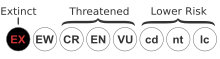
Punctuated equilibrium is a theory in evolutionary biology which proposes that once species appear in the fossil record the population will become stable, showing little evolutionary change for most of its geological history. This state of little or no morphological change is called stasis. When significant evolutionary change occurs, the theory proposes that it is generally restricted to rare and geologically rapid events of branching speciation called cladogenesis. Cladogenesis is the process by which a species splits into two distinct species, rather than one species gradually transforming into another.

Zalophus is a genus of the family Otariidae of order Carnivora. It includes these species, of which one became recently extinct:

The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species, founded in 1965, has evolved to become the world's most comprehensive inventory of the global conservation status of biological species. It uses a set of criteria to evaluate the extinction risk of thousands of species and subspecies. These criteria are relevant to all species and all regions of the world. With its strong scientific base, the IUCN Red List is recognized as the most authoritative guide to the status of biological diversity. A series of Regional Red List are produced by countries or organizations, which assess the risk of extinction to species within a political management unit.

Chinchillas are either of two species of crepuscular rodents of the parvorder Caviomorpha. They are slightly larger and more robust than ground squirrels, and are native to the Andes mountains in South America. They live in colonies called "herds" at high elevations of up to 4,270 m (14,000 ft). Historically, chinchillas lived in an area that included parts of Bolivia, Peru, Argentina, and Chile, but today, colonies in the wild are known only in Chile. Along with their relatives, viscachas, they make up the family Chinchillidae. They are also related to the chinchilla rat.

The nuthatches constitute a genus, Sitta, of small passerine birds belonging to the family Sittidae. Characterised by large heads, short tails, and powerful bills and feet, nuthatches advertise their territory using loud, simple songs. Most species exhibit grey or bluish upperparts and a black eye stripe.
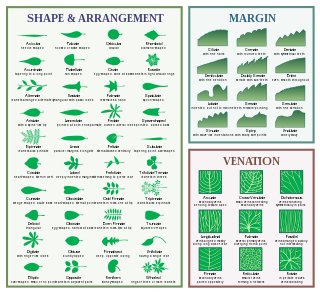
The following is a defined list of terms which are used to describe leaf morphology in the description and taxonomy of plants. Leaves may be simple or compound. The edge of the leaf may be regular or irregular, may be smooth or bearing hair, bristles or spines. For more terms describing other aspects of leaves besides their overall morphology see the leaf article.

The Nilgiri Biosphere Reserve is an International Biosphere Reserve in the Western Ghats and Nilgiri Hills ranges of South India. The Nilgiri Sub-Cluster is a part of the Western Ghats, which was declared a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 2012. It includes the Aralam, Mudumalai, Mukurthi, Nagarhole, Bandipur and Silent Valley national parks, as well as the Wayanad and Sathyamangalam wildlife sanctuaries.

Box turtles are North American turtles of the genus Terrapene. Although box turtles are superficially similar to tortoises in terrestrial habits and overall appearance, they are actually members of the American pond turtle family (Emydidae). The twelve taxa which are distinguished in the genus are distributed over four species. They are largely characterized by having a domed shell, which is hinged at the bottom, allowing the animal to close its shell tightly to escape predators.
The genus Eligmodontia consists of five or six species of South American sigmodontine mice restricted to Bolivia, Chile, and Argentina. Species of Eligmodontia occur along the eastern side of the Andes Mountains, in Patagonia, and in the Chaco thorn forest of South America. They can be found in arid and semiarid habitats and in both high and low elevation areas. These rodents are commonly known as gerbil mice or by their local name lauchas. Sometimes they are also called silky desert mice, highland desert mice or silky-footed mice. The closest living relatives are probably the chaco mice (Andalgalomys), the leaf-eared mice, and Salinomys.

A critically endangered (CR) species is one that has been categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) as facing an extremely high risk of extinction in the wild.

A species that is extinct in the wild (EW) is one that has been categorized by the International Union for Conservation of Nature as known only by living members kept in captivity or as a naturalized population outside its historic range due to massive habitat loss.

The big-headed Amazon River turtle, also known as the big-headed sideneck, is a species of turtle in the family Podocnemididae. The species is monotypic within the genus Peltocephalus.

Dichomeris is a genus of moths, in the family Gelechiidae, described by Jacob Hübner in 1818.

Placopsis is a genus of lichenized fungi in the family Agyriaceae.

Colpodella is a genus of alveolates comprising 5 species, and two further possible species: They share all the synapomorphies of apicomplexans, but are free-living, rather than parasitic. Many members of this genus were previously assigned to a different genus - Spiromonas.

Caesioperca is a genus of ray-finned fish in the sub-family Anthiadinae in the sea bass family Serranidae. It contains just two species, found in the ocean off Southern Australia and New Zealand.
Tentaoculus balantiophaga is a species of small sea snail, a marine gastropod mollusk in the family Pseudococculinidae, the false limpets.
Placopsis perrugosa is a placodioid lichen in the Agyriaceae family.
Apicystis is a genus of parasitic alveolates of the phylum Apicomplexa.