
Blue cheese is any of a wide range of cheeses made with the addition of cultures of edible molds, which create blue-green spots or veins through the cheese. Blue cheeses vary in taste from very mild to strong, and from slightly sweet to salty or sharp; in colour from pale to dark; and in consistency from liquid or very soft to firm or hard. They may have a distinctive smell, either from the mold or from various specially cultivated bacteria such as Brevibacterium linens.
Penicillium crustosum is a blue-green or blue-grey mold that can cause food spoilage, particularly of protein-rich foods such as meats and cheeses. It is identified by its complex biseriate conidiophores on which phialides produce asexual spores. It can grow at fairly low temperatures, and in low water activity environments.
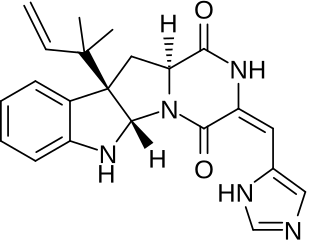
Roquefortine C is a mycotoxin that belongs to a class of naturally occurring 2,5-diketopiperazines produced by various fungi, particularly species from the genus Penicillium. It was first isolated from a strain of Penicillium roqueforti, a species commercially used as a source of proteolytic and lipolytic enzymes during maturation of the blue-veined cheeses, Roquefort, Danish Blue, Stilton and Gorgonzola.

Penicillium chrysogenum is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium. It is common in temperate and subtropical regions and can be found on salted food products, but it is mostly found in indoor environments, especially in damp or water-damaged buildings. It has been recognised as a species complex that includes P. notatum, P. meleagrinum, and P. cyaneofulvum. Molecular phylogeny has established that Alexander Fleming's first discovered penicillin producing strain is of a distinct species, P. rubens, and not of P. notatum. It has rarely been reported as a cause of human disease. It is the source of several β-lactam antibiotics, most significantly penicillin. Other secondary metabolites of P. chrysogenum include roquefortine C, meleagrin, chrysogine, 6-MSA YWA1/melanin, andrastatin A, fungisporin, secalonic acids, sorbicillin, and PR-toxin.
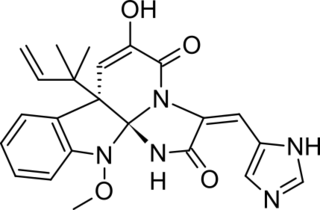
Meleagrin and its derivatives such as oxaline are bio-active benzylisoquinoline alkaloids made by various species of Penicillium fungi. It is similar to other fungal alkaloids, such as Roquefortine C, which is made as an intermediate in the same biosynthetic pathway.
Penicillium carneum is a fungus species of the genus of Penicillium.Penicillium roqueforti var. carneum was reclassified to Penicillium carneum.P. carneum was isolated from spoiled meat products, silage, rye bread, water, beer, cheese, mouldy barkers yeast and cork. P. carneum produces patulin, penicillic acid, penitrem A, mycophenolic acid roquefortines.
Penicillium concentricum is a coprophilic, anamorph fungus species of the genus of Penicillium which produces roquefortine C and patulin.
Penicillium coprobium is an anamorph fungus species of the genus of Penicillium which produces pyripyropene A, roquefortine C, penicillic acid and patulin.
Penicillium coprophilum is a species of the genus of Penicillium which produces roquefortine C, griseofulvin and oxaline.
Penicillium flavigenum is a species of the genus of Penicillium which produces penitrem A, penicillin and roquefortine C.

Penicillium glandicola is an anamorph species of the genus of Penicillium which produces penitrem A, patulin, 2,4,6-trichloroanisole and roquefortine C
Penicillium hordei is a species of the genus of Penicillium which produces corymbiferone and roquefortine C.
Penicillium marinum is a species in the genus Penicillium which produces patulin and roquefortine C.
Penicillium megasporum is a species in the genus Penicillium which produces xanthomegin, verrucosidin, roquefortine C and penitrem A. Penicillium megasporum occurs in grain
Penicillium palitans is an anamorph species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which was isolated from cheese and ancient permafrost deposits. Penicillium palitans produces viridicatin, cyclopiazonic acid, roquefortine, palitantin and ochratoxin A
Penicillium paneum is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which can spoil cereal grains. Penicillium paneum produces 1-Octen-3-ol and penipanoid A, penipanoid B, penipanoid C, patulin and roquefortine C
Penicillium persicinum is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which was isolated from soil from the Qinghai Province in China. Penicillium persicinum produces griseofulvin, lichexanthone, roquefortine C, roquefortine D, patulin and chrysogine
Penicillium radicicola is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which produces Roquefortine C and occurs on onions.
Penicillium tulipae is a species of fungus in the genus Penicillium which produces penicillic acid, roquefortine C, roquefortine D, terrestric acid, glandicoline A, glandicoline B, meleagrin, oxaline, penitrem A and epineoxaline.
Penicillium commune is an indoor fungus belonging to the genus Penicillium. It is known as one of the most common fungi spoilage moulds on cheese. It also grows on and spoils other foods such as meat products and fat-containing products like nuts and margarine. Cyclopiazonic acid and regulovasine A and B are the most important mycotoxins produced by P. commune. The fungus is the only known species to be able to produce both penitrem A and roquefortine. Although this species does not produce penicillin, it has shown to have anti-pathogenic activity. There are no known plant, animal or human diseases caused by P. commune.




