Related Research Articles

The Principality of Ruhuna, also referred to as the Kingdom of Ruhuna, is a region of present-day Southern and Eastern Sri Lanka. It was the center of a flourishing civilisation and the cultural and economic centres of ancient Sri Lanka. Magama, Tissamaharama and Mahanagakula were established here.

The Sinhala Kingdom or Sinhalese Kingdom refers to the successive Sinhalese kingdoms that existed in what is today Sri Lanka. The Sinhalese kingdoms are kingdoms known by the city at which its administrative centre was located. These are in chronological order: the kingdoms of Tambapanni, Upatissa Nuwara, Anuradhapura, Polonnaruwa, Dambadeniya, Gampola, Kotte, Sitawaka and Kandy.

Chandrabhanu or Chandrabhanu Sridhamaraja was the King of Tambralinga Kingdom in present-day Thailand, Malaysia and Sumatra and the Jaffna Kingdom in northern Sri Lanka. A Javaka, he was known to have ruled from during the period of 1230 until 1262. He was also known for building a well-known Buddhist stupa in southern Thailand. He spent more than 30 years in his attempt to conquer Sri Lanka. He was eventually defeated by the forces of the Pandyan Dynasty from Tamil Nadu in 1262 and was killed by the brother of the south Indian Emperor Jatavarman Sundara Pandyan.
Alagakkonara, also known as Alakeshwara, were a prominent feudal family that provided powerful ministers and military rulers during the medieval period in Sri Lanka. Some historians claim that the family was of Tamil origin, possibly from Madurai or Kanchipuram in Tamil Nadu, India. The family arrived in Sri Lanka around the 13th century and naturalized themselves in Sri Lanka.

Gampola is a town located in Kandy District, Central Province, Sri Lanka, governed by an Urban Council. Gampola was made the capital of the island by King Buwanekabahu IV, who ruled for four years in the mid-fourteenth century. The last king of Gampola was King Buwanekabahu V, who ruled the island for 29 years. A separate city was built in Kotte during this time by a noble known as Alagakkonara. The longest sleeping Buddha statue in South Asia is located in the Saliyalapura Temple, Gampola.
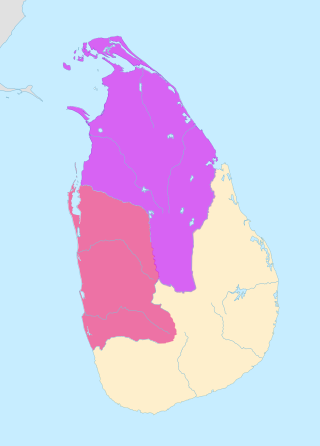
The Kingdom of Polonnaruwa was the Sinhalese kingdom that expanded across the island of Sri Lanka and several overseas territories, from 1070 until 1232. The kingdom started expanding its overseas authority during the reign of Parakramabahu the Great.

The Gal Vihara, and known originally as the Uttararama, is a rock temple of the Buddha situated in the ancient city Polonnaruwa, the capital of the ancient Kingdom of Polonnaruwa, now present-day Polonnaruwa, in North Central Province, Sri Lanka. It was fashioned in the 12th century by King Parakramabahu I. The central feature of the temple is four rock relief statues of the Buddha, which have been carved into the face of a large granite gneiss rock. The images consist of a large seated figure, another smaller seated figure inside an artificial cavern, a standing figure, and a reclining figure. These are considered to be some of the best examples of ancient Sinhalese sculpting and carving arts, and have made the Gal Vihara the most visited monument at Polonnaruwa.
Vira Alakesvara, also known as Vijayabahu VI, was the last King of Gampola who ruled from 1397 to 1411. He was the last prominent member of the Alagakkonara family.
Martanda Cinkaiariyan ascended the throne of Jaffna Kingdom under the throne name Pararasasekaram III. He is one of the early Aryacakravarti kings about whom historical and epigraphical evidence is available. He was noted by Ibn Battuta in his well-known travelogue as well as he has left behind a few inscriptions. He oversaw the international trade of the Jaffna kingdom with Yemen via the kingdom's powerful trading ships. Martanda Cinkaiariyan accompanied Battuta to the peak of Sivanoli Padam Malai along with Yogis and other Hindus and companions of the king who visited the sacred Shiva site annually.

The current legislative capital of Sri Lanka is Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte and the executive and judicial capital is Colombo. Over the course of the island's history, the national capital has been in several locations other than Sri Jayawardenepura Kotte, the following is a list of cities which have historically served as the capital city of Sri Lanka and its predecessor states.

The Kingdom of Kotte, named after its capital, Kotte, was a Sinhalese kingdom that flourished in Sri Lanka during the 15th century.
Lankapura Dandanatha, more commonly referred to as simply Lankapura, was a Senapati of the Sinhala Army during the reign of King Parakramabahu I. He led an expeditionary force to South India in support of the Pandyan king Parakrama Pandyan I, bringing parts of South India under their control. Lankapura succeeded in restoring the Pandyan prince to the throne, and ordered the use of Sri Lankan currency in areas under his control. Whether he died during the invasion is unclear, since Sri Lankan sources claim that Lankapura returned to Sri Lanka as a war hero.However, Rameswaram and many areas of India, remained under the rule of the Sri Lankan Monarchs until the reign of Nissanka Malla, which shows that general Lankapura was never defeated.

The Anuradhapura period was a period in the history of Sri Lanka of the Anuradhapura Kingdom from 377 BCE to 1017 CE. The period begins when Pandukabhaya, King of Upatissa Nuwara moved the administration to Anuradhapura, becoming the kingdom's first monarch. Anuradhapura is heralded as an ancient cosmopolitan citadel with diverse populations.

Statue of Parakramabahu I, located near the Pothgul Vehera in Polonnaruwa is a stone sculpture dating back to the Polonnaruwa period of ancient Sri Lanka. Its identity is uncertain, although the widely accepted theory is that it is a statue of Parakramabahu I. However, it has also been suggested as the statue of a sage. Carved on a large boulder, the statue depicts a majestic figure with a grave expression, holding a book or yoke in his hands.
Vira Parakramabahu VIII, also known as Ambulagala Kumara, was King of Kotte in the fifteenth century, who ruled from 1484 to 1518. He succeeded Parakramabahu VII and was succeeded by his son Dharma Parakramabahu IX. Another son Vijayabahu VII also became king.
Vikramabahu III was King of Gampola who ruled from 1357 to 1374. He succeeded his Uncle Parakramabahu V as King of Gampola and was succeeded by his nephew Bhuvanaikabahu V.

Parakramabahu II, also known as Panditha Parakramabāhu, was the King of Dambadeniya in 13th century, whose reign lasted from 1236 to 1270. As a pioneer in literature, he was bestowed with the honorary title "Kalikala Sahitya Sarvagna Pandita". Parakramabahu's reign is notable for the creation of numerous Sinhalese literal works such as, Kausilumina, Pūjāvaliya, Pāli Vishuddḥi Mārgaya, Thūpavaṃsa and Sidhath Sangarāva. He launched a campaign against the Eastern Ganga invader Kalinga Magha, and successfully expelled him in 1255, unifying Sri Lanka under one rule. He succeeded his father Vijayabahu III as King of Dambadeniya, and was succeeded by his elder son, Vijayabahu IV, after his death.

The Transitional period of Sri Lanka spans from the end of the Kingdom of Polonnaruwa, in 1232, to the start of the Kandyan period in 1597. The period is characterised by the succession of capitals that followed the fall of the Polonnaruwa Kingdom and the creation of the Jaffna kingdom and Crisis of the Sixteenth Century.
1157 Ruhuna Rebellion, also known as the Rebellion of Queen Sugala, was a revolt led-by Queen Sugala of Ruhuna against the Kingdom of Polonnaruwa ruled by Parakramabahu the Great. The rebellion was suppressed by the army of Parakramabahu, and the kingdom of Ruhuna was annexed as a part of Polonnaruwa in 1158.
References
- ↑ Guṇavardhana, Raṇavīra; Rōhaṇadīra, Măndis (2000). Reflections on a Heritage: Historical Scholarship on Premodern Sri Lanka. Central Cultural Fund, Ministry of Cultural and Religious Affairs. p. 270. ISBN 978-955-613-108-6.
- ↑ Herath, Dharmaratna (1994). The Tooth Relic and the Crown. Herath. p. 74. ISBN 978-955-95663-0-4.
