
Chroma subsampling is the practice of encoding images by implementing less resolution for chroma information than for luma information, taking advantage of the human visual system's lower acuity for color differences than for luminance.

SMPTE color bars are a television test pattern used where the NTSC video standard is utilized, including countries in North America. The Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE) refers to the pattern as Engineering Guideline (EG) 1-1990. Its components are a known standard, and created by test pattern generators. Comparing it as received to the known standard gives video engineers an indication of how an NTSC video signal has been altered by recording or transmission and what adjustments must be made to bring it back to specification. It is also used for setting a television monitor or receiver to reproduce NTSC chrominance and luminance information correctly.

Dolby Laboratories, Inc. is a British-American technology corporation specializing in audio noise reduction, audio encoding/compression, spatial audio, and HDR imaging. Dolby licenses its technologies to consumer electronics manufacturers.

YCbCr, Y′CbCr, or Y Pb/Cb Pr/Cr, also written as YCBCR or Y′CBCR, is a family of color spaces used as a part of the color image pipeline in video and digital photography systems. Y′ is the luma component and CB and CR are the blue-difference and red-difference chroma components. Y′ is distinguished from Y, which is luminance, meaning that light intensity is nonlinearly encoded based on gamma corrected RGB primaries.
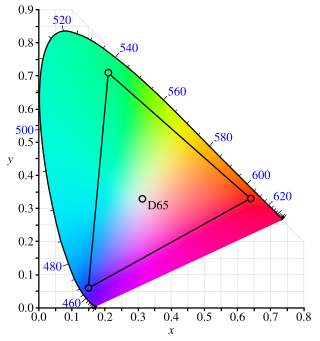
The Adobe RGB (1998) color space or opRGB is a color space developed by Adobe Inc. in 1998. It was designed to encompass most of the colors achievable on CMYK color printers, but by using RGB primary colors on a device such as a computer display. The Adobe RGB (1998) color space encompasses roughly 30% of the visible colors specified by the CIELAB color space – improving upon the gamut of the sRGB color space, primarily in cyan-green hues. It was subsequently standardized by the IEC as IEC 61966-2-5:1999 with a name opRGB and is used in HDMI.

YPbPr or Y'PbPr, also written as YPBPR, is a color space used in video electronics, in particular in reference to component video cables. Like YCBCR, it is based on gamma corrected RGB primaries; the two are numerically equivalent but YPBPR is designed for use in analog systems while YCBCR is intended for digital video. The EOTF may be different from common sRGB EOTF and BT.1886 EOTF. Sync is carried on the Y channel and is a bi-level sync signal, but in HD formats a tri-level sync is used and is typically carried on all channels.
In video, luma represents the brightness in an image. Luma is typically paired with chrominance. Luma represents the achromatic image, while the chroma components represent the color information. Converting R′G′B′ sources into luma and chroma allows for chroma subsampling: because human vision has finer spatial sensitivity to luminance differences than chromatic differences, video systems can store and transmit chromatic information at lower resolution, optimizing perceived detail at a particular bandwidth.

Rec. 709, also known as Rec.709, BT.709, and ITU 709, is a standard developed by ITU-R for image encoding and signal characteristics of high-definition television.

Dolby Vision is a set of technologies developed by Dolby Laboratories for high dynamic range (HDR) video. It covers content creation, distribution, and playback. It includes dynamic metadata that define the aspect ratio and adjust the picture based on a display's capabilities on a per-shot or even per-frame basis, optimizing the presentation.

The hybrid log–gamma (HLG) transfer function is a transfer function jointly developed by the BBC and NHK for high dynamic range (HDR) display. It's backward compatible with the transfer function of SDR. It was approved as ARIB STD-B67 by the Association of Radio Industries and Businesses (ARIB). It is also defined in ATSC 3.0, Digital Video Broadcasting (DVB) UHD-1 Phase 2, and International Telecommunication Union (ITU) Rec. 2100.

HDR10 Media Profile, more commonly known as HDR10, is an open high-dynamic-range video (HDR) standard announced on August 27, 2015, by the Consumer Technology Association. It is the most widespread HDR format.
Standard-dynamic-range video is a video technology which represents light intensity based on the brightness, contrast and color characteristics and limitations of a cathode ray tube (CRT) display. SDR video is able to represent a video or picture's colors with a maximum luminance around 100 cd/m2, a black level around 0.1 cd/m2 and Rec.709 / sRGB color gamut. It uses the gamma curve as its electro-optical transfer function.

Ultra HD Forum is an organization whose goal is to help solve the real world hurdles in deploying Ultra HD video and thus to help promote UHD deployment. The Ultra HD Forum will help navigate amongst the standards related to high dynamic range (HDR), high frame rate (HFR), next generation audio (NGA), and wide color gamut (WCG). The Ultra HD Forum is an industry organisation that is complementary to the UHD Alliance, covering different aspects of the UHD ecosystem.

ICTCP, ICtCp, or ITP is a color representation format specified in the Rec. ITU-R BT.2100 standard that is used as a part of the color image pipeline in video and digital photography systems for high dynamic range (HDR) and wide color gamut (WCG) imagery. It was developed by Dolby Laboratories from the IPT color space by Ebner and Fairchild. The format is derived from an associated RGB color space by a coordinate transformation that includes two matrix transformations and an intermediate nonlinear transfer function that is informally known as gamma pre-correction. The transformation produces three signals called I, CT, and CP. The ICTCP transformation can be used with RGB signals derived from either the perceptual quantizer (PQ) or hybrid log–gamma (HLG) nonlinearity functions, but is most commonly associated with the PQ function.
ITU-R Recommendation BT.2100, more commonly known by the abbreviations Rec. 2100 or BT.2100, introduced high-dynamic-range television (HDR-TV) by recommending the use of the perceptual quantizer or hybrid log–gamma (HLG) transfer functions instead of the traditional "gamma" previously used for SDR-TV.
High-dynamic-range television (HDR-TV) is a technology that uses high dynamic range (HDR) to improve the quality of display signals. It is contrasted with the retroactively-named standard dynamic range (SDR). HDR changes the way the luminance and colors of videos and images are represented in the signal, and allows brighter and more detailed highlight representation, darker and more detailed shadows, and more intense colors.
HDR10+ is a high dynamic range (HDR) video technology that adds dynamic metadata to HDR10 source files. The dynamic metadata are used to adjust and optimize each frame of the HDR video to the consumer display's capabilities in a way based on the content creator's intentions.
Images and videos use specific transfer functions to describe the relationship between electrical signal, scene light and displayed light.
ITU-R BT.1886 is the reference EOTF of SDR-TV. It is a gamma 2.4 transfer function considered as a satisfactory approximation of the response characteristic of CRT to electrical signal. It has been standardized by ITU in March 2011. It is used for Rec. 709 (HD-TV) and Rec. 2020 (UHD-TV).

The EBU colour bars are a television test card used to check if a video signal has been altered by recording or transmission, and what adjustments must be made to bring it back to specification. It is also used for setting a television monitor or receiver to reproduce chrominance and luminance information correctly. The EBU bars are most commonly shown arranged side-by-side in a vertical manner, though some broadcasters – such as TVP in Poland, and Gabon Télévision in Gabon – were known to have aired a horizontal version of the EBU bars.























