
Semiconductor device fabrication is the process used to manufacture semiconductor devices, typically integrated circuits (ICs) such as computer processors, microcontrollers, and memory chips that are present in everyday electronic devices. It is a multiple-step photolithographic and physio-chemical process during which electronic circuits are gradually created on a wafer, typically made of pure single-crystal semiconducting material. Silicon is almost always used, but various compound semiconductors are used for specialized applications.
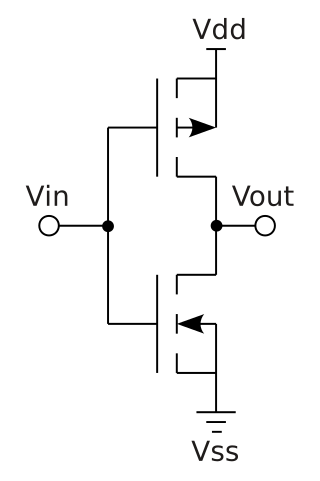
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor is a type of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) fabrication process that uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type MOSFETs for logic functions. CMOS technology is used for constructing integrated circuit (IC) chips, including microprocessors, microcontrollers, memory chips, and other digital logic circuits. CMOS technology is also used for analog circuits such as image sensors, data converters, RF circuits, and highly integrated transceivers for many types of communication.

Cypress Semiconductor was an American semiconductor design and manufacturing company. It offered NOR flash memories, F-RAM and SRAM Traveo microcontrollers, PSoC programmable system-on-chip solutions, analog and PMIC Power Management ICs, CapSense capacitive touch-sensing controllers, Wireless BLE Bluetooth Low-Energy and USB connectivity solutions.

Infineon Technologies AG is Germany's largest semiconductor manufacturer. The company was spun-off from Siemens AG in 1999. Infineon has about 58,600 employees in 2023 and is one of the ten largest semiconductor manufacturers worldwide. In 2023 the company achieved sales of €16.309 billion.
Silicon on sapphire (SOS) is a hetero-epitaxial process for metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) integrated circuit (IC) manufacturing that consists of a thin layer of silicon grown on a sapphire wafer. SOS is part of the silicon-on-insulator (SOI) family of CMOS technologies.
In semiconductor manufacturing, silicon on insulator (SOI) technology is fabrication of silicon semiconductor devices in a layered silicon–insulator–silicon substrate, to reduce parasitic capacitance within the device, thereby improving performance. SOI-based devices differ from conventional silicon-built devices in that the silicon junction is above an electrical insulator, typically silicon dioxide or sapphire. The choice of insulator depends largely on intended application, with sapphire being used for high-performance radio frequency (RF) and radiation-sensitive applications, and silicon dioxide for diminished short-channel effects in other microelectronics devices. The insulating layer and topmost silicon layer also vary widely with application.

Diosdado P. Banatao is a Filipino entrepreneur and engineer working in the high-tech industry, credited with having developed the first 10-Mbit Ethernet CMOS with silicon coupler data-link control and transceiver chip, the first system logic chip set for IBM's PC-XT and the PC-AT, and the local bus concept and the first Windows Graphics accelerator chip for personal computers. A three-time start-up veteran, he co-founded Mostron, Chips and Technologies, and S3 Graphics.

Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd. is a Japanese manufacturer of electronic components, based in Nagaokakyo, Kyoto. It produces ceramic passive electronic components, primarily capacitors, and has a majority marketshare worldwide in ceramic filters, high-frequency parts, and sensors. As of March 31, 2013 Murata Manufacturing has 24 subsidiaries in Japan and 52 overseas in the United States, Canada, Mexico, Brazil, Germany, France, Italy, the United Kingdom, Switzerland, the Netherlands, Spain, Hungary, Finland, China, Taiwan, South Korea, Singapore, Malaysia, the Philippines, Thailand, Hong Kong, Vietnam and India.
Soitec is an international company based in France, that manufactures substrates used in the creation of semiconductors.
Microchip Technology Incorporated is a publicly listed American corporation that manufactures microcontroller, mixed-signal, analog, and Flash-IP integrated circuits. Its products include microcontrollers, Serial EEPROM devices, Serial SRAM devices, embedded security devices, radio frequency (RF) devices, thermal, power and battery management analog devices, as well as linear, interface and wireless products.
RF Micro Devices, was an American company that designed and manufactured high-performance radio frequency systems and solutions for applications that drive wireless and broadband communications. Headquartered in Greensboro, North Carolina, RFMD traded on the NASDAQ under the symbol RFMD. The Company was founded in Greensboro, North Carolina, in 1991. RF Micro had 3500 employees, 1500 of them in Guilford County, North Carolina.

The X-FAB Silicon Foundries is a group of semiconductor foundries. The group specializes in the fabrication of analog and mixed-signal integrated circuits for fabless semiconductor companies, as well as MEMS and solutions for high voltage applications. The holding company named "X-FAB Silicon Foundries SE" is based in Tessenderlo, Belgium while its headquarters is located in Erfurt, Germany.

Cadence Design Systems, Inc., is a multinational technology and computational software company. Headquartered in San Jose, California, Cadence was formed in 1988 through the merger of SDA Systems and ECAD. Initially specialized in electronic design automation (EDA) software for the semiconductor industry, currently the company makes software and hardware for designing products such as integrated circuits, systems on chips (SoCs), printed circuit boards, and pharmaceutical drugs, also licensing intellectual property for the electronics, aerospace, defense and automotive industries, among others.
The term die shrink refers to the scaling of metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) devices. The act of shrinking a die creates a somewhat identical circuit using a more advanced fabrication process, usually involving an advance of lithographic nodes. This reduces overall costs for a chip company, as the absence of major architectural changes to the processor lowers research and development costs while at the same time allowing more processor dies to be manufactured on the same piece of silicon wafer, resulting in less cost per product sold.

Silicon Laboratories, Inc. is a fabless global technology company that designs and manufactures semiconductors, other silicon devices and software, which it sells to electronics design engineers and manufacturers in Internet of Things (IoT) infrastructure worldwide.

MaxLinear is an American hardware company. Founded in 2003, it provides highly integrated radio-frequency (RF) analog and mixed-signal semiconductor products for broadband communications applications. It is a New York Stock Exchange-traded company.

Tower Semiconductor Ltd. is an Israeli company that manufactures integrated circuits using specialty process technologies, including SiGe, BiCMOS, Silicon Photonics, SOI, mixed-signal and RFCMOS, CMOS image sensors, non-imaging sensors, power management (BCD), and non-volatile memory (NVM) as well as MEMS capabilities. Tower Semiconductor also owns 51% of TPSCo, an enterprise with Nuvoton Technology Corporation Japan (NTCJ).
The IEEE International Electron Devices Meeting (IEDM) is an annual micro- and nanoelectronics conference held each December that serves as a forum for reporting technological breakthroughs in the areas of semiconductor and related device technologies, design, manufacturing, physics, modeling and circuit-device interaction.
Ronald Reedy is an American businessman, scientist and researcher. In the semiconductor industry, he advanced silicon on sapphire (SOS) and CMOS technology.
RF CMOS is a metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) integrated circuit (IC) technology that integrates radio-frequency (RF), analog and digital electronics on a mixed-signal CMOS RF circuit chip. It is widely used in modern wireless telecommunications, such as cellular networks, Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, GPS receivers, broadcasting, vehicular communication systems, and the radio transceivers in all modern mobile phones and wireless networking devices. RF CMOS technology was pioneered by Pakistani engineer Asad Ali Abidi at UCLA during the late 1980s to early 1990s, and helped bring about the wireless revolution with the introduction of digital signal processing in wireless communications. The development and design of RF CMOS devices was enabled by van der Ziel's FET RF noise model, which was published in the early 1960s and remained largely forgotten until the 1990s.








