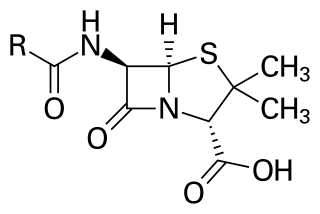
Penicillins are a group of β-lactam antibiotics originally obtained from Penicillium moulds, principally P. chrysogenum and P. rubens. Most penicillins in clinical use are synthesised by P. chrysogenum using deep tank fermentation and then purified. A number of natural penicillins have been discovered, but only two purified compounds are in clinical use: penicillin G and penicillin V. Penicillins were among the first medications to be effective against many bacterial infections caused by staphylococci and streptococci. They are still widely used today for different bacterial infections, though many types of bacteria have developed resistance following extensive use.

Penicillium is a genus of ascomycetous fungi that is part of the mycobiome of many species and is of major importance in the natural environment, in food spoilage, and in food and drug production.
Talaromyces marneffei, formerly called Penicillium marneffei, was identified in 1956. The organism is endemic to southeast Asia where it is an important cause of opportunistic infections in those with HIV/AIDS-related immunodeficiency. Incidence of T. marneffei infections has increased due to a rise in HIV infection rates in the region.

Blue cheese is any of a wide range of cheeses made with the addition of cultures of edible molds, which create blue-green spots or veins through the cheese. Blue cheeses vary in taste from very mild to strong, and from slightly sweet to salty or sharp; in colour from pale to dark; and in consistency from liquid or very soft to firm or hard. They may have a distinctive smell, either from the mold or from various specially cultivated bacteria such as Brevibacterium linens.

The Trichocomaceae are a family of fungi in the order Eurotiales. Taxa are saprobes with aggressive colonization strategies, adaptable to extreme environmental conditions. Family members are cosmopolitan in distribution, ubiquitous in soil, and common associates of decaying plant and food material.

Penicillium roqueforti is a common saprotrophic fungus in the genus Penicillium. Widespread in nature, it can be isolated from soil, decaying organic matter, and plants.

Mevastatin is a hypolipidemic agent that belongs to the statins class.
Decylcitrate synthase (EC 2.3.3.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction in enzymology.

Penicillium chrysogenum is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium. It is common in temperate and subtropical regions and can be found on salted food products, but it is mostly found in indoor environments, especially in damp or water-damaged buildings. It has been recognised as a species complex that includes P. notatum, P. meleagrinum, and P. cyaneofulvum. Molecular phylogeny has established that Alexander Fleming's first discovered penicillin producing strain is of a distinct species, P. rubens, and not of P. notatum. It has rarely been reported as a cause of human disease. It is the source of several β-lactam antibiotics, most significantly penicillin. Other secondary metabolites of P. chrysogenum include roquefortine C, meleagrin, chrysogine, 6-MSA YWA1/melanin, andrastatin A, fungisporin, secalonic acids, sorbicillin, and PR-toxin.
George II Xiphilinos or Xiphilinus was the Patriarch of Constantinople between 1191 and 1198 AD. According to Balsamon, George, during the reign of Alexios I Komnenos, added one member to the Exocatacoeli, making it six.

Charles Thom was an American microbiologist and mycologist. Born and raised in Illinois, he received his PhD from the University of Missouri, the first such degree awarded by that institution. He studied the microbiology of dairy products and soil fungi, and in particular researched the genera Aspergillus and Penicillium. His work influenced the establishment of standards for food handling and processing in the USA. He pioneered the use of culture media to grow microorganisms, and, with food chemist James N. Currie, developed a process to mass-produce citric acid using Aspergillus. Thom played an important role in the development of penicillin in World War II.
Apateona hispanicum is a moth of the family Autostichidae and the only species in the genus Apateona. It is found in Spain.
Caryocolum hispanicum is a moth of the family Gelechiidae. It is found in Spain and Greece.
Penicillium citrinum is an anamorph, mesophilic fungus species of the genus of Penicillium which produces tanzawaic acid A-D, ACC, Mevastatin, Quinocitrinine A, Quinocitrinine B, and nephrotoxic citrinin. Penicillium citrinum is often found on moldy citrus fruits and occasionally it occurs in tropical spices and cereals. This Penicillium species also causes mortality for the mosquito Culex quinquefasciatus. Because of its mesophilic character, Penicillium citrinum occurs worldwide. The first statin (Mevastatin) was 1970 isolated from this species.

Aizoanthemum hispanicum, or Spanish aizoon, is a species of plant in the family Aizoaceae. It is native to northern Africa, the Mediterranean region and the Middle East where it grows on arid sandy plains, saline areas and in semi-arid habitats. It was first described as Aizoon hispanicum by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in 1753 and was in 2002 placed in the genus Aizoanthemum by the German botanist Heidrun Hartmann.
Methylobacterium hispanicum is a bacterium from the genus of Methylobacterium which has been isolated from drinking water in Seville in Spain.
Chryseobacterium hispanicum is a bacterium from the genus Chryseobacterium which has been isolated from a drinking water distribution system in Sevilla in Spain.
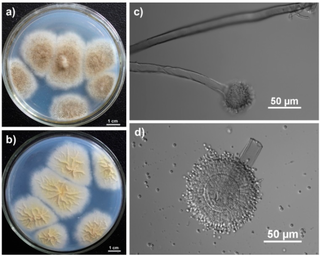
Czapek medium, also called Czapek's agar (CZA) or Czapek-Dox medium, is a growth medium for propagating fungi and other organisms in a laboratory. It was named after its inventors, Czech botanist Friedrich Johann Franz Czapek and American chemist Arthur Wayland Dox. It was developed to grow Aspergillus niger and Penicillium camemberti. It works well for many saprophytic fungi and soil bacteria such as species of Aspergillus, Candida, Penicillium, and Paecilomyces.










