
Catfish are a diverse group of ray-finned fish. Named for their prominent barbels, which resemble a cat's whiskers, catfish range in size and behavior from the three largest species alive, the Mekong giant catfish from Southeast Asia, the wels catfish of Eurasia, and the piraíba of South America, to detritivores, and even to a tiny parasitic species commonly called the candiru, Vandellia cirrhosa. Neither the armour-plated types nor the naked types have scales. Despite their name, not all catfish have prominent barbels or "whiskers". Members of the Siluriformes order are defined by features of the skull and swimbladder. Catfish are of considerable commercial importance; many of the larger species are farmed or fished for food. Many of the smaller species, particularly the genus Corydoras, are important in the aquarium hobby. Many catfish are nocturnal, but others are crepuscular or diurnal.

Clarias is a genus of catfishes of the family Clariidae, the airbreathing catfishes. The name is derived from the Greek chlaros, which means lively, in reference to the ability of the fish to live for a long time out of water.

The tentacled flathead, also known as the Indian Ocean crocodilefish, Madagascar flathead or longhead flathead, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Platycephalidae, the flatheads. This species is in the western Indian Ocean, including the Red Sea and the Mediterranean, having invaded as a Lessepsian migrant through the Suez Canal. It is the only species in the monotypic genus Papilloculiceps.
Dolichamphilius is a genus of loach catfishes endemic to the Democratic Republic of the Congo. There are currently two recognized species in this genus.
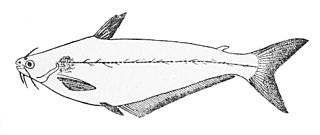
The African butter catfish is a species of fish in the family Schilbeidae. It is native to many major river systems in Africa. Other common names for the fish include butter fish, butter barbel, African glass catfish, lubangu, mystus catfish, silver barbel, and silver catfish. It was originally described as Silurus mystus by Carl Linnaeus in 1758.

Synodontis nigrita, known as the false upside down catfish, is a species of upside-down catfish that occurs widely in northern Africa. It was first described by French zoologist Achille Valenciennes in 1840. The type specimen is in the Muséum National d' Histoire Naturelle de Paris.

Coptodon deckerti is a critically endangered species of fish in the cichlid family, endemic to Lake Ejagham in western Cameroon. It is threatened by pollution and sedimentation from human activities, and potentially also by emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2) from the lake's bottom (compare Lake Nyos), although Ejagham is too shallow to contain very high amounts of this gas. A species of catfish from the genus Parauchenoglanis has recently been introduced to the lake, and this probably presents a serious threat to the endemic cichlids.

Clarias gariepinus or African sharptooth catfish is a species of catfish of the family Clariidae, the airbreathing catfishes.

Parauchenoglanis is a genus of claroteid catfishes native to Africa.

Auchenoglanis is a genus of relatively large, up to 70 cm (2.3 ft) SL, claroteid catfishes native to various freshwater habitats in Africa.
Dolichamphilius longiceps is a species of loach catfish endemic to the Democratic Republic of the Congo where it is found in the Wagenia Rapids on the Lualaba River. It reaches a length of 4.2 cm.

Heterobranchus bidorsalis, the African catfish or eel-like fattyfin catfish, is an airbreathing catfish found in Africa. It is closely related to the vundu catfish, which is well known among fishermen.
Lake Ejagham is a small lake near Eyumodjock in the Southwest Region of Cameroon. Unlike many other lakes in the region, it is not a volcanic lake, but is likely a solution basin formed by groundwater during the last Ice Age. This highly isolated lake is roughly oval in shape, lacks an inflow, but has an outflow into the Munaya River. The outflow is impassable to most fishes because of a waterfall.
Coptodon fusiforme is a species of fish in the cichlid family, endemic to Lake Ejagham in western Cameroon. It was only scientifically described in 2010, so has not been rated by the IUCN, but it likely faces the same risks as the critically endangered C. deckerti, which is threatened by pollution and sedimentation from human activities, a catfish from the genus Parauchenoglanis that has been introduced to the lake, and potentially also by large emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2) from the lake's bottom (compare Lake Nyos), although Ejagham is too shallow to contain very high amounts of this gas.
Coptodon ejagham is a species of fish in the cichlid family. It is endemic to Lake Ejagham in western Cameroon. It was only scientifically described in 2010 and has therefore not been rated by the IUCN, but it likely faces the same risks as the critically endangered C. deckerti, which is threatened by pollution and sedimentation from human activities, a catfish from the genus Parauchenoglanis that has been introduced to the lake, and potentially also by large emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2) from the lake's bottom (compare Lake Nyos), although Ejagham is too shallow to contain very high amounts of this gas.
Coptodon nigrans is a species of fish in the cichlid family. It is endemic to Lake Ejagham in western Cameroon. It was only scientifically described in 2010 and has therefore not been rated by the IUCN, but it likely faces the same risks as the critically endangered C. deckerti, which is threatened by pollution and sedimentation from human activities, a catfish from the genus Parauchenoglanis that has been introduced to the lake, and potentially also by large emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2) from the lake's bottom (compare Lake Nyos), although Ejagham is too shallow to contain very high amounts of this gas.
Sarotherodon lamprechti is a species of cichlid endemic to Lake Ejagham in western Cameroon. This phytoplanktivore can reach a length of 9.9 centimetres (3.9 in) SL. It has not yet been rated by the IUCN, but it likely faces the same risks as the critically endangered Coptodon deckerti, which is threatened by pollution and sedimentation from human activities, a catfish from the genus Parauchenoglanis that has been introduced to the lake, and potentially also by large emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2) from the lake's bottom (compare Lake Nyos), although Ejagham is too shallow to contain very high amounts of this gas.
Sarotherodon knauerae is a species of cichlid endemic to Lake Ejagham in western Cameroon. This species can reach a length of 7.5 centimetres (3.0 in) SL and feeds on detritus. It has not yet been rated by the IUCN, but it likely faces the same risks as the critically endangered Coptodon deckerti, which is threatened by pollution and sedimentation from human activities, a catfish from the genus Parauchenoglanis that has been introduced to the lake, and potentially also by large emissions of carbon dioxide (CO2) from the lake's bottom (compare Lake Nyos), although Ejagham is not deep enough to contain very high amounts of this gas.
Astroblepus longiceps is a species of catfish of the family Astroblepidae. It can be found on the Madeira River in Brazil and Bolivia.
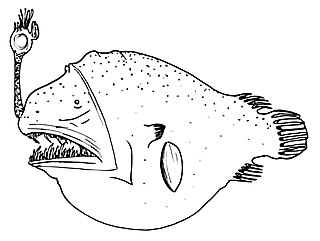
Chaenophryne longiceps, the can-opener smoothdream, longhead dreamer or smooth-head dreamer, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Oneirodidae, the dreamers, a family of deep sea anglerfishes. This predatory, deep-sea fish is found in tropical and subtropical oceans around the world. Like other deep-sea anglerfishes, it is sexually dimorphic with the metamorphosed females dwarfing the metamorphosed males, though the males are not sexual parasites.











