Related Research Articles

Bipolar disorder, previously known as manic depression, is a mood disorder characterized by periods of depression and periods of abnormally-elevated happiness that last from days to weeks each. If the elevated mood is severe or associated with psychosis, it is called mania; if it is less severe, it is called hypomania. During mania, an individual behaves or feels abnormally energetic, happy or irritable, and they often make impulsive decisions with little regard for the consequences. There is usually also a reduced need for sleep during manic phases. During periods of depression, the individual may experience crying and have a negative outlook on life and poor eye contact with others. The risk of suicide is high; over a period of 20 years, 6% of those with bipolar disorder died by suicide, while 30–40% engaged in self-harm. Other mental health issues, such as anxiety disorders and substance use disorders, are commonly associated with bipolar disorder.

Kay Redfield Jamison is an American clinical psychologist and writer. Her work has centered on bipolar disorder, which she has had since her early adulthood. She holds the post of the Dalio Professor in Mood Disorders and Psychiatry at Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine and is an Honorary Professor of English at the University of St Andrews.
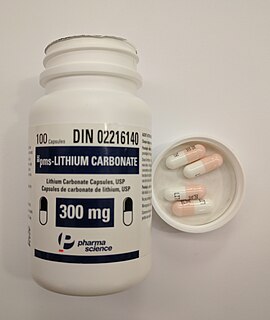
A mood stabilizer is a psychiatric medication used to treat mood disorders characterized by intense and sustained mood shifts, such as bipolar disorder and the bipolar type of schizoaffective disorder.
Schizoaffective disorder is a mental disorder characterized by abnormal thought processes and an unstable mood. This diagnosis is made when the person has symptoms of both schizophrenia and a mood disorder: either bipolar disorder or depression. The main criterion for a diagnosis of schizoaffective disorder is the presence of psychotic symptoms for at least two weeks without any mood symptoms present. Schizoaffective disorder can often be misdiagnosed when the correct diagnosis may be psychotic depression, bipolar I disorder, schizophreniform disorder, or schizophrenia. It is imperative for providers to accurately diagnose patients, as treatment and prognosis differ greatly for each of these diagnoses.
Biological psychiatry or biopsychiatry is an approach to psychiatry that aims to understand mental disorder in terms of the biological function of the nervous system. It is interdisciplinary in its approach and draws on sciences such as neuroscience, psychopharmacology, biochemistry, genetics, epigenetics and physiology to investigate the biological bases of behavior and psychopathology. Biopsychiatry is the branch of medicine which deals with the study of the biological function of the nervous system in mental disorders.
The emphasis of the treatment of bipolar disorder is on effective management of the long-term course of the illness, which can involve treatment of emergent symptoms. Treatment methods include pharmacological and psychological techniques.
Cyclical variations in moods and energy levels have been recorded at least as far back as several thousand years. The words "melancholia" and "mania" have their etymologies in Ancient Greek. The word melancholia is derived from melas/μελας, meaning "black", and chole/χολη, meaning "bile" or "gall", indicative of the term's origins in pre-Hippocratic humoral theories. A man known as Aretaeus of Cappadocia has the first records of analyzing the symptoms of depression and mania in the 1st century of Greece. There is documentation that explains how bath salts were used to calm those with manic symptoms and also help those who are dealing with depression. Even today, lithium is used as a treatment to bipolar disorder which is significant because lithium could have been an ingredient in the Greek bath salt. Centuries passed and very little was studied or discovered. It wasn't until the mid-19th century that a French psychiatrist by the name of Jean-Pierre Falret wrote an article describing "circular insanity" and this is believed to be the first recorded diagnosis of bipolar disorder. Years later, in the early 1900s, Emil Kraepelin, a German psychiatrist, analyzed the influence of biology on mental disorders, including bipolar disorder. His studies are still used as the basis of classification of mental disorders today.
Bipolar disorder in children, or pediatric bipolar disorder (PBD), is a controversial mental disorder in children and adolescents that is mainly diagnosed in the United States, and is hypothesized to be like bipolar disorder (BD) in adults, thus is proposed as an explanation for extreme changes in mood and behavior accompanying periods of depressed or irritable moods and periods of elevated moods so called manic or hypomanic episodes. These shifts are sometimes quick, but usually are gradual. The average age of onset of pediatric bipolar disorder is unclear, but the risk increases with the onset of puberty. Bipolar disorder is rare in childhood. Pediatric bipolar disorder is typically more severe and has a poorer prognosis than bipolar disorder with onset in late-adolescence or adulthood.

Dennis S. Charney is an American biological psychiatrist and researcher, with expertise in the neurobiology and treatment of mood and anxiety disorders. He is the author of Neurobiology of Mental Illness, The Physician's Guide to Depression and Bipolar Disorders and Molecular Biology for the Clinician, as well as the author of over 600 original papers and chapters.
Guy Goodwin is a senior research fellow and until recently was the W.A. Handley Professor of Psychiatry at the University of Oxford (2014). A fellow of the Academy of Medical Sciences, Goodwin has served as principal investigator in many clinical trials for the treatment of bipolar disorder. He is also an Emeritus Senior Investigator at the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) and has been on the advisory boards of numerous research councils. He was President of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology from 2013 to 2016.

Philip Manley Boyce is an Australian psychiatrist. He is a professor of psychiatry and head of discipline of psychiatry at the University of Sydney, and head of Perinatal Psychiatry Clinical Research Unit at Westmead Hospital. He has published more than 170 articles, and frequently contributes to psychiatric textbooks. He currently serves as associate editor of Australian and New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry. He has a long clinical and research interest in anxiety disorders, mood disorders, psychosomatic disorders, and perinatal psychiatry. He has also taken leadership roles in the profession as president of the RANZCP and the international Marcé society, in the development of clinical practice guidelines, and in the development of a competency-based training program for the college.
Ronald Robert Fieve was an American psychiatrist known for his work on the use of lithium in treatment of mood disorders. He has authored four popular science books, "Moodswing", "Bipolar II", "Prozac" and "Bipolar Breakthrough".
Augustus John Rush is an internationally renowned psychiatrist. He is a professor emeritus in Duke-NUS Medical School at the National University of Singapore (NUS), and adjunct professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Duke University School of Medicine. He has authored and edited more than 10 books, and over 600 scientific journal articles that are largely focused on the diagnosis and treatment of depressive and bipolar disorders.

Lori Altshuler was a Professor at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA) Department of Psychiatry and Biobehavioral Sciences and held the Julia S. Gouw Endowed Chair for Mood Disorders. Altshuler was the Director of the UCLA Mood Disorders Research Program and the UCLA Women's Life Center, each being part of the Neuropsychiatric Hospital at UCLA.
Ellen Frank is a psychologist and Distinguished Professor Emeritus of Psychiatry and Distinguished Professor of Psychology at the University of Pittsburgh. She is known in the field of Psychotherapy as one of the developers of Interpersonal and Social Rhythm Therapy, which aims to treat bipolar disorder by correcting disruptions in the circadian rhythm while promoting increased regularity of daily social routines. Frank is the co-founder and Chief Scientific Officer of HealthRhythms, a company that uses mobile technology to monitor the health and mental health of clients, facilitate the detection of changes in their status, and better manage mental health conditions.
Gregor Hasler, M.D. is a Swiss psychiatry researcher, psychiatrist and psychotherapist. He is professor and chair of psychiatry and psychotherapy at the University of Fribourg (Switzerland). His research areas covers stress, depression, bipolar disorders, and eating disorders.
Secondary mania, also known as organic mania, is a variation of bipolar disorder that is caused by physical trauma or illness. Bipolar disorder has a one percent prevalence rate in the United States and secondary mania is likely a small subset of that percentage. Secondary mania exhibits symptoms similar to that of mania in bipolar I and bipolar II disorders. This includes an elevated mood or affect, psychotic state, accelerated speech, increased motor activity, irritability, and flight ideas. A unique criterion for secondary mania is the lack of history of mental illness that causes mania, such as bipolar disorder. Unlike bipolar disorder, which has an average age of onset at 25 years, secondary mania has an average age of onset at 45 years. Little is known about secondary mania, as much of the research on it is case studies and retrospective accounts. However, it has been connected to several causes such as traumatic brain injury, HIV/AIDS, and stroke.

Prof. Robert Haim Belmaker, is an Israeli psychiatrist who has had major academic positions in Israeli psychiatry since 1974. He had a formative influence on biological directions in Israeli psychiatry. He was Hoffer-Vickar Professor of Psychiatry at Ben-Gurion University of the Negev, Beersheva Israel until his retirement and is now Emeritus.
Mauricio Tohen is a Mexican American research psychiatrist, Distinguished Professor, and Chairman of the Department of Psychiatry & Behavioral Sciences at the University of New Mexico. Tohen's research has focused on the epidemiology, outcome, and treatment of bipolar and psychotic disorders, and is especially known for innovating the design of clinical trials and the criteria to determine outcome in such diseases. Tohen has edited several books on his specialties. His social awareness has been noted in the promotion of programs to improve mental health care in areas such as substance abuse, bipolar disorder and schizophrenia.
Susan Lynn McElroy is Chief Research Officer at Lindner Center of HOPE.
References
- ↑ Altman, Lawrence K.; M.D. (21 May 1991). "THE DOCTOR'S WORLD; President's Thyroid: Questions Of Mood". The New York Times. p. 1. Retrieved 5 June 2011.