Related Research Articles

The Arsenal VG-33 was one of a series of fast French light fighter aircraft under development at the start of World War II, but which matured too late to see extensive service in the French Air Force during the Battle of France.

The PZL P.7 was a Polish fighter aircraft designed in the early 1930s at the PZL factory in Warsaw. It was the main fighter of the Polish Air Force between 1933 and 1935. The PZL P.7 was replaced in Polish service by its follow-up design, the PZL P.11c. More than 30 PZL P.7 fighters remained in service during the Invasion of Poland, scoring several kills despite its obsolescence.

PZL.46 Sum (sheatfish) was a light bomber of the Polish Air Force before World War II, which, was directed to serial production in the spring of 1939. These planes were in production, but the Polish industry did not manage to produce them before the outbreak of the war.

The PZL.50 Jastrząb (hawk) was a Polish pre-war fighter aircraft design by Wsiewołod Jakimiuk of the PZL works. The single-seat low-wing monoplane was to serve as a multi-purpose fighter and escort to replace all other fighters in the Polish Air Force. Designed after 1936, its prototype first flew in February 1939. A further two prototypes were under construction by the time of the Invasion of Poland, but the fighter never entered mass production.

The Ikarus S-49 was a Yugoslav single-seat, single-engine fighter aircraft built for the Yugoslav Air Force shortly after World War II. Following the Tito–Stalin Split in 1948, the RV i PVO was left with an aircraft inventory consisting of mostly Soviet aircraft. Unable to acquire new aircraft or spare parts for its existing fleet, the RV i PVO turned to its domestic aviation industry in order to create an indigenous design to fulfill the need for additional aircraft.

The PZL P.6 was a Polish fighter, designed by the engineer Zygmunt Puławski, manufactured by PZL state-owned factory. It remained a prototype.

PZL.26 was a Polish sports plane built in 1934 in the PZL works. Ordered by the Ministry of Defence, it was specifically designed for the upcoming Challenge 1934 International Touring Aircraft Contest.
The PZL.48 Lampart (leopard) was a Polish heavy fighter-bomber design, that remained only a project, owing to the outbreak of World War II.

The Bartel BM 6 was a Polish biplane trainer fighter aircraft of 1930. It did not advance beyond the prototype stage.

The PZL P.1 was a Polish fighter, designed by the engineer Zygmunt Puławski, manufactured by the PZL state-owned factory. It remained a prototype, but it was the first of the Polish PZL gull wing fighter series, leading to the PZL P.7, PZL P.11 and PZL P.24.
The Renard Epervier was a Belgian prototype single-seat all-metal fighter monoplane designed by Alfred Renard at the Societé Anonyme Avions et Moteurs Renard for a government-sponsored design contest in 1928. The Epervier Type 2 was built and flown in 1928, by Belgian aircraft manufacturer Stampe et Vertongen. It carried an armament of two synchronised 7.7mm guns and was lost in September 1928 after failing to recover from a flat spin. A second prototype, the Epervier Type 2bis, introduced revised streamlined fairings for the cantilever mainwheel legs, mainwheel spats and cylinder aft-fairings and was built by SABCA.
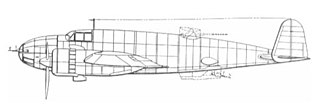
The PZL.49 Miś was a Polish twin-engined medium bomber design that remained only a project due to the outbreak of World War II. The PZL.49 was based on the contemporary PZL.37 Łoś and was to replace it at production lines at the PZL works.
PZL.56 Kania (buzzard) was a Polish pre-war initial project of a fighter aircraft designed by Wsiewołod Jakimiuk of the PZL works. A single-seat low-wing monoplane was a development of PZL.50 Jastrząb fighter, modified to house a new Hispano-Suiza 12Y engine, then under development in France.

The Bernard SIMB AB 14 was a 1920s French single-seat sesquiplane fighter aircraft designed and built by the Société Industrielle des Métaux et du Bois (SIMB). With a reluctance of the French authorities to purchase monoplanes the Bernard 14 was designed as a sesquiplane with Y-form struts bracing the wings on each side. It was powered by a Hispano-Suiza 12Hb inline piston engine and had a fixed tailskid landing gear. While on a test flight on 22 February 1926 the aircraft suffered a catastrophic structural failure of the upper wing and the only Bernard 14 was destroyed.

The Bernard 20 was a 1920s French single-seat monoplane fighter aircraft designed and built by the Société des Avions Bernard. Originally displayed as a mock-up at the 1928 Paris Air Show it was a low-wing monoplane based on the Bernard V2 racer. The prototype powered by a 400 hp (298 kW) Hispano-Suiza 12Jb inline piston engine first flew in July 1929 from Orly. With its racing inheritance, in 1930 the aircraft flew at a speed of 280 km/h (174 mph). With the lack of interest by the French authorities for monoplanes the project was abandoned after 18 months of test flying.
The Bréguet 790 Nautilus was a prototype French three-seat coastal patrol flying-boat designed and built by Bréguet Aviation to meet a requirement from the French navy.
The Gabardini G.8 was an Italian single-seat aircraft produced in both fighter and trainer versions by Gabardini in 1923.
The Bréguet 482 was a French four-engined bomber aircraft of the 1940s. It was designed prior to the outbreak of the Second World War, two prototypes were nearing completion when Germany invaded France in 1940, with one being flown after the end of the war as an experimental platform.
The Blériot 118 was a 1920s French amphibian flying-boat fighter designed by Léon Kirste, only one was built and it was not ordered into production.

P.Z.L. P.8 was a fighter designed by Ing. Zygmunt Puławski and constructed by P.Z.L. from 1930.
References
Bibliography
- Glass, Andrzej. Polskie Konstrukcje Lotnicze Vol.3 (In Polish). Sandomierz, Poland: Wydawnictwo Stratus, 2008.