits of cullin-based E3 ubiquitin ligases, which are active only when NEDDylated. Their NEDDylation is critical for the recruitment of E2 to the ligase complex, thus facilitating ubiquitin conjugation. NEDD8 modification has therefore been implicated in cell cycle progression and cytoskeletal regulation.

Cullin-4A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CUL4A gene. CUL4A belongs to the cullin family of ubiquitin ligase proteins and is highly homologous to the CUL4B protein. CUL4A regulates numerous key processes such as DNA repair, chromatin remodeling, spermatogenesis, haematopoiesis and the mitotic cell cycle. As a result, CUL4A has been implicated in several cancers and the pathogenesis of certain viruses including HIV. A component of a CUL4A complex, Cereblon, was discovered to be a major target of the teratogenic agent thalidomide.

CDC34 is a gene that in humans encodes the protein Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 R1. This protein is a member of the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme family, which catalyzes the covalent attachment of ubiquitin to other proteins.

Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 D3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UBE2D3 gene.

Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 G2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UBE2G2 gene.

Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 E3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UBE2E3 gene.

Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 C is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UBE2C gene.

Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 G1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UBE2G1 gene.

Tripartite motif-containing protein 32 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TRIM32 gene. Since its discovery in 1995, TRIM32 has been shown to be implicated in a number of diverse biological pathways.

Ubiquitin-like modifier-activating enzyme 7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the UBA7 gene.




















