
The PZL-101 Gawron (rook) is a Polish agricultural and utility aircraft designed and built by WSK-Okęcie.

The PWS-24 was a Polish single-engine passenger aircraft for 4 passengers, built in PWS factory, used from 1933 to 1936 by LOT Polish Airlines. In spite of its limited capacity, it was the only series-built airliner of domestic design ever used by the LOT.

PZL M-4 Tarpan was a Polish trainer and sports aircraft prototype of the 1960s, designed in WSK-Mielec.

The PZL.44 Wicher (gale) was a prototype of 14-seat, twin-engine Polish airliner, built in the Państwowe Zakłady Lotnicze (PZL) in 1938. It was to compete with the DC-2 and Lockheed Super Electra.

The LWD Szpak (starling) was a Polish utility aircraft of 1945, the first Polish aircraft designed after World War II and built in a short series.

The LWD Żak was a Polish touring and trainer aircraft of the late 1940s, designed in the LWD and built in a short series.

The PZL S-4 Kania 2 was a Polish trainer and glider towing aircraft of the 1950s, not built in series. The first prototype was designated S-3 Kania. There is also a helicopter named PZL Kania.

The Lublin R-XVI was a Polish passenger and air ambulance aircraft, designed in the 1930s in the Plage i Laśkiewicz factory in Lublin and built in a small series.

The BŻ-4 Żuk, formerly known as GIL-4, was a Polish four-seat light helicopter built in the 1950s. Although it pioneered a novel rotor and transmission system, it never entered series production.

The PWS-21 was a Polish passenger aircraft for 4 passengers, built in PWS factory in 1930, that remained a prototype.

The PZL.4 was a Polish three-engine passenger aircraft for 10 passengers, built in PZL factory in 1932, which remained a prototype. It was the first Polish-designed and produced multi-engine plane.

The PZL S-1 was a Polish trainer and liaison aircraft of 1945, which remained a prototype. It was the second aircraft built in Poland after World War II.

PZL M-2 was a Polish trainer aircraft prototype of 1958, a low-wing monoplane with fixed gear. Designed at WSK-Mielec, it did not enter production.

The SZD-10 Czapla was a two-seat training glider aircraft that was designed and built in Poland from 1953.

The SZD-11 Albatros was a single-seat glider aircraft that was designed and built in Poland at Szybowcowy Zakład Doświadczalny - Glider Experimental Works in Bielsko-Biała in 1954. Only one prototype was completed and flown.

The SZD-14X Jaskółka M was a single-seat glider designed and built in Poland at Szybowcowy Zakład Doświadczalny - Glider Experimental Works in Bielsko-Biała in 1954. This was an experimental prototype, and only one unit was constructed.

The SZD-15 Sroka was a single-seat glider designed and built in Poland in 1956.
The SZD-25A Lis was a single-seat glider aircraft that was designed and built in Poland from 1955, derived from the SZD-16 Gil and SZD-25 Nov.

The SZD-18 Czajka was a single-seat glider designed and built in Poland in 1956.
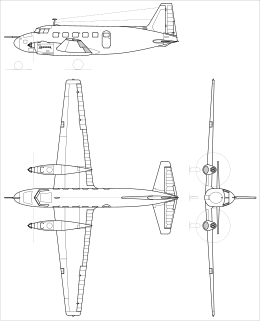
The CSS-12 was a prototype Polish twin-engined feederliner of the 1950s. A single example was built and flown in 1950, but no production followed.




















