
Multituberculata is an extinct taxon of rodent-like allotherian mammals that existed for approximately 166 million years, the longest fossil history of any mammal lineage. They eventually declined from the late Paleocene onwards, disappearing from the known fossil record in the late Eocene, though gondwanatheres lived into the Miocene, and may have been multituberculates. More than 200 species are known, ranging from mouse-sized to beaver-sized. These species occupied a diversity of ecological niches, ranging from burrow-dwelling to squirrel-like arborealism to jerboa-like hoppers. Multituberculates are usually placed as crown mammals outside either of the two main groups of living mammals—Theria, including placentals and marsupials, and Monotremata—but closer to Theria than to monotremes. Nonetheless, at least one study found a potential status as sister taxa to monotremes/Australosphenida.

Bubalus is a genus of Asiatic bovines that was proposed by Charles Hamilton Smith in 1827. Bubalus and Syncerus form the subtribe Bubalina, the true buffaloes.
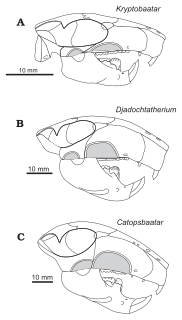
Djadochtatherium is a mammal genus that lived in Mongolia during the Upper Cretaceous. It coexisted with some of the late dinosaurs. This animal was a member of the extinct order of Multituberculata. It is within the suborder of Cimolodonta, and a member of the family Djadochtatheriidae. It was named by G. G. Simpson in 1925, the name meaning "Djadokhta beast".
Prionessus is a genus of extinct mammal from the Paleocene of Central Asia. It was a member of the extinct order Multituberculata within the suborder Cimolodonta and superfamily Taeniolabidoidea. The genus was named by Matthew W.D. and Granger W. in 1925 and is based on a single species.

The Drosophilidae are a diverse, cosmopolitan family of flies, which includes fruit flies. Another unrelated family of flies, Tephritidae, also includes species known as "small fruit flies". The best known species of the Drosophilidae is Drosophila melanogaster, within the genus Drosophila, and this species is used extensively for studies concerning genetics, development, physiology, ecology and behaviour. This fruit fly is mostly composed of post-mitotic cells, has a very short lifespan, and shows gradual aging. As in other species, temperature influences the life history of the animal. Several genes have been identified that can be manipulated to extend the lifespan of these insects. Additionally, Drosophila subobscura, also within the genus Drosophila, has been reputed as a model organism for evolutionary-biological studies.

Tapinoma is a genus of ants that belongs to the subfamily Dolichoderinae. The genus currently comprises 74 described species distributed worldwide in tropical and temperate regions. Members of are generalized foragers, nesting in a wide variety of habitats, ranging from grasslands, open fields, woodlands, to inside buildings. The majority of species nest in the ground under objects such as stones or tree logs, other species build nests under bark of logs and stumps, in plant cavities, insect galls or refuse piles.

The Harvard Art Museums are part of Harvard University and comprise three museums: the Fogg Museum, the Busch-Reisinger Museum, and the Arthur M. Sackler Museum and four research centers: the Archaeological Exploration of Sardis, the Center for the Technical Study of Modern Art, the Harvard Art Museums Archives, and the Straus Center for Conservation and Technical Studies. The three museums that constitute the Harvard Art Museums were initially integrated into a single institution under the name Harvard University Art Museums in 1983. The word "University" was dropped from the institutional name in 2008.

Lycaenops ("wolf-face") is a genus of carnivorous therapsids. It lived during the late mid-Permian to the early Late Permian, about 270.6-251 mya, in what is now South Africa.
The Reisinger national bridge championship is held at the fall American Contract Bridge League (ACBL) North American Bridge Championship (NABC).

The Lecithoceridae, or long-horned moths, are a family of small moths described by Simon Le Marchand in 1947. Although lecithocerids are found throughout the world, the great majority are found in the Indomalayan realm and the southern part of the Palaearctic realm.

Enidae is a family of air-breathing land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod mollusks.

Stefan Reisinger is a German retired footballer and manager.
Pseudospora is a genus of parasitic cercozoans.
The Amphidontidae are a family of extinct mammals from the Early Cretaceous, belonging to the triconodonts. It contains most of the species previously belonged to Amphilestidae.

Uteodon is a genus of herbivorous iguanodontian dinosaur. It is a basal iguanodontian which lived during the late Jurassic period in what is now Uintah County, Utah. It is known from the middle of the Brushy Basin Member, Morrison Formation. The genus was named by Andrew T. McDonald in 2011 and the type species is Uteodon aphanoecetes.

Opecoelidae is a family of trematodes. It is the largest digenean family with over 90 genera and nearly 900 species, almost solely found in marine and freshwater teleost fishes. It was considered by Bray et al. to belong in the superfamily Opecoeloidea Ozaki, 1925 or the Brachycladioidea Odhner, 1905.
Reisinger is a surname. Notable people with the surname include:
Paropisthopatus is a monospecific genus of velvet worm containing the single species Paropisthopatus umbrinus. The type locality is in central Chile.
Doris Reisinger is a German former nun and philosopher, theologian and author.

J. Monroe "Roe" Reisinger was an American soldier who fought with the Union Army in the American Civil War. Reisinger received his country's highest award for bravery during combat, the Medal of Honor, for actions taken on July 1, 1863 during the Battle of Gettysburg.












