Related Research Articles

South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere. It can also be described as a southern subcontinent of the Americas. The reference to South America instead of other regions has increased in the last decades due to changing geopolitical dynamics.

Misiones is one of the 23 provinces of Argentina, located in the northeastern corner of the country in the Mesopotamia region. It is surrounded by Paraguay to the northwest, Brazil to the north, east and south, and Corrientes Province of Argentina to the southwest.

Francisco Solano López Carrillo was President of Paraguay from 1862 until his death in 1870. He was the eldest son of Juana Pabla Carrillo and of President Carlos Antonio López, Francisco's predecessor.

The Paraguayan War, also known as the War of the Triple Alliance was a South American war fought from 1864 to 1870, between Paraguay and the Triple Alliance of Argentina, the Empire of Brazil, and Uruguay. It was the deadliest and bloodiest inter-state war in Latin America's history. It particularly devastated Paraguay, which suffered catastrophic losses in population and was forced to cede disputed territory to Argentina and Brazil.

The Paraná River is a river in south Central South America, running through Brazil, Paraguay, and Argentina for some 4,880 kilometres (3,030 mi). It is second in length only to the Amazon River among South American rivers. The name Paraná is an abbreviation of the phrase "para rehe onáva", which comes from the Tupi language and means "like the sea". It merges first with the Paraguay River and then farther downstream with the Uruguay River to form the Río de la Plata and empties into the Atlantic Ocean.

The Paraguay national football team represents Paraguay in men's international football competitions, and are controlled by the Paraguayan Football Association. Paraguay is a member of CONMEBOL. The Albirroja has qualified for eight FIFA World Cup competitions, with their best performance coming in 2010 when they reached the quarter-finals. A regular participant at the Copa América, Paraguay have been crowned champions of the competition on two occasions. Paraguay's highest FIFA World Rankings was 8th and their lowest was 103. Paraguay was awarded second place with Best Move of the Year in 1996 for their rise in the FIFA Rankings.
The sixth edition of the South American Championship was scheduled to be held in Chile, but Brazil asked to host it as part of its 100th anniversary independence celebrations. Thus it was held in Rio de Janeiro between September 17 and October 22, 1922.

The Gran Chaco or Dry Chaco is a sparsely populated, hot and semiarid lowland natural region of the Río de la Plata basin, divided among eastern Bolivia, western Paraguay, northern Argentina, and a portion of the Brazilian states of Mato Grosso and Mato Grosso do Sul, where it is connected with the Pantanal region. This land is sometimes called the Chaco Plain.

The seventeenth edition of the South American Championship was held in Montevideo, Uruguay from January 10 to February 7.

The Battle of Curupayty was a key battle in the Paraguayan War. On the morning of September 22, 1866, the joint force of Brazilian, Argentine, and Uruguayan armies attacked Paraguayan fortified trenches on Curupaity. The Paraguayans were led by General José E. Díaz. This position was held by 5,000 men and 49 cannons, some of them in hidden places out of the attackers view. The Brazilian Navy gave support to the 20,000 assailants, but the ships had to keep some distance from the guns at the fortress of Humaitá, which led to the lack of accuracy and impact of the ship's fire. The navy's failure was crucial at the later ground battle result.

The Treaty of the Triple Alliance was a treaty that allied the Empire of Brazil, Argentina, and Uruguay against Paraguay. Signed in 1865, after the outbreak of the Paraguayan War, its articles prescribed the allies' actions both during and after the war. The war led to the near-annihilation of Paraguay.

The Paraguay national rugby team is governed by the Paraguayan Rugby Union. They compete regularly in the South American Rugby Championship, but have yet to qualify for the Rugby World Cup.

The military history of Brazil comprises centuries of armed actions in the territory encompassing modern Brazil, and the role of the Brazilian Armed Forces in conflicts and peacekeeping worldwide. For several hundreds of years, the area was the site of intertribal wars of indigenous peoples. Beginning in the 16th century, the arrival of Portuguese explorers led to conflicts with the aboriginal peoples; a notable example being the revolt of the Tamoio Confederation. Sporadic revolts of African slaves also marked the colonial period, with a notable rebellion led by Zumbi dos Palmares. Conflicts were encountered with other European nations as well – two notable examples being the France Antarctique affair, and a conflict with the Netherlands in the early 17th century over control of much of the Northeast. Although Portugal retained its possessions during conflicts with other nations, it lost control of the colony after the Brazilian war of Independence, which led to the establishment of the Empire of Brazil.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to South America.
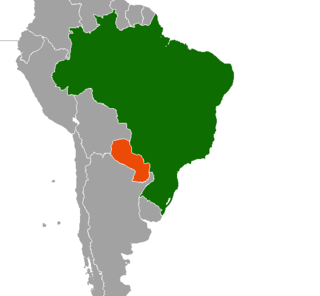
Brazil–Paraguay relations are foreign relations between Brazil and Paraguay.
The FIA CODASUR Rally Championship is an international rally championship which is run by Confederacion Deportiva Automovilismo Sudamericana (CODASUR) under the auspices of the FIA and held across South America, although some events in the northernmost reaches of South America compete in the NACAM Rally Championship zone rather than Codasur.

The Battle of Boquerón was fought on 16 July 1866 and the Battle of Sauce on 18 July 1866, between an allied force of Uruguayans, Brazilian, and Argentines on one side and Paraguay on the other in the Paraguayan War. The Spanish-born Uruguayan officer León de Pallejas (1816–1866) and the Paraguayan officer Elizardo Aquino were killed in the battle.
References
- ↑ Pareuchaetes at Markku Savela's Lepidoptera and Some Other Life Forms
| This Phaegopterina-related article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |