
Wallis and Futuna, officially the Territory of the Wallis and Futuna Islands, is a French island collectivity in the South Pacific, situated between Tuvalu to the northwest, Fiji to the southwest, Tonga to the southeast, Samoa to the east, and Tokelau to the northeast.
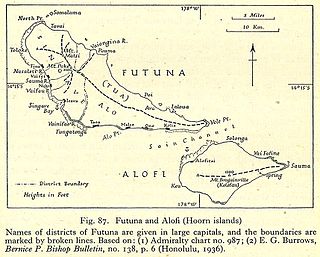
Futuna is the largest island in Hoorn Islands or Îles Horne, located in the Pacific Ocean, part of the French overseas collectivity of Wallis and Futuna. The island occupies an area of 80 km2 (30 sq mi) and as of 2018 it has a population of 10,912.

Politics of Wallis and Futuna takes place in a framework of a parliamentary representative democratic French overseas collectivity, whereby the President of the Territorial Assembly is the head of government, and of a multi-party system. Executive power is exercised by the government.

Peter Louis Marie Chanel, SM, was a Catholic priest, missionary, and martyr. Chanel was a member of the Society of Mary and was sent as a missionary to Oceania. He arrived on the island of Futuna in November 1837. Chanel was clubbed to death in April 1841 at the instigation of a chief upset because his son converted.

Tomasi Kulimoetoke II was the 50th Lavelua (King) of Uvea, which is one of the three traditional kingdoms in the French overseas territory of Wallis and Futuna, from 1959 until his death in 2007.

Wallis is a Polynesian atoll/island in the Pacific Ocean belonging to the French overseas collectivity of Wallis and Futuna. It lies north of Tonga, northeast of Fiji, east-northeast of the Hoorn Islands, east of Fiji's Rotuma, southeast of Tuvalu, southwest of Tokelau and west of Samoa. Its area is almost 100 km2 (39 sq mi) with 8,333 people. Its capital is Mata Utu. Roman Catholicism is the predominant religion. Its highest point is Mount Lulu Fakahega. Wallis is of volcanic origin with fertile soil and some remaining lakes. Rainfall is plentiful.

The Voice of the Wallis and Futuna Peoples is a political party in the French collectivité d'outre-mer of Wallis and Futuna. It was established during the political realignment around the 2002 Wallis and Futuna Territorial Assembly election, when some members of the Rally for the Republic and the People's Union for Wallis and Futuna formed a coalition following the election of Patalione Kanimoa as President of the Assembly. In response, former President Soane Uhila and five other Assembly members formed the VPWF.

Mata Utu is the capital city of Wallis and Futuna, an overseas collectivity of France. It is located on the island of Uvéa (ʻUvea), in the district of Hahake, of which it is also the capital. It is one of two ports in Wallis and Futuna, the other being at Leava on Futuna. Hihifo Airport, the main airport serving the island and city, is 5.6 kilometres (3.5 mi) to the northwest. Its population was 1,029 in 2018, up from 815 in 1998.

Sigavé is one of the three official chiefdoms of the French territory of Wallis and Futuna in Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean.
Kapeliele "Gabriel" Faupala was the 51st Lavelua (King) of Wallis Island (Uvea), one of the three traditional kingdoms which comprise the French overseas territory of Wallis and Futuna. Faupala was officially crowned Lavelua on July 25, 2008, succeeding Tomasi Kulimoetoke II, who died in May 2007. He was removed from office in September 2014.
There are six monarchies in Oceania where supreme power resides with an individual hereditary head, who is recognised as the head of state. Each is a constitutional monarchy, wherein the sovereign inherits his or her office, usually keeps it until death or abdication, and is bound by laws and customs in the exercise of their powers. Five of these independent states share King Charles III as their respective head of state, making them part of a global grouping known as the Commonwealth realms; in addition, all monarchies of Oceania are members of the Commonwealth of Nations. The only sovereign monarchy in Oceania that does not share a monarch with another state is Tonga. Australia and New Zealand have dependencies within the region and outside it, although five non-sovereign constituent monarchs are recognized by New Zealand, Papua New Guinea and France.
A non-sovereign monarchy, subnational monarchy or constituent monarchy is one in which the head of the monarchical polity, and the polity itself, are subject to a temporal authority higher than their own. The constituent states of the German Empire or the princely states of the Indian Empire during British rule provide historical examples; while the Zulu king, whose power derives from the Constitution of South Africa, is a contemporary one.

The Catholic Church in Wallis and Futuna is part of the worldwide Catholic Church, which, inspired by the life, death and teachings of Jesus Christ, and under the spiritual leadership of the Pope and Roman curia in the Vatican City is the largest Christian church in the world. The French who were the first Europeans to settle in the territory, with the arrival of missionaries in 1837, who converted the population to Catholicism. Today, the population of the Pacific island French territory is overwhelmingly Catholic. Bishop Ghislain Marie Raoul Suzanne de Rasilly, S.M., was ordained Bishop of Wallis et Futuna in 2005.

Territorial Assembly elections were held in Wallis and Futuna on 25 March 2012. Thirty party lists contested to fill the twenty seats. The major election issues were the cost of living, economic development, and wallis and Futuna's relationship with France. Turnout was 85.95%.
Nivaleta Iloai was a politician from Wallis and Futuna. She served as the first female president of the Territorial Assembly of Wallis and Futuna from April 1 to December 11, 2013, as well as November 26, 2020 to March 25, 2022.
Mikaele Kulimoetoke is a Wallisian politician and member of the Territorial Assembly of Wallis and Futuna. He was president of the Territorial Assembly of Wallis and Futuna from 2014 to 2017. He has represented Wallis and Futuna in the Senate of France since 2020.
Hervé Jean Albert Jonathan is a senior French civil servant. He has previously served as sub-prefect of Bayonne. Since November 2020 he has served as Administrator Superior of Wallis and Futuna.








