
The Rothschild family is a wealthy Ashkenazi Jewish family originally from Frankfurt that rose to prominence with Mayer Amschel Rothschild (1744–1812), a court factor to the German Landgraves of Hesse-Kassel in the Free City of Frankfurt, Holy Roman Empire, who established his banking business in the 1760s. Unlike most previous court factors, Rothschild managed to bequeath his wealth and established an international banking family through his five sons, who established businesses in London, Paris, Frankfurt, Vienna, and Naples. The family was elevated to noble rank in the Holy Roman Empire and the United Kingdom. The family's documented history starts in 16th century Frankfurt; its name is derived from the family house, Rothschild, built by Isaak Elchanan Bacharach in Frankfurt in 1567.

Nathaniel Mayer Victor Rothschild, 3rd Baron Rothschild was a British banker, scientist, intelligence officer during World War II, and later a senior executive with Royal Dutch Shell and N M Rothschild & Sons, and an advisor to the Edward Heath and Margaret Thatcher governments of the UK. He was a member of the prominent Rothschild family.

Lionel Walter Rothschild, 2nd Baron Rothschild, Baron de Rothschild, was a British banker, politician, zoologist and soldier, who was a member of the Rothschild family. As a Zionist leader, he was presented with the Balfour Declaration, which pledged British support for a Jewish national home in Palestine. Rothschild was the president of the Board of Deputies of British Jews from 1925 to 1926.

Ernst Johann Otto Hartert was a widely published German ornithologist.

Jeanne Stuart, born Ivy Sweet, was a British stage and film actress.

Collita griseola, the dingy footman, is a moth of the family Erebidae. The species was first described by Jacob Hübner in 1803. It is found in Europe and North and South-East Asia.

Ischnocampa is a genus of moths in the family Erebidae.

Leucanopsis is a genus of moths in the family Erebidae. The genus was described by Alfredo Rei do Régo Barros in 1956.

Paidia is a genus of moths in the family Erebidae erected by Jacob Hübner in 1819.
Paracles is a genus of moths in the subfamily Arctiinae. The genus was described by Francis Walker in 1855. The species range from Panama to Patagonia, with quite a few in the southern temperate region of South America.

Spilosoma is a genus of moths in the family Erebidae originally described by John Curtis in 1825. A very heterogeneous group, it is in need of review by the scientific community, as certain species probably need reclassification into their own genera.

Symphlebia is a genus of moths in the family Erebidae. The genus was erected by Felder in 1874.
Crypsotidia is a genus of moths in the family Erebidae.
Sinarella is a genus of moths of the family Erebidae. The genus was erected by Felix Bryk in 1949.
Casama is a genus of tussock moths in the family Erebidae.

Nephopterix is a genus of moths of the family Pyralidae erected by Jacob Hübner in 1825.
Nephopterix griseola is a species of snout moth in the genus Nephopterix. It was described by Walter Rothschild in 1915. It is found in Algeria.
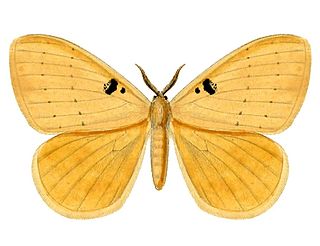
Hemijana is a genus of moths in the family Eupterotidae.
Hemijana griseola is a moth in the family Eupterotidae. It was described by Rothschild in 1917. It is found in South Africa.











