
The Dytiscidae – based on the Greek dytikos (δυτικός), "able to dive" – are the predaceous diving beetles, a family of water beetles. They occur in virtually any freshwater habitat around the world, but a few species live among leaf litter. The adults of most are between 1 and 2.5 cm (0.4–1.0 in) long, though much variation is seen between species. The European Dytiscus latissimus and Brazilian Megadytes ducalis are the largest, reaching up to 4.5 and 4.75 cm respectively. In contrast, the smallest is likely the Australian Limbodessus atypicali of subterranean waters, which only is about 0.9 mm (0.035 in) long. Most are dark brown, blackish, or dark olive in color with golden highlights in some subfamilies. The larvae are commonly known as water tigers due to their voracious appetite. They have short, but sharp mandibles and immediately upon biting, they deliver digestive enzymes into prey to suck their liquefied remains. The family includes more than 4,000 described species in numerous genera.

Copelatus is a large genus of small diving beetles. There are some 470 described species in the genus, found worldwide, but they are most diverse in tropical South America, Africa and South-East Asia. Copelatus are often black or brown in color, many species of Copelatus possessing visible longitudinal furrows down the dorsal side of the wings of both sexes.

Rhantus is a genus of beetle in family Dytiscidae. There are about 100 species distributed worldwide. They often live in pools and marshy habitat types. Several species have colonized oceanic islands and become endemics.

Laccophilus is a genus of water beetle found in nearly every temperate or tropical region in the world including but not limited to Europe, the Near East, the Nearctic, North Africa and the Oriental region. It contains the following species:

Hyphydrus is a genus of diving beetle native to the Palearctic, the Afro-tropical region, the Near East, North Africa. It contains the following species:
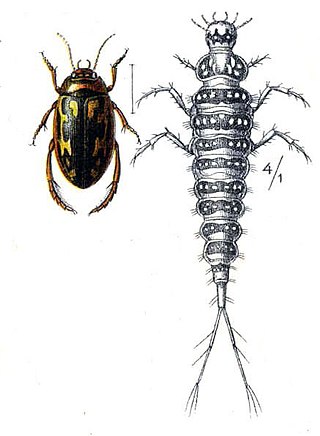
Platambus is a genus of beetle native to the Palearctic, including Europe, the Near East and North Africa. It distinguished by a wide epipleuron. The ventral surface has spot markings.

Hydaticus is a genus of predatory water beetle belonging to the family Dytiscidae. Hydaticus can be found throughout most of the world. There are 150 described species and 12 subspecies in two subgenera in the genus Hydaticus.

Platynectes is a genus of beetles in the family Dytiscidae, containing the following species:

Coptotomus is a genus of predaceous diving beetles in the family Dytiscidae, the only genus of the subfamily Coptotominae. There are about six described species in Coptotomus, found in North America and the Neotropics.

Prodaticus is a subgenus of beetles of the genus Hydaticus in the family Dytiscidae. These 143 species are in the subgenus Prodaticus:
Clypeodytes is a genus of beetles in the family Dytiscidae, containing the following species:
Agnoshydrus is a genus of beetles in the family Dytiscidae, containing the following eight species:

Neptosternus is a genus of diving beetles in the family Dytiscidae. There are more than 90 described species in Neptosternus, found mainly in Africa and Southern Asia.
Copelatus masculinus is a species of diving beetle. It is part of the genus Copelatus, which is in the subfamily Copelatinae of the family Dytiscidae. It was described by Régimbart in 1899.
Carabdytes plantaris is a naturally uncommon species of diving beetle in the family Dytiscidae. It is endemic to New Zealand. For over a century, it was known from just a single specimen collected in 1880 "near Dunedin", and doubts were cast on whether it was actually a New Zealand species at all. In 1986, it was rediscovered when several were collected from a roadside pond near Lake Ellesmere. Carabdytes plantaris is now classed as "naturally uncommon" by the Department of Conservation.

Laccophilinae is a subfamily of ground and water beetles in the family Dytiscidae. There are at least 410 described species in Laccophilinae.
Bidessini is a tribe of predaceous diving beetles in the family Dytiscidae. There are at least 40 genera and at least 630 described species in Bidessini.

Neobidessodes is a genus of predaceous diving beetles in the family Dytiscidae. There are about 10 described species in Neobidessodes. They are found in Australasia. The genus was first described in 2009, and the type species is N. denticulatus.
Hydrovatus lyratus, is a species of predaceous diving beetle widespread in South Asia, South East Asia and Australian region.













