
Penicillium is a genus of ascomycetous fungi that is part of the mycobiome of many species and is of major importance in the natural environment, in food spoilage, and in food and drug production.

Blue cheese is any of a wide range of cheeses made with the addition of cultures of edible molds, which create blue-green spots or veins through the cheese. Blue cheeses vary in taste from very mild to strong, and from slightly sweet to salty or sharp; in colour from pale to dark; and in consistency from liquid or very soft to firm or hard. They may have a distinctive smell, either from the mold or from various specially cultivated bacteria such as Brevibacterium linens.
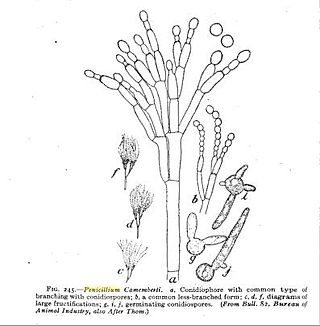
Penicillium camemberti is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium. It is used in the production of Camembert, Brie, Langres, Coulommiers, and Cambozola cheeses, on which colonies of P. camemberti form a hard, white crust. It is responsible for giving these cheeses their distinctive flavors. An allergy to the antibiotic penicillin does not necessarily imply an allergy to cheeses made using P. camemberti.

Myelochroa is a genus of foliose lichens in the family Parmeliaceae. They are commonly known as axil-bristle lichens. It was created in 1987 to contain species formerly placed in genus Parmelina that had a yellow-orange medulla due to the presence of secalonic acids. Characteristics of the genus include tightly attached thalli with narrow lobes, cilia on the axils, and a rhizinate black lower surface. Chemical characteristics are the production of zeorin and related triterpenoids in the medulla. Myelochroa contains about 30 species, most of which grow on bark. The genus has centres of distribution in Asia and North America.

Penicillium chrysogenum is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium. It is common in temperate and subtropical regions and can be found on salted food products, but it is mostly found in indoor environments, especially in damp or water-damaged buildings. It has been recognised as a species complex that includes P. notatum, P. meleagrinum, and P. cyaneofulvum. Molecular phylogeny has established that Alexander Fleming's first discovered penicillin producing strain is of a distinct species, P. rubens, and not of P. notatum. It has rarely been reported as a cause of human disease. It is the source of several β-lactam antibiotics, most significantly penicillin. Other secondary metabolites of P. chrysogenum include roquefortine C, meleagrin, chrysogine, 6-MSA YWA1/melanin, andrastatin A, fungisporin, secalonic acids, sorbicillin, and PR-toxin.

Penicillium brevicompactum is a mould species in the genus Penicillium.

Secalonic acids are a group of xanthone derivatives closely related to ergoflavin and ergochrysin A that are collectively called ergochromes and belong to a class of mycotoxins initially isolated as major ergot pigments from the fungi Claviceps purpurea that grows parasitically on rye grasses. From early times and particularly in medieval Europe the consumption of grains containing ergot has repeatedly lead to mass poisonings known as ergotism which was caused by toxic ergot alkaloids and mycotoxins such as the ergochromes, due to contamination of flour by C. purpurea. A cluster of genes responsible for the synthesis of secalonic acids in C. purpurea has been identified. Secalonic acid D the enantiomer of secalonic acid A is a major environmental toxin, isolated from the fungus Penicillium oxalicum, and is a major microbial contaminant of freshly-harvested corn which causes toxicity through contamination of foodstuffs.
Medicinal fungi are fungi that contain metabolites or can be induced to produce metabolites through biotechnology to develop prescription drugs. Compounds successfully developed into drugs or under research include antibiotics, anti-cancer drugs, cholesterol and ergosterol synthesis inhibitors, psychotropic drugs, immunosuppressants and fungicides.
Penicillium carneum is a fungus species of the genus of Penicillium.Penicillium roqueforti var. carneum was reclassified to Penicillium carneum.P. carneum was isolated from spoiled meat products, silage, rye bread, water, beer, cheese, mouldy barkers yeast and cork. P. carneum produces patulin, penicillic acid, penitrem A, mycophenolic acid roquefortines.
Penicillium citrinum is an anamorph, mesophilic fungus species of the genus of Penicillium which produces tanzawaic acid A-D, ACC, Mevastatin, Quinocitrinine A, Quinocitrinine B, and nephrotoxic citrinin. Penicillium citrinum is often found on moldy citrus fruits and occasionally it occurs in tropical spices and cereals. This Penicillium species also causes mortality for the mosquito Culex quinquefasciatus. Because of its mesophilic character, Penicillium citrinum occurs worldwide. The first statin (Mevastatin) was 1970 isolated from this species.
Penicillium fennelliae is an anamorph species of the genus of Penicillium which produces patulin, orsellinic acid and penicillinic acid.
Penicillium gladioli is a species of the genus of Penicillium which occurs on corms of the plant Gladiolus debtis. Penicillium gladioli produces gladiolic acid and patulin.
Penicillium isariiforme is an anamorph, phototropic species of the genus of Penicillium which produce secalonic acid D and F.
Penicillium oxalicum is an anamorph species of the genus Penicillium which was isolated from rhizosphere soil of pearl millet. Penicillium oxalicum produces secalonic acid D, chitinase, oxalic acid, oxaline and β-N-acetylglucosaminidase and occurs widespread in food and tropical commodities. This fungus could be used against soilborne diseases like downy mildew of tomatoes
Penicillium steckii is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which produces citrinin, tanzawaic acid E, tanzawaic acid F.
Penicillium tardochrysogenum is a filamentous species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which produces penicillin, secalonic acids D and secalonic acids F.

Penicillium digitatum is a mesophilic fungus found in the soil of citrus-producing areas. It is a major source of post-harvest decay in fruits and is responsible for the widespread post-harvest disease in Citrus fruit known as green rot or green mould. In nature, this necrotrophic wound pathogen grows in filaments and reproduces asexually through the production of conidiophores and conidia. However, P. digitatum can also be cultivated in the laboratory setting. Alongside its pathogenic life cycle, P. digitatum is also involved in other human, animal and plant interactions and is currently being used in the production of immunologically based mycological detection assays for the food industry.
Penicillium commune is an indoor fungus belonging to the genus Penicillium. It is known as one of the most common fungi spoilage moulds on cheese. It also grows on and spoils other foods such as meat products and fat-containing products like nuts and margarine. Cyclopiazonic acid and regulovasine A and B are the most important mycotoxins produced by P. commune. The fungus is the only known species to be able to produce both penitrem A and roquefortine. Although this species does not produce penicillin, it has shown to have anti-pathogenic activity. There are no known plant, animal or human diseases caused by P. commune.

Penicillium spinulosum is a non-branched, fast-growing fungus with a swelling at the terminal of the stipe (vesiculate) in the genus Penicillium. P. spinulosum is able to grow and reproduce in environment with low temperature and low water availability, and is known to be acidotolerant. P. spinulosum is ubiquitously distributed, and can often be isolated from soil. Each individual strain of P. spinulosum differs from others in their colony morphology, including colony texture, amount of sporulation and roughness of conidia and conidiophores.








