
The Achelata is an infra-order of the decapod crustaceans, holding the spiny lobsters, slipper lobsters and their fossil relatives.

Slipper lobsters are a family (Scyllaridae) of about 90 species of achelate crustaceans, in the Decapoda clade Reptantia, found in all warm oceans and seas. They are not true lobsters, but are more closely related to spiny lobsters and furry lobsters. Slipper lobsters are instantly recognisable by their enlarged antennae, which project forward from the head as wide plates. All the species of slipper lobsters are edible, and some, such as the Moreton Bay bug and the Balmain bug are of commercial importance.

The crustacean order Tanaidacea make up a minor group within the class Malacostraca. There are about 940 species in this order.
Epicaridea is a former suborder of isopods, now treated as an infraorder in suborder Cymothoida. They are ectoparasites that inhabit other crustaceans, namely ostracods, copepods, barnacles and malacostracans. Epicarideans are found globally. Epicaridea are generally less well researched than other isopods.
Langobardisaurus is an extinct genus of tanystropheid archosauromorph reptile, with one known species, L. pandolfii. Its fossils have been found in Italy and Austria, and it lived during the Late Triassic period, roughly 228 to 201 million years ago. The Langobardisaurus was first discovered by Italian paleontologist Silvio Renesto in 1994 from the Calcare di Zorzino Formation in Northern Italy.

The Solnhofen Plattenkalk, a collective term of multiple Late Jurassic lithographic limestones in southeastern Germany, is famous for its well preserved fossil flora and fauna dating to the late Jurassic.
Aeschronectida is an extinct order of mantis shrimp-like crustaceans which lived in the Mississippian subperiod in what is now Montana. They exclusively lived in the Carboniferous, or the age of amphibians. They have been found mostly in the U.S. and in the British Isles, in 1979 species were found in the Madera Formation in New Mexico. Aeschronectida was first identified appearing in Continental Europe in around 2014. While sharing similar characteristics to Stomatopoda, they lack certain physical characteristics of that taxon. The first species of Aeschronectida is accredited to Frederick R. Schram. They diverge substantially from typical hoplocaridan morphology by having more unmodified thoracopods. It's theorized that these thoracopods evolved to become more specialized, making them potential ancestors to Stomatopoda.

Crustaceans may pass through a number of larval and immature stages between hatching from their eggs and reaching their adult form. Each of the stages is separated by a moult, in which the hard exoskeleton is shed to allow the animal to grow. The larvae of crustaceans often bear little resemblance to the adult, and there are still cases where it is not known what larvae will grow into what adults. This is especially true of crustaceans which live as benthic adults, more-so than where the larvae are planktonic, and thereby easily caught.

Cyclida is an extinct order of crab-like fossil arthropods that lived from the Carboniferous to the Jurassic and possibly Cretaceous. Their classification is uncertain, but they are generally interpreted as crustaceans, likely belonging to the superclass Multicrustacea.

Cancrinos is a genus of fossil crustaceans closely allied with the slipper lobsters. One species is known, C. claviger from the Jurassic of southern Germany.
Skara is a genus of maxillopod crustacean known from the Upper Cambrian Orsten deposit of Sweden and similarly aged deposits in China. It is the only genus in the order Skaracarida and family Skaraidae, and contains three species:
This list of fossil arthropods described in 2014 is a list of new taxa of trilobites, fossil insects, crustaceans, arachnids and other fossil arthropods of every kind that have been described during the year 2014. The list only includes taxa at the level of genus or species.
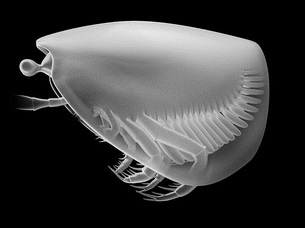
Thylacares is a genus of Thylacocephalan containing only the single species Thylacares brandonensis. Found in Silurian period strata from the Brandon Bridge Formation in Waukesha, Wisconsin, U.S., the species is distinguishable from other Thylacocephalans by its smaller raptorial appendages and compound eyes. The body is fully encased in a bivalve shell, with only the eyes protruding on stalks. The species' trunk is composed of about 22 segments.
This list of fossil arthropods described in 2016 is a list of new taxa of trilobites, fossil insects, crustaceans, arachnids and other fossil arthropods of every kind that have been described during the year 2016, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to arthropod paleontology that occurred in the year 2016.
This list of fossil arthropods described in 2017 is a list of new taxa of trilobites, fossil insects, crustaceans, arachnids and other fossil arthropods of every kind that are scheduled to be described during the year 2017, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to arthropod paleontology that are scheduled to occur in the year 2017.
This list of fossil arthropods described in 2019 is a list of new taxa of trilobites, fossil insects, crustaceans, arachnids and other fossil arthropods of every kind that are scheduled to be described during the year 2019, as well as other significant discoveries and events related to arthropod paleontology that are scheduled to occur in the year 2019.
Charbelicaris is a prehistoric genus of crustacean that lived during the Upper Cretaceous in what is now Lebanon. It is named for Charbel Makhlouf, a Lebanese Maronite saint.

Palinurina is an extinct genus of crustaceans, belonging to the decapods. These animals lived between the Lower Jurassic and the Upper Jurassic and their fossils can be found in Europe. This crustacean is considered one of the oldest lobsters.

Tyrannosculda is an extinct genus of mantis shrimp which lived during the Late Jurassic in southern Germany. It was named in 2021, with T. laurae as the type and only species. Several fossil specimens are known, representing various growth stages.

Sculda is an extinct genus of mantis shrimp known from the late Jurassic to late Cretaceous of Germany and Lebanon. Although several species have been assigned to it, some are now deemed dubious or moved to different genera. It was a moderate-sized crustacean, measuring no more than 50 mm (2.0 in) long. Sculda would have lived in a marine environment and been a predatory animal, likely smashing its prey with the widened segment of its raptorial appendages before cutting it with the sharp appendage tips.










