Mycotoxicology is the branch of mycology that focuses on analyzing and studying the toxins produced by fungi, known as mycotoxins. In the food industry it is important to adopt measures that keep mycotoxin levels as low as practicable, especially those that are heat-stable. These chemical compounds are the result of secondary metabolism initiated in response to specific developmental or environmental signals. This includes biological stress from the environment, such as lower nutrients or competition for those available. Under this secondary path the fungus produces a wide array of compounds in order to gain some level of advantage, such as incrementing the efficiency of metabolic processes to gain more energy from less food, or attacking other microorganisms and being able to use their remains as a food source.
Penicillium concentricum is a coprophilic, anamorph fungus species of the genus of Penicillium which produces roquefortine C and patulin.
Penicillium coprobium is an anamorph fungus species of the genus of Penicillium which produces pyripyropene A, roquefortine C, penicillic acid and patulin.
Penicillium dendriticum is an anamorph species of the genus of Penicillium which produces Secalonic acid D and Secalonic acid F.
Penicillium dipodomyicola is a species of the genus of Penicillium which produces peniphenone A, peniphenone B, peniphenone C, peniphenone D, cyclopiazonic acid and patulin.
Penicillium fennelliae is an anamorph species of the genus of Penicillium which produces patulin, orsellinic acid and penicillinic acid.
Penicillium flavigenum is a species of the genus of Penicillium which produces penitrem A, penicillin and roquefortine C.
Penicillium formosanum is a species of the genus of Penicillium which produces patulin and asteltoxin.
Penicillium freii is a psychrophilic species of the genus of Penicillium which produces xanthomegnin and patulin. Penicillium freii occurs in meat, meat products, barley and wheat
Penicillium gorlenkoanum is a species of the genus of Penicillium which produces citrinin, costaclavine and epicostaclavine.
Penicillium allahabadense is an anamorph species of the genus of Penicillium which produces rugulosin.
Penicillium marinum is a species in the genus Penicillium which produces patulin and roquefortine C.
Penicillium megasporum is a species in the genus Penicillium which produces xanthomegin, verrucosidin, roquefortine C and penitrem A. Penicillium megasporum occurs in grain
Penicillium mononematosum is an anamorph species of the genus Penicillium which produces viriditoxin.
Penicillium novae-zelandiae is an anamorph species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which was isolated from the plant Festuca novae-zelandiae. Penicillium novae-zelandiae produces patulin, 3-hydroxybenzyl alcohol and gentisyl alcohol
Penicillium persicinum is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which was isolated from soil from the Qinghai Province in China. Penicillium persicinum produces griseofulvin, lichexanthone, roquefortine C, roquefortine D, patulin and chrysogine
Penicillium radicicola is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which produces Roquefortine C and occurs on onions.
Penicillium steckii is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which produces citrinin, tanzawaic acid E, tanzawaic acid F.
Penicillium tricolor is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which was isolated from wheat in Canada. Penicillium tricolor produces xanthomegnin, viomellein, vioxanthin, terrestric acid, rugulosuvine, verrucofortine, puberuline, asteltoxin
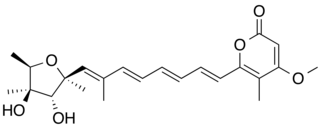
Citreoviridin is a mycotoxin which is produced by Penicillium and Aspergillus species. If rice, corn, cereals or meat products are contaminated with Penicillin citreoviridin, citreoviridin can be produced if the food is stored in a damp place. Consuming food which is contaminated with citreoviridin can cause the disease cardiac beri beri. Furthermore it damages liver and kidneys.
