
Butterflies are insects in the macrolepidopteran clade Rhopalocera from the order Lepidoptera, which also includes moths. Adult butterflies have large, often brightly coloured wings, and conspicuous, fluttering flight. The group comprises the large superfamily Papilionoidea, which contains at least one former group, the skippers, and the most recent analyses suggest it also contains the moth-butterflies. Butterfly fossils date to the Paleocene, about 56 million years ago.

Lepidoptera is an order of insects that includes butterflies and moths. About 180,000 species of the Lepidoptera are described, in 126 families and 46 superfamilies, 10 percent of the total described species of living organisms. It is one of the most widespread and widely recognizable insect orders in the world. The Lepidoptera show many variations of the basic body structure that have evolved to gain advantages in lifestyle and distribution. Recent estimates suggest the order may have more species than earlier thought, and is among the four most speciose orders, along with the Hymenoptera, Diptera, and Coleoptera.

Moths are a paraphyletic group of insects that includes all members of the order Lepidoptera that are not butterflies, with moths making up the vast majority of the order. There are thought to be approximately 160,000 species of moth, many of which have yet to be described. Most species of moth are nocturnal, but there are also crepuscular and diurnal species.

Biological control or biocontrol is a method of controlling pests, such as insects, mites, weeds, and plant diseases, using other organisms. It relies on predation, parasitism, herbivory, or other natural mechanisms, but typically also involves an active human management role. It can be an important component of integrated pest management (IPM) programs.

The Sphingidae are a family of moths (Lepidoptera) called sphinx moths, also colloquially known as hawk moths, with many of their caterpillars known as “hornworms”; it includes about 1,450 species. It is best represented in the tropics, but species are found in every region. They are moderate to large in size and are distinguished among moths for their agile and sustained flying ability, similar enough to that of hummingbirds as to be reliably mistaken for them. Their narrow wings and streamlined abdomens are adaptations for rapid flight. The family was named by French zoologist Pierre André Latreille in 1802.

The Hepialidae are a family of insects in the lepidopteran order. Moths of this family are often referred to as swift moths or ghost moths.

Pharmacis is a genus of moths of the family Hepialidae. There are eight described species found in Eurasia.

The 2016 UEFA European Football Championship, commonly referred to as UEFA Euro 2016 or simply Euro 2016, was the 15th UEFA European Championship, the quadrennial international men's football championship of Europe organised by UEFA. It was held in France from 10 June to 10 July 2016. Spain were the two-time defending champions, having won the 2008 and 2012 tournaments, but were eliminated in the round of 16 by Italy. Portugal won the tournament for the first time, following a 1–0 victory after extra time over the host team, France, in the final played at the Stade de France.

The gold swift is a moth belonging to the family Hepialidae. Until recently it was placed in the genus Hepialus. The species was first described by Carl Linnaeus in his 1758 10th edition of Systema Naturae. Moths of the Hepialidae are considered to be primitive moths; they do not have a proboscis and are unable to feed. The gold swift is a widespread species found in Europe and Asia, including Japan.

The map-winged swift is a moth belonging to the family Hepialidae and has a patchy distribution throughout Eurasia. The species was first described by Charles De Geer in 1778. It was previously placed in the genus Hepialus and some references still place it there.

Eugnosta is a genus of moths belonging to the family Tortricidae.

Pharmacis carna is a moth of the family Hepialidae. It is mainly found in mountainous areas, mostly in the Alps and the Carpathian Mountains, although it is also present in Hungary.

Pharmacis aemilianus is a moth of the family Hepialidae. It is known from Italy.
Pharmacis anselminae is a moth of the family Hepialidae. It is known from Italy.
Pharmacis castillanus is a moth of the family Hepialidae. It is known from Spain.
Pharmacis claudiae is a moth of the family Hepialidae. It is known from Italy.
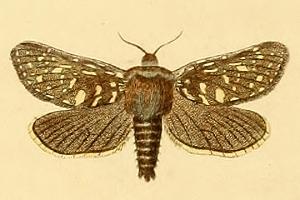
Pharmacis pyrenaicus is a moth of the family Hepialidae. It is known from France and Spain.
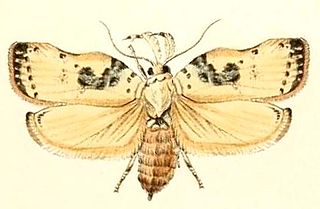
Tonica is a genus of moths of the family Depressariidae.
Tonica pharmacis is a moth in the family Depressariidae. It was described by Alexey Diakonoff in 1966. It is found on Sumatra.
Hugues-Fleury Donzel was a French entomologist specialising in butterflies and moths.












