
Hermit crabs are anomuran decapod crustaceans of the superfamily Paguroidea that have adapted to occupy empty scavenged mollusc shells to protect their fragile exoskeletons. There are over 800 species of hermit crab, most of which possess an asymmetric abdomen concealed by a snug-fitting shell. Hermit crabs' soft (non-calcified) abdominal exoskeleton means they must occupy shelter produced by other organisms or risk being defenseless.

The Coenobitidae are the family of terrestrial hermit crabs, widely known for their land-living habits as adults. They are found in coastal tropical regions around the world and require access to the ocean to breed.

Pagurus bernhardus is the common marine hermit crab of Europe's Atlantic coasts. It is sometimes referred to as the common hermit crab or soldier crab. Its carapace reaches 3.5 centimetres (1.4 in) long, and is found in both rocky and sandy areas, from the Arctic waters of Iceland, Svalbard and Russia as far south as southern Portugal, but its range does not extend as far as the Mediterranean Sea. It can be found in pools on the upper shore and at the mean tide level down to a depth of approximately 140 metres (460 ft), with smaller specimens generally found in rock pools around the middle shore and lower shore regions, with larger individuals at depth. P. bernhardus is an omnivorous detritivore that opportunistically scavenges for carrion, and which can also filter feed when necessary.

The Diogenidae are a family of hermit crabs, sometimes known as "left-handed hermit crabs" because in contrast to most other hermit crabs, its left chela (claw) is enlarged instead of the right. It comprises 429 extant species, and a further 46 extinct species, making it the second-largest family of marine hermit crabs, after the Paguridae.

The Paguridae are a family of hermit crabs of the order Decapoda. The king crabs, Lithodidae, are now widely understood to be derived from deep within the Paguridae, with some authors placing their ancestors within the genus Pagurus.

Pagurus is a genus of hermit crabs in the family Paguridae. Like other hermit crabs, their abdomen is not calcified and they use snail shells as protection. These marine decapod crustaceans are omnivorous, but mostly prey on small animals and scavenge carrion. Trigonocheirus and Pagurixus used to be considered subgenera of Pagurus, but the former is nowadays included in Orthopagurus, while the latter has been separated as a distinct genus.

Pagurus novizealandiae, or the New Zealand hermit crab is a hermit crab of the family Paguridae, endemic to New Zealand. It is not the only hermit crab in New Zealand, as there are more than sixty species.

Calcinus is a genus of hermit crabs in the family Diogenidae, containing the following species:
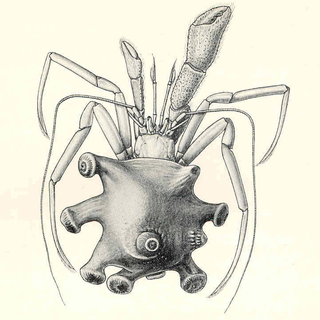
The Parapaguridae are a family of marine hermit crabs from deep waters. Instead of carrying empty gastropod shells like other hermit crabs, they carry colonies of dozen or more sea anemones or zoanthids. Some genera, such as Bivalvopagurus and Tylaspis, do not inhabit shells. The following genera are included:

Paguristes is a genus of hermit crab in the family Diogenidae. It includes the following species :

Pagurus sinuatus is a large species of hermit crab found in Australia and the Kermadec Islands. It is red or orange in colour with coloured bands on the legs and patches on the body.
The Pylojacquesidae are a small family of hermit crabs, comprising only two monotypic genera. The family was erected in 2001, after two specimens at Museum für Naturkunde at the Humboldt University of Berlin were recognised as being quite distinct from other described hermit crabs. The family members differ from other hermit crabs in that their mandibles are chitinous and toothed.

Pagurus samuelis, the blueband hermit crab, is a species of hermit crab from the west coast of North America, and the most common hermit crab in California. It is a small species, with distinctive blue bands on its legs. It prefers to live in the shell of the black turban snail, and is a nocturnal scavenger of algae and carrion.
Porcellanopagurus edwardsi is a species of hermit crab that lives in the waters around New Zealand and its subantarctic islands.
Porcellanopagurus is a genus of hermit crabs. The genus occurs in the Pacific and Indian Oceans.

Cancellus is a genus of hermit crabs in the family Diogenidae. Members of this genus are most commonly found living in small crevices in the outer continental shelf at mesophotic depths. They can be found living in rocks, sponges, and algae among other places. The genus has a cosmopolitan distribution. Four species are known from the western Atlantic.
Jacques Forest was a French carcinologist.
Paragiopagurus is a genus of hermit crabs in the family Parapaguridae, that contains 25 species. Members of this genus live at depths from 116 to 2,067 meters.
Pseudopaguristes is a genus of hermit crabs in the family Diogenidae.
Patsy Ann "Pat" McLaughlin, was an American carcinologist and was regarded as one of the most influential scientists in her field. The crab genus Patagurus was named in her honor in 2013.













