
In vascular plants, the roots are the organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often below the surface of the soil, but roots can also be aerial or aerating, that is, growing up above the ground or especially above water.

Rhizobia are diazotrophic bacteria that fix nitrogen after becoming established inside the root nodules of legumes (Fabaceae). To express genes for nitrogen fixation, rhizobia require a plant host; they cannot independently fix nitrogen. In general, they are gram negative, motile, non-sporulating rods.

Ensifer meliloti are an aerobic, Gram-negative, and diazotrophic species of bacteria. S. meliloti are motile and possess a cluster of peritrichous flagella. S. meliloti fix atmospheric nitrogen into ammonia for their legume hosts, such as alfalfa. S. meliloti forms a symbiotic relationship with legumes from the genera Medicago, Melilotus and Trigonella, including the model legume Medicago truncatula. This symbiosis promotes the development of a plant organ, termed a root nodule. Because soil often contains a limited amount of nitrogen for plant use, the symbiotic relationship between S. meliloti and their legume hosts has agricultural applications. These techniques reduce the need for inorganic nitrogenous fertilizers.

Root nodules are found on the roots of plants, primarily legumes, that form a symbiosis with nitrogen-fixing bacteria. Under nitrogen-limiting conditions, capable plants form a symbiotic relationship with a host-specific strain of bacteria known as rhizobia. This process has evolved multiple times within the legumes, as well as in other species found within the Rosid clade. Legume crops include beans, peas, and soybeans.
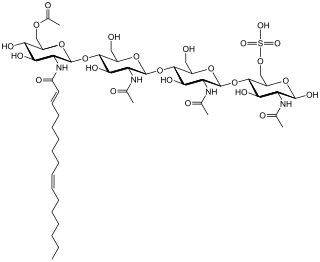
Nod factors, are signaling molecules produced by soil bacteria known as rhizobia in response to flavonoid exudation from plants under nitrogen limited conditions. Nod factors initiate the establishment of a symbiotic relationship between legumes and rhizobia by inducing nodulation. Nod factors produce the differentiation of plant tissue in root hairs into nodules where the bacteria reside and are able to fix nitrogen from the atmosphere for the plant in exchange for photosynthates and the appropriate environment for nitrogen fixation. One of the most important features provided by the plant in this symbiosis is the production of leghemoglobin, which maintains the oxygen concentration low and prevents the inhibition of nitrogenase activity.
Penicillium bilaiae is a species of native soil fungus that can be used as a PGPM. R. Kucey first identified that organic acids excreted by the microorganism can solubilize soil-bound phosphate. The organism can live in symbiosis with several plant species by enhancing phosphate uptake by the root structure while feeding off plant waste products. Native soil populations are often low and can be increased by application as an agricultural inoculant.

Frankia is a genus of nitrogen-fixing bacteria that live in symbiosis with actinorhizal plants, similar to the Rhizobium bacteria found in the root nodules of legumes in the family Fabaceae. Frankia also initiate the forming of root nodules.
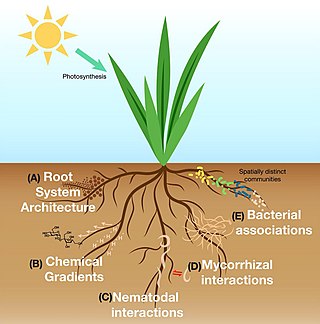
The rhizosphere is the narrow region of soil or substrate that is directly influenced by root secretions and associated soil microorganisms known as the root microbiome. Soil pores in the rhizosphere can contain many bacteria and other microorganisms that feed on sloughed-off plant cells, termed rhizodeposition, and the proteins and sugars released by roots, termed root exudates. This symbiosis leads to more complex interactions, influencing plant growth and competition for resources. Much of the nutrient cycling and disease suppression by antibiotics required by plants, occurs immediately adjacent to roots due to root exudates and metabolic products of symbiotic and pathogenic communities of microorganisms. The rhizosphere also provides space to produce allelochemicals to control neighbours and relatives.

Bradyrhizobium is a genus of Gram-negative soil bacteria, many of which fix nitrogen. Nitrogen fixation is an important part of the nitrogen cycle. Plants cannot use atmospheric nitrogen (N2); they must use nitrogen compounds such as nitrates.

Ecological dominance is the degree to which one or several species have a major influence controlling the other species in their ecological community or make up more of the biomass. Both the composition and abundance of species within an ecosystem can be affected by the dominant species present.

An ectomycorrhiza is a form of symbiotic relationship that occurs between a fungal symbiont, or mycobiont, and the roots of various plant species. The mycobiont is often from the phyla Basidiomycota and Ascomycota, and more rarely from the Zygomycota. Ectomycorrhizas form on the roots of around 2% of plant species, usually woody plants, including species from the birch, dipterocarp, myrtle, beech, willow, pine and rose families. Research on ectomycorrhizas is increasingly important in areas such as ecosystem management and restoration, forestry and agriculture.
Mesorhizobium mediterraneum is a bacterium from the genus Mesorhizobium, which was isolated from root nodule of the Chickpea in Spain. The species Rhizobium mediterraneum was subsequently transferred to Mesorhizobium mediterraneum. This species, along with many other closely related taxa, have been found to promote production of chickpea and other crops worldwide by forming symbiotic relationships.

The root microbiome is the dynamic community of microorganisms associated with plant roots. Because they are rich in a variety of carbon compounds, plant roots provide unique environments for a diverse assemblage of soil microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi, and archaea. The microbial communities inside the root and in the rhizosphere are distinct from each other, and from the microbial communities of bulk soil, although there is some overlap in species composition.
Penicillium kananaskense is an anamorph species of the genus of Penicillium which was isolated from soil of a forest in Alberta in Canada.
Penicillium oxalicum is an anamorph species of the genus Penicillium which was isolated from rhizosphere soil of pearl millet. Penicillium oxalicum produces secalonic acid D, chitinase, oxalic acid, oxaline and β-N-acetylglucosaminidase and occurs widespread in food and tropical commodities. This fungus could be used against soilborne diseases like downy mildew of tomatoes
A phytobiome consists of a plant (phyto) situated in its specific ecological area (biome), including its environment and the associated communities of organisms which inhabit it. These organisms include all macro- and micro-organisms living in, on, or around the plant including bacteria, archaea, fungi, protists, insects, animals, and other plants. The environment includes the soil, air, and climate. Examples of ecological areas are fields, rangelands, forests. Knowledge of the interactions within a phytobiome can be used to create tools for agriculture, crop management, increased health, preservation, productivity, and sustainability of cropping and forest systems.

Salix repens, the creeping willow, is a small, shrubby species of willow in the family Salicaceae, growing up to 1.5 metres in height. Found amongst sand dunes and heathlands, it is a polymorphic species, with a wide range of variants. In the UK, at least, these range from small, prostrate, hairless plants at one end of the spectrum to taller, erect or ascending silky-leaved shrubs at the other. This wide variation in form has resulted in numerous synonyms.
Arcopilus aureus is a plant and soil fungus in the genus Arcopilus. It was first identified by A. H. Chivers in 1912, who named it Chaetomium aureum. It was later transferred to the genus Arcopilus by Wang and colleagues. The fungus has recently been recognized to have industrial use for the production of the metabolites resveratrol. and sclerotiorin Additionally, A. aureus has high lead tolerance and clearance, suggesting a potential role in environmental biotechnology.

Fungal DNA barcoding is the process of identifying species of the biological kingdom Fungi through the amplification and sequencing of specific DNA sequences and their comparison with sequences deposited in a DNA barcode database such as the ISHAM reference database, or the Barcode of Life Data System (BOLD). In this attempt, DNA barcoding relies on universal genes that are ideally present in all fungi with the same degree of sequence variation. The interspecific variation, i.e., the variation between species, in the chosen DNA barcode gene should exceed the intraspecific (within-species) variation.

Alnus parvifolia is an extinct species of flowering plant in the family Betulaceae related to the modern birches. The species is known from fossil leaves and possible fruits found in early Eocene sites of northern Washington state, United States, and central British Columbia, Canada.













