
Bryozoa are a phylum of simple, aquatic invertebrate animals, nearly all living in sedentary colonies. Typically about 0.5 millimetres long, they have a special feeding structure called a lophophore, a "crown" of tentacles used for filter feeding. Most marine bryozoans live in tropical waters, but a few are found in oceanic trenches and polar waters. The bryozoans are classified as the marine bryozoans (Stenolaemata), freshwater bryozoans (Phylactolaemata), and mostly-marine bryozoans (Gymnolaemata), a few members of which prefer brackish water. 5,869 living species are known. Originally all of the crown group Bryozoa were colonial, but as an adaptation to a mesopsammal life or to deep-sea habitats, secondarily solitary forms have since evolved. Solitary species has been described in four genera; Aethozooides, Aethozoon, Franzenella and Monobryozoon). The latter having a statocyst-like organ with a supposed excretory function.

The Caribbean Sea is a sea of the North Atlantic Ocean in the tropics of the Western Hemisphere, located south of the Gulf of Mexico and southwest of the Sargasso Sea. It is bounded by the Greater Antilles to the north from Cuba to Puerto Rico, the Lesser Antilles to the east from the Virgin Islands to Trinidad and Tobago, South America to the south from the Venezuelan coastline to the Colombian coastline, and Central America and the Yucatán Peninsula to the west from Panama to Mexico. The geopolitical region centered around the Caribbean Sea, including the numerous islands of the West Indies and adjacent coastal areas in the mainland of the Americas, is known as the Caribbean.
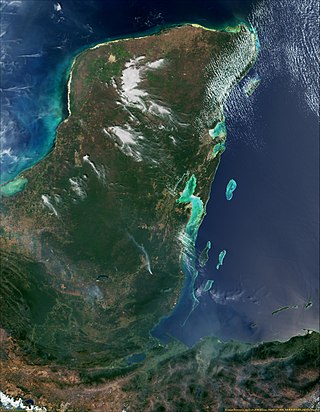
The Gulf or Bay of Honduras is a large inlet of the Caribbean Sea, indenting the coasts of Belize, Guatemala, and Honduras. From north to south, it runs for approximately 200 km from Dangriga, Belize, to La Ceiba, Honduras.

Pillar coral is a hard coral found in the western Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea. It is the only species in the monotypic genus Dendrogyra. It is a digitate coral -that is, it resembles fingers or a cluster of cigars, growing up from the sea floor without any secondary branching. It is large and can grow on both flat and sloping surfaces at depths down to 20 m (65 ft). It is one of the few types of hard coral in which the polyps can commonly be seen feeding during the day.

Porites astreoides, commonly known as mustard hill coral or yellow porites, is a colonial species of stony coral in the family Poritidae.
Bacalar Chico National Park and Marine Reserve (BCNPMR) is a protected area and UNESCO World Heritage Site on the northern part of Ambergris Caye in Belize.

Ecteinascidia turbinata, commonly known as the mangrove tunicate, is a species of tunicate in the family Perophoridae. It was described to science in 1880 by William Abbott Herdman. The cancer drug trabectedin can be isolated from this species.

Perophora is a sea squirt genus in the family Perophoridae. Most species are found in shallow warm water but a few are found in higher latitudes. A colony consists of a number of zooids which bud off from a long slender stolon.
Maritigrella crozierae, the tiger flatworm, is a species of marine polyclad flatworm in the family Euryleptidae. It is found on the eastern coasts of North America and the Caribbean Sea where it feeds on colonial sea squirts.

Didemnum molle is a species of colonial tunicate in the family Didemnidae. It is commonly known as the tall urn ascidian, the green barrel sea squirt or the green reef sea-squirt. It is native to the Red Sea and the tropical waters of the Indo-Pacific region.
Perophora viridis, the honeysuckle tunicate, is a species of colonial sea squirt in the genus Perophora found in the tropical western Atlantic Ocean.
Amathia vidovici is a species of colonial bryozoans with a tree-like structure. It is found in shallow waters over a wide geographical range, being found in both the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans and adjoining seas.
Lobophora variegata is a species of small thalloid brown alga which grows intertidally or in shallow water in tropical and warm temperate seas. It has three basic forms, being sometimes ruffled, sometimes reclining and sometimes encrusting, and each form is typically found in a different habitat. This seaweed occurs worldwide. It is the type species of the genus Lobophora, the type locality being the Antilles in the West Indies.

Amathia verticillata, commonly known as the spaghetti bryozoan, is a species of colonial bryozoans with a bush-like structure. It is found in shallow temperate and warm waters in the western Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea and has spread worldwide as a fouling organism. It is regarded as an invasive species in some countries.
Perophora multiclathrata is a species of colonial sea squirt in the genus Perophora. It is native to the tropical Indo-Pacific and the western Atlantic Ocean.
Dioithona oculata is a species of small crustacean, a marine copepod in the order Cyclopoida. It is native to the Indo-Pacific region but has spread to other parts of the world. It is a free-swimming epipelagic species found near the surface of the water. It was first described as Oithona oculata by the Irish zoologist George Philip Farran in 1913.

Cryptosula pallasiana is a species of colonial bryozoan in the order Cheilostomatida. It is native to the Atlantic Ocean where it occurs in northwestern Europe and northern Africa, and the eastern seaboard of North America. It has been accidentally introduced to the western coast of North America and to other parts of the world.

Zoothamnium niveum is a species of ciliate protozoan which forms feather-shaped colonies in marine coastal environments. The ciliates form a symbiosis with sulfur-oxidizing chemosynthetic bacteria of the species "Candidatus Thiobios zoothamnicoli", which live on the surface of the colonies and give them their unusual white color.

Caulerpa sertularioides, also known as green feather algae, is a species of seaweed in the Caulerpaceae family found in warm water environments.

Chorizopora brongniartii is a species of bryozoan in the family Chorizoporidae. It is an encrusting bryozoan, the colonies forming spreading patches. It has a widespread distribution in tropical and temperate seas.













