
The zebu, sometimes known in the plural as indicine cattle, Camel cow or humped cattle, is a species or subspecies of domestic cattle originating in South Asia. Zebu, like many Sanga cattle breeds, differs from taurine cattle by a fatty hump on their shoulders, a large dewlap, and sometimes drooping ears. They are well adapted to withstanding high temperatures and are farmed throughout the tropics.

The red-wattled lapwing is an Asian lapwing or large plover, a wader in the family Charadriidae. Like other lapwings they are ground birds that are incapable of perching. Their characteristic loud alarm calls are indicators of human or animal movements and the sounds have been variously rendered as did he do it or pity to do it leading to the colloquial name of did-he-do-it bird. Usually seen in pairs or small groups not far from water, they sometimes form large aggregations in the non-breeding season (winter). They nest in a ground scrape laying three to four camouflaged eggs. Adults near the nest fly around, diving at potential predators while calling noisily. The cryptically patterned chicks hatch and immediately follow their parents to feed, hiding by lying low on the ground or in the grass when threatened.

The Indian prawn is one of the major commercial prawn species of the world. It is found in the Indo-West Pacific from eastern and south-eastern Africa, through India, Malaysia and Indonesia to southern China and northern Australia. Adult shrimp grow to a length of about 22 cm (9 in) and live on the seabed to depths of about 90 m (300 ft). The early developmental stages take place in the sea before the larvae move into estuaries. They return to the sea as sub-adults.

The Malayan tapir, also called Asian tapir, Asiatic tapir, oriental tapir, Indian tapir, piebald tapir, or black-and-white tapir, is the only living Tapir species outside of the Americas. It is native to Southeast Asia from the Malay Peninsula to Sumatra. It has been listed as Endangered on the IUCN Red List since 2008, as the population is estimated to comprise fewer than 2,500 mature individuals.
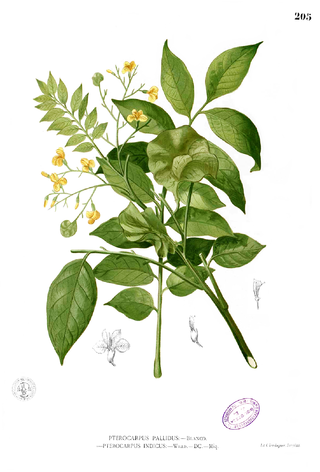
Pterocarpus indicus is a species of Pterocarpus native to southeastern Asia, northern Australasia, and the western Pacific Ocean islands, in Cambodia, southernmost China, East Timor, Indonesia, Malaysia, Papua New Guinea, the Philippines, the Ryukyu Islands, the Solomon Islands, Thailand, and Vietnam.

The smallbelly catshark is a catshark of the family Scyliorhinidae found in the western Indian Ocean near Somalia, the Gulf of Aden, and Oman, at depths between 1,300 and 1,840 m. Its length is up to 34 cm, although this measurement is of an immature specimen. The smallbelly catshark is not well known. It is found on continental slopes, and is probably caught by bottom trawlers. The reproduction of the smallbelly catshark is oviparous.

The Bankeraceae are a family of fungi in the order Thelephorales. Taxa are terrestrial, and ectomycorrhizal with plant species in families such as Pinaceae or Fagaceae. The family was circumscribed by Marinus Anton Donk in 1961. According to a 2008 estimate, the family contains 6 genera and 98 species.

Phellodon is a genus of tooth fungi in the family Bankeraceae. Species have small- to medium-sized fruitbodies with white spines on the underside from which spores are released. All Phellodon have a short stalk or stipe, and so the genus falls into the group known as stipitate hydnoid fungi. The tough and leathery flesh usually has a pleasant, fragrant odor, and develops a cork-like texture when dry. Neighboring fruitbodies can fuse, sometimes producing large mats of joined caps. Phellodon species produce a white spore print, while the individual spores are roughly spherical to ellipsoid in shape, with spiny surfaces.

Phellodon sinclairii is a native tooth fungus found in beech forests of New Zealand. It was first described by Miles Joseph Berkeley in 1867 as a species of Hydnum in Joseph Dalton Hooker's work Handbook of the New Zealand Flora. The type locality was on Maungatua. Gordon Herriot Cunningham transferred the species to the genus Phellodon in 1958.

Phellodon secretus is a rare species of tooth fungus in the family Bankeraceae. Described as new to science in 2003, it is found in Finland, where it grows under the fallen trunks of pine trees. It somewhat resembles Phellodon connatus, but has a thinner stipe, a softer, cotton-like cap, and smaller, rounder spores.
Phellodon putidus is a species of tooth fungus in the family Bankeraceae. Found in North America, it was first described scientifically by George F. Atkinson as Hydnum putidum in 1900. Howard James Banker transferred it to the genus Phellodon in 1906.
Phellodon tenuis is a species of tooth fungus in the family Bankeraceae. Found in Brazil, it was described as new to science in 1988 by Richard Baird.
Phellodon mississippiensis is a species of tooth fungus in the family Bankeraceae. It was described as new to science by mycologist Richard Baird in 2014 from collections made in the Tombigbee National Forest in Mississippi. It is one of the few Phellodon species with clamp connections in the hyphae.

Phellodon atratus is a species of tooth fungus in the family Bankeraceae. Found in North America, it was described as new to science in 1964 by Canadian mycologist Kenneth A. Harrison. It occurs most frequently closer to the Pacific coast and under Sitka spruce.
Phellodon fibulatus is a species of tooth fungus in the family Bankeraceae. Found in the United States, the fungus was described as new to science in 1972 by Canadian mycologist Kenneth A. Harrison. It is one of the few species of Phellodon that possess clamp connections in its hyphae.
Phellodon maliensis is a species of tooth fungus in the family Bankeraceae. Found in Australia, it was originally described as a new species by Curtis Gates Lloyd in 1923. It was originally placed in Hydnum, until Dutch mycologist Rudolph Arnold Maas Geesteranus transferred it to the genus Phellodon in 1966.

Phellodon niger, commonly known as the black tooth, is a species of tooth fungus in the family Bankeraceae, and the type species of the genus Phellodon. It was originally described by Elias Magnus Fries in 1815 as a species of Hydnum. Petter Karsten included it as one of the original three species when he circumscribed Phellodon in 1881. The fungus is found in Europe and North America, although molecular studies suggest that the North American populations represent a similar but genetically distinct species.

Phellodon confluens, commonly known as the fused cork hydnum, is a species of tooth fungus in the family Bankeraceae. It was originally described in 1825 as Hydnum confluens by Christiaan Hendrik Persoon. Czech mycologist Zdenek Pouzar transferred it to the genus Phellodon in 1956. The fungus is found in Asia, Europe, and North America. It is considered vulnerable in Switzerland.

Phellodon melaleucus, commonly known as the grey tooth, is a species of tooth fungus in the family Bankeraceae. It was originally described by Elias Magnus Fries in 1815 as a species of Hydnum. In 1881, Petter Karsten included it as one of the original three species in his newly circumscribed genus Phellodon. The fungus is widely distributed in Europe and North America, where it associates mycorrhizally with a wide range of host trees. It is considered vulnerable in Switzerland.












