
Euglenozoa are a large group of flagellate Discoba. They include a variety of common free-living species, as well as a few important parasites, some of which infect humans. Euglenozoa are represented by three major clades, i.e., Kinetoplastea, Diplonema and Symbiontida. Euglenozoa are unicellular, mostly around 15–40 μm (0.00059–0.00157 in) in size, although some euglenids get up to 500 μm (0.020 in) long.

The family Vampyrellidae is a subgroup of the order Aconchulinida within the phylum Cercozoa. Based on molecular sequence data, the family currently comprises the genus Vampyrella, and maybe several other vampyrellid amoebae. The cells are naked and characterised by radiating, filose pseudopodia and an orange colouration of the main cell body.

Cercozoa is a phylum of diverse single-celled eukaryotes. They lack shared morphological characteristics at the microscopic level, and are instead defined by molecular phylogenies of rRNA and actin or polyubiquitin. They were the first major eukaryotic group to be recognized mainly through molecular phylogenies. They are the natural predators of many species of microbacteria and Archea. They are closely related to the phylum Retaria, comprising amoeboids that usually have complex shells, and together form a supergroup called Rhizaria.
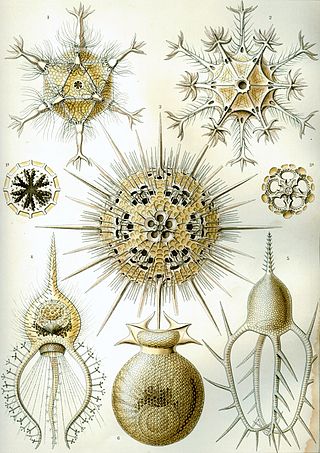
Phaeodarea, or Phaeodaria, is a group of amoeboid cercozoan organisms. They are traditionally considered radiolarians, but in molecular trees do not appear to be close relatives of the other groups, and are instead placed among the Cercozoa. They are distinguished by the structure of their central capsule and by the presence of a phaeodium, an aggregate of waste particles within the cell.

Amorphea are members of a taxonomic supergroup that includes the basal Amoebozoa and Obazoa. That latter contains the Opisthokonta, which includes the Fungi, Animals and the Choanomonada, or Choanoflagellates. The taxonomic affinities of the members of this clade were originally described and proposed by Thomas Cavalier-Smith in 2002.

Cercomonads are small flagellates, widespread in aqueous habitats and common in soils.

The tectofilosids are a group of filose amoebae with shells. These are composed of organic materials and sometimes collected debris, in contrast to the euglyphids, which produce shells from siliceous scales. The shell usually has a single opening, but in Amphitrema and a few other genera it has two on opposite ends. The cell itself occupies most of the shell. They are most often found on marsh plants such as Sphagnum.

Monadofilosa is a grouping of Cercozoa. These organisms are single-celled amoeboid protists.

The spongomonads are a group of flagellated protists in the phylum Cercozoa. Taxonomically, they compose the family Sarcomonadidae and order Sarcomonadida. They were originally placed among the Reticulofilosa, but were later transferred to Monadofilosa. It includes only two genera:

The sarcomonads or class Sarcomonadea are a group of amoeboid biciliate protists in the phylum Cercozoa. They are characterized by a propensity to move through gliding on their posterior cilium or through filopodia, a lack of scales or external theca, a soft cell surface without obvious cortical filamentous or membranous skeleton, two cilia without scales or hairs, tubular mitochondrial cristae, near-spherical extrusomes, and a microbody attached to the nucleus.
Neocercomonas is a protist genus of the order Cercomonadida. It consists of single-celled bacteriophagous organisms that usually live on or nearby terrestrial plants, both above and belowground. Species are biflagellate and may grow up to 60 micrometers long, with a trailing tail-like mass of protoplasm at their posterior end and a pair of roots connecting their posterior flagellum to the cytoskeleton.
The paracercomonads are a group of cercozoan protists. Taxonomically, they comprise the family Paracercomonadidae, order Paracercomonadida and subclass Paracercomonada. Due to their morphological similarities to the cercomonads, members of this family were grouped with Cercomonas and similar taxa from the beginning. However, their similarities are due to convergent evolution.

Ventrifilosa is a highly diverse group of phagotrophic protists that glide through their flagella and emit filose pseudopods from their ventral side for feeding. Because of their mixture of amoeba and flagellate characteristics, they are amoeboflagellates. Members of this group are the Imbricatea, Sarcomonadea and Thecofilosea.
Cryptofilida is an order of small heterotrophic protists in the phylum Cercozoa. They are filose amoebae that lack cilia and gliding, and are instead characterized by movement through branching or unbranched granular filopodia that are appressed to the substrate during their feeding.

The glissomonads are a group of bacterivorous gliding flagellated protists that compose the order Glissomonadida, in the amoeboflagellate phylum Cercozoa. They comprise a vast, largely undescribed diversity of soil and freshwater organisms. They are the sister group to cercomonads; the two orders form a solid clade of gliding soil-dwelling flagellates called Pediglissa.

Euglyphia is a group of imbricate protists in the phylum Cercozoa. They are unicellular eukaryotes characterized by a cell body covered in large imbricate scales, and an apical aperture through which they extend either filose pseudopodia or two cilia of different sizes that are not used for gliding.
Pediglissa is a subclass of phagotrophic protists that inhabit soil or freshwater habitats. They were defined in 2018 according to phylogenetic analyses that showed a clade containing the orders Cercomonadida and Glissomonadida. They're the sister group of Paracercomonadida.

Viridiraptoridae, previously known as clade X, is a clade of heterotrophic protists in the phylum Cercozoa. They're a family of glissomonads, a group containing a vast, mostly undescribed diversity of soil and freshwater organisms.
Viridiraptor is a genus of heterotrophic protists, containing the single species Viridiraptor invadens. It belongs to the family Viridiraptoridae, in the phylum Cercozoa.
Aurigamonas is a genus of predatory protists of an unusual cell structure, with two flagella and numerous haptopodia. It is a monotypic genus, composed by a single species, Aurigamonas solis. It is the only genus of the family Aurigamonadidae.








