
The Kuomintang (KMT), also referred to as the Guomindang (GMD), the Nationalist Party of China (NPC) or the Chinese Nationalist Party (CNP), is a political party in the Republic of China, initially based on the Chinese mainland and then in Taiwan since 1949. The KMT is a centre-right to right-wing party and the largest in the Pan-Blue Coalition, one of the two main political groups in Taiwan. Its primary rival is the Democratic Progressive Party (DPP), the largest party in the Pan-Green Coalition. As of 2024, the KMT is the largest single party in the Legislative Yuan. The current chairman is Eric Chu.

Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is governed in a framework of a representative democratic republic under a five-power system first envisioned by Sun Yat-sen in 1906, whereby under the constitutional amendments, the President is head of state and the Premier is head of government, and of a multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the Executive Yuan. Legislative power is vested primarily in the Legislative Yuan. Taiwan's judiciary is independent of the executive and the legislature. In addition, the Examination Yuan is in charge of validating the qualification of civil servants, and the Control Yuan inspects, reviews, and audits the policies and operations of the government.

Lee Teng-hui was a Taiwanese politician and agriculturist who served as the 4th president of the Republic of China (Taiwan) under the 1947 Constitution and chairman of the Kuomintang (KMT) from 1988 to 2000. He was the first president to be born in Taiwan, the last to be indirectly elected and the first to be directly elected.

James Soong Chu-yu is a Taiwanese politician who is the founder and chairman of the People First Party. Soong was the first and only elected governor of Taiwan Province from 1994 and 1998. He was a candidate in the 2000 presidential election, which he lost to Chen Shui-bian of the Democratic Progressive Party (DPP).
The Taiwan Solidarity Union (TSU) is a political party in Taiwan which advocates Taiwan independence, and is affiliated with the Taiwanese localization movement. It was officially founded on 12 August 2001 and is considered part of the Pan-Green Coalition. Unlike the Democratic Progressive Party, its larger companion party in the Pan-Green Coalition, the TSU actively campaigns for the creation of a de jure Republic of Taiwan.

Ma Ying-jeou is a Taiwanese politician and lawyer who served as the 6th president of the Republic of China from 2008 to 2016. Previously, he served as the 14th justice minister from 1993 to 1996 and mayor of Taipei from 1998 to 2006. He served as chairman of the Kuomintang (KMT) from 2005 to 2007 and from 2009 to 2014.

The Revolutionary Committee of the Chinese Kuomintang, commonly abbreviated in Chinese as Minge (民革), is one of the eight minor political parties in the People's Republic of China under the direction of the Chinese Communist Party.

Vincent C. Siew or Siew Wan-chang is a Taiwanese politician who served as the Vice President of the Republic of China (Taiwan) from 2008 to 2012. He was the first Taiwanese-born Premier of the Republic of China and former vice-chairman of the Kuomintang (KMT).
As a result of the surrender and occupation of Japan at the end of World War II, the islands of Taiwan and Penghu were placed under the governance of the Republic of China (ROC), ruled by the Kuomintang (KMT), on 25 October 1945. Following the February 28 massacre in 1947, martial law was declared in 1949 by the Governor of Taiwan, Chen Cheng, and the ROC Ministry of National Defense. Following the end of the Chinese Civil War in 1949, the ROC government retreated from the mainland as the Chinese Communist Party (CCP) proclaimed the establishment of the People's Republic of China. The KMT retreated to Taiwan and declared Taipei the temporary capital of the ROC. For many years, the ROC and PRC each continued to claim in the diplomatic arena to be the sole legitimate government of "China". In 1971, the United Nations expelled the ROC and replaced it with the PRC.

This is a timeline of the Republic of China.

Cross-strait relations are the political and economic relations between China and Taiwan across the Taiwan Strait. Due to the existing controversy over the status of Taiwan and the Chinese legitimacy question, they are also not defined as diplomatic relations by either side.

The Kuomintang (KMT) is a Chinese political party that ruled mainland China from 1927 to 1949 prior to its relocation to Taiwan as a result of the Chinese Civil War. The name of the party translates as "China's National People's Party" and was historically referred to as the Chinese Nationalists. The party was initially founded on 23 August 1912, by Sun Yat-sen but dissolved in November 1913. It reformed on October 10, 1919, again led by Sun Yat-sen, and became the ruling party in China. After Sun's death, the party was dominated from 1927 to 1975 by Chiang Kai-shek. After the KMT lost the civil war with the Chinese Communist Party in 1949, the party retreated to Taiwan and remains a major political party of the Republic of China based in Taiwan.
Alan Rechuldak Seid is a Palauan businessman and politician of partially American Jewish origin. He was elected into House of Delegates of Palau from 1989 until 2000. He along with Chen Ding-nan agreed to build the Palasia Hotel in 1995. He was a senator in the Senate of Palau from 2005 to 2009 In the 2008 presidential election he was the running mate of Elias Camsek Chin.

Eric Li-luan Chu is a Taiwanese politician who is currently the chairman of the Kuomintang (KMT).
The Sixth Chen–Chiang summit is the 6th part of the Chen-Chiang summit of cross-strait meetings. It is held between the Association for Relations Across the Taiwan Straits (ARATS) represented by Chen Yun-lin and Straits Exchange Foundation (SEF) represented by Chiang Pin-kung.
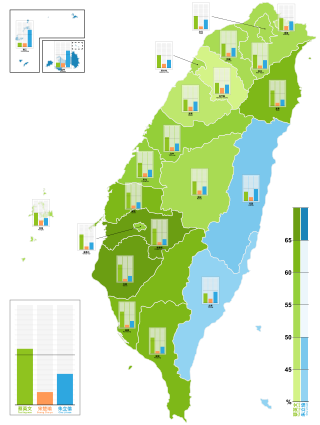
Presidential elections were held in Taiwan on 16 January 2016. Democratic Progressive Party (DPP) candidate Tsai Ing-wen with her independent running mate Chen Chien-jen won over Eric Chu of the Kuomintang (KMT) and James Soong of the People First Party (PFP). Tsai became the first female president in Taiwan, as well as in the Chinese-speaking world.

The Ill-gotten Party Assets Settlement Committee is an independent government agency of Taiwan established in 2016 by the Act on Promoting Transitional Justice. It is responsible for the investigation and recovery of ill-gotten assets of political parties and their affiliated organizations obtained during the martial law period in Taiwan. All parties established before the lifting of martial law, 15 July 1987, are required to report their party assets to the committee. As the dominant party during the martial law period, the Kuomintang (KMT) and its affiliate organizations are the main targets of this investigation. The committee is headquartered in Zhongshan District, Taipei.
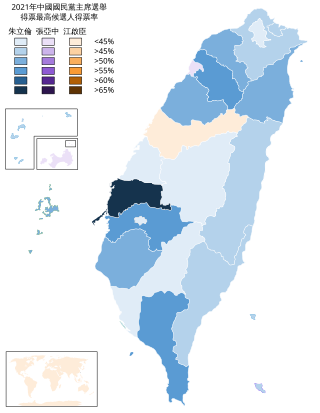
The 2021 Kuomintang chairmanship election was scheduled to be held in July 2021. It was postponed due to the COVID-19 pandemic, and eventually rescheduled for 25 September 2021. It was the tenth direct election of the party leader in Kuomintang (KMT) history. All registered, due-paying KMT party members were eligible to vote.

Palau–Taiwan relations are the bilateral relations between the Republic of Palau and the Republic of China (Taiwan). Palau maintains an embassy in Taipei and Taiwan maintains an embassy in Koror City. Exchanges between the two nations range from agriculture, culture, education, fishery, medical services, tourism and water supply infrastructure. As of 28 December 2024, Palau is one of only 12 United Nations member states to have formal diplomatic relations with Taiwan.

















