
Mindanao is the second-largest island in the Philippines, after Luzon, and seventh-most populous island in the world. Located in the southern region of the archipelago, the island is part of an island group of the same name that also includes its adjacent islands, notably the Sulu Archipelago. According to the 2020 census, Mindanao has a population of 26,252,442 people, while the entire island group has an estimated population of 27,021,036 according to the 2021 census.

Mount Apo, also known locally as Apo Sandawa, is a large solfataric, dormant stratovolcano on the island of Mindanao, Philippines. With an elevation of 2,954 meters (9,692 ft) above sea level, it is the highest-mountain in the Philippine Archipelago, Mindanao and 24th-highest peak of an island on Earth. Located on the tripartite border of Davao City and Davao del Sur in the Davao Region, and Cotabato in Soccsksargen, Mount Apo is the most-prominent mountain in the Philippines. The peak overlooks from Davao City 45 kilometers (28 mi) to the northeast, Digos 25 kilometers (16 mi) to the southeast, and Kidapawan 20 kilometers (12 mi) to the west. It is a protected area and a Natural Park of the Philippines.

Bukidnon, officially the Province of Bukidnon, is a landlocked province in the Philippines located in the Northern Mindanao region. Its capital is the city of Malaybalay. The province borders, clockwise from the north, Misamis Oriental, Agusan del Sur, Davao del Norte, Cotabato, Lanao del Sur, and Lanao del Norte. According to the 2020 census, the province is inhabited by 1,541,308 residents. The province is composed of 2 component cities and 20 municipalities. It is the third largest province in the country in terms of total area of jurisdiction behind Palawan and Isabela respectively.

Agusan del Sur, officially the Province of Agusan del Sur, is a province in Caraga region, Mindanao, Philippines. Its capital is the municipality of Prosperidad. It is bordered on the northwest by Agusan del Norte and Misamis Oriental; east by Surigao del Sur; southeast by Davao Oriental; mid-south by Davao de Oro; southwest by Davao del Norte and, mid-west by Bukidnon. It is the fourth largest province in the country in terms of area, with the size of 3,856 sq miles.

Surigao del Sur, officially the Province of Surigao del Sur, is a province in the Philippines located in the Caraga region in Mindanao. Its capital is Tandag City. Surigao del Sur is situated at the eastern coast of Mindanao and faces the Philippine Sea to the east.

Davao del Norte, officially the Province of Davao del Norte, is a province in the Philippines located in the Davao Region in Mindanao. Its capital and largest city is Tagum. The province also includes Samal Island to the south in Davao Gulf.

Davao de Oro, officially the Province of Davao de Oro, is a province in the Philippines located in the Davao Region in Mindanao. Its capital is Nabunturan. It used to be part of the province of Davao del Norte until it was made a separate province in 1998.

Caraga, officially the Caraga Administrative Region and designated as Region XIII, is an administrative region in the Philippines occupying the northeastern section of Mindanao. The region was created through Republic Act No. 7901 on February 23, 1995. The region comprises five provinces: Agusan del Norte, Agusan del Sur, Dinagat Islands, Surigao del Norte, and Surigao del Sur; six cities: Bayugan, Bislig, Butuan, Cabadbaran, Surigao and Tandag; 67 municipalities and 1,311 barangays. Butuan, the most urbanized city in Caraga, serves as the regional administrative center.

Loreto, officially the Municipality of Loreto, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Agusan del Sur, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 43,880 people. Loreto is the largest Municipality in terms of land area in Mindanao.

San Francisco, officially the Municipality of San Francisco, is a 1st class municipality in the province of Agusan del Sur, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 80,760 people.

The Lumad are a group of Austronesian indigenous peoples in the southern Philippines. It is a Cebuano term meaning "native" or "indigenous". The term is short for Katawhang Lumad, the autonym officially adopted by the delegates of the Lumad Mindanao Peoples Federation (LMPF) founding assembly on 26 June 1986 at the Guadalupe Formation Center, Balindog, Kidapawan, Cotabato, Philippines. Usage of the term was accepted in Philippine jurisprudence when President Corazon Aquino signed into law Republic Act 6734, where the word was used in Art. XIII sec. 8(2) to distinguish Lumad ethnic communities from the islands of Mindanao.

The Manobo languages are a group of languages spoken in the Philippines. Their speakers are primarily located around Northern Mindanao, Central Mindanao and Caraga regions where they are natively spoken. Some outlying groups make Manobo geographically discontiguous as other speakers can be located as far as the southern peninsula of Davao Oriental, most of Davao Occidental and coastal areas of Sultan Kudarat. The Kagayanen speakers are the most extremely remote and can be found in certain portions of Palawan.
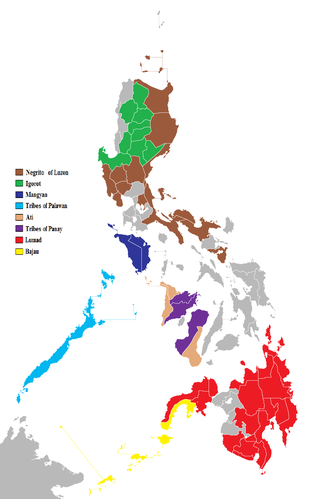
The indigenous peoples of the Philippines are ethnolinguistic groups or subgroups that maintain partial isolation or independence throughout the colonial era, and have retained much of their traditional pre-colonial culture and practices.
The Manobo are an indigenous people group from Mindanao in the Philippines, whose core lands cover most of the Mindanao island group, from Sarangani island into the Mindanao mainland in the regions of Agusan, Davao, Bukidnon, Surigao, Misamis, and Cotabato. The Manobo are considered the most diverse among the many indigenous peoples of the Philippines, with the largest number of subgroups within its family of languages. The Philippine Statistics Authority listed 644,904 persons as Manobo in its 2020 Census of Population and Housing.
Agusan is a Manobo language of northeastern Mindanao in the Philippines.
Nepenthes manobo is a tropical pitcher plant endemic in the Philippines discovered in the Pantaron Range on the island of Mindanao, where it grows at a narrow elevation range of 1000–1020 m above sea level.
Busdi is a rural barangay of the Upper Pulangi District of Malaybalay, Bukidnon, Philippines. According to the 2015 census, it has a population of 2,377 people. It is bounded to the north by Barangay Bulonay of Impasug-ong, to the east by the Municipality of La Paz, Agusan del Sur, to the south by Saint Peter and Kulaman, and to the west by Kibalabag and Manalog.

Eufemia Campos Cullamat, also known as Ka Femia, is a Filipina farmer, activist, and politician. She was a member of the Philippine House of Representatives for the 18th Congress under the Bayan Muna party-list group. She is the second Manobo to serve in Congress after former Cotabato Representative Nancy Catamco.
Bai Bibyaon Ligkayan Bigkay was a Filipino Lumad leader and environmentalist. She was the first and only female chieftain in the history of the Manobo people and has been described as "Mother of the Lumads". She was an advocate of indigenous peoples' rights and had been a defender of Manobo ancestral lands and the Pantaron Mountain Range from 1994.
Lorena Mandacawan is a Matigsalog Manobo activist and spokesperson for the Salugpongan Schools' Parent Teachers Community Association. She also serves as a Barangay Health Worker (BHW), and is the chairperson of Sabokahan. She has spoken against efforts to close Salugpongan schools, against sexual harassment and threats from the military, and against the sexist attitudes propagated by President Duterte.














