In chemistry, the term phosphonium describes polyatomic cations with the chemical formula PR+
4. These cations have tetrahedral structures. The salts are generally colorless or take the color of the anions.

Triphenylphosphine (IUPAC name: triphenylphosphane) is a common organophosphorus compound with the formula P(C6H5)3 and often abbreviated to PPh3 or Ph3P. It is versatile compound that is widely used as a reagent in organic synthesis and as a ligand for transition metal complexes, including ones that serve as catalysts in organometallic chemistry. PPh3 exists as relatively air stable, colorless crystals at room temperature. It dissolves in non-polar organic solvents such as benzene and diethyl ether.

Phosphorous acid is the compound described by the formula H3PO3. This acid is diprotic, not triprotic as might be suggested by this formula. Phosphorous acid is an intermediate in the preparation of other phosphorus compounds. Organic derivatives of phosphorous acid, compounds with the formula RPO3H2, are called phosphonic acids.

Lawesson's reagent (LR) is a chemical compound used in organic synthesis as a thiation agent. Lawesson's reagent was first made popular by Sven-Olov Lawesson, who did not, however, invent it. Lawesson's reagent was first made in 1956 during a systematic study of the reactions of arenes with P4S10.

A phosphorane (IUPAC name: λ5-phosphane) is a functional group in organophosphorus chemistry with pentavalent phosphorus. Phosphoranes have the general formula PR5.
Organophosphorus chemistry is the scientific study of the synthesis and properties of organophosphorus compounds, which are organic compounds containing phosphorus. They are used primarily in pest control as an alternative to chlorinated hydrocarbons that persist in the environment. Some organophosphorus compounds are highly effective insecticides, although some are extremely toxic to humans, including sarin and VX nerve agents.
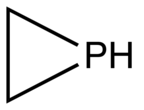
Phosphole is the organic compound with the chemical formula C
4H
4PH; it is the phosphorus analog of pyrrole. The term phosphole also refers to substituted derivatives of the parent heterocycle. These compounds are of theoretical interest but also serve as ligands for transition metals and as precursors to more complex organophosphorus compounds.

Dicarbon monoxide is a molecule that contains two carbon atoms and one oxygen atom. It is a linear molecule that, because of its simplicity, is of interest in a variety of areas. It is, however, so extremely reactive that it is not encountered in everyday life. It is classified as a carbene, cumulene and an oxocarbon.

Triphenylphosphine oxide (often abbreviated TPPO) is the organophosphorus compound with the formula OP(C6H5)3, also written as Ph3PO or PPh3O (Ph = C6H5). This colourless crystalline compound is a common but potentially useful waste product in reactions involving triphenylphosphine. It is a popular reagent to induce the crystallizing of chemical compounds.

Trimethylphosphine is an organophosphorus compound with the formula P(CH3)3, commonly abbreviated as PMe3. This colorless liquid has a strongly unpleasant odor, characteristic of alkylphosphines. The compound is a common ligand in coordination chemistry.
Organophosphines are organophosphorus compounds with the formula PRnH3−n, where R is an organic substituent. These compounds can be classified according to the value of n: primary phosphines (n = 1), secondary phosphines (n = 2), tertiary phosphines (n = 3). All adopt pyramidal structures. Organophosphines are generally colorless, lipophilic liquids or solids. The parent of the organophosphines is phosphine (PH3).

Triphenyl phosphite is the organophosphorus compound with the formula P(OC6H5)3. It is a colourless viscous liquid.

Triethyl phosphite is an organophosphorus compound, specifically a phosphite ester, with the formula P(OCH2CH3)3, often abbreviated P(OEt)3. It is a colorless, malodorous liquid. It is used as a ligand in organometallic chemistry and as a reagent in organic synthesis.

Diphenylphosphine, also known as diphenylphosphane, is an organophosphorus compound with the formula (C6H5)2PH. This foul-smelling, colorless liquid is easily oxidized in air. It is a precursor to organophosphorus ligands for use as catalysts.
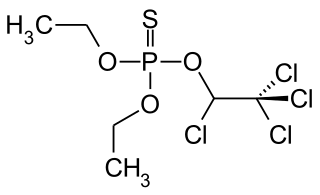
Chlorethoxyfos is an organophosphate acetylcholinesterase inhibitor used as an insecticide. It is registered for the control of corn rootworms, wireworms, cutworms, seed corn maggot, white grubs and symphylans on corn. The insecticide is sold under the trade name Fortress by E.I. du Pont de Nemours & Company.

Tetraethyl pyrophosphate, abbreviated TEPP, is an organophosphate compound with the formula [(C2H5O)2P(O)]2O. It is the tetraethyl derivative of pyrophosphate (P2O74-). It is a colorless oil that solidifies near room temperature. It is used as an insecticide. The compound hydrolyzes rapidly.

Dimethylphosphite is an organophosphorus compound with the formula (CH3O)2P(O)H, known as dimethyl hydrogen phosphite (DMHP). Dimethylphosphite, is a minor tautomer of the phosphorus(V) derivative. It is a reagent for generating other organophosphorus compounds, exploiting the high reactivity of the P-H bond. The molecule is tetrahedral. It is a colorless liquid. The compounds can be prepared by methanolysis of phosphorus trichloride or by heating diethylphosphite in methanol.
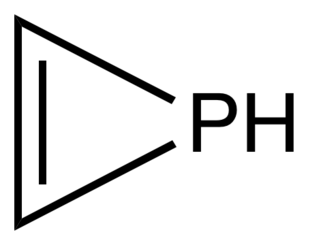
Phosphirene is the hypothetical organophosphorus compound with the formula C2H2PH. As the simplest cyclic, unsaturated organophosphorus compound, phosphirene is the prototype of a family of related compounds that have attracted attention from researchers.
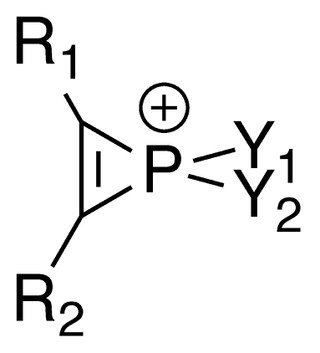
Phosphirenium ions are a series of organophosphorus compounds containing unsaturated three-membered ring phosphorus (V) heterocycles and σ*-aromaticity is believed to be present in such molecules. Many of the salts containing phosphirenium ions have been isolated and characterized by NMR spectroscopy and X-ray crystallography.

Methylfluorophosphonylcholine (MFPCh) is an extremely toxic chemical compound related to the G-series nerve agents. It is an extremely potent acetylcholinesterase inhibitor which is around 100 times more potent than sarin at inhibiting acetylcholinesterase in vitro, and around 10 times more potent in vivo, depending on route of administration and animal species tested. MFPCh is resistant to oxime reactivators, meaning the acetylcholinesterase inhibited by MFPCh can't be reactivated by cholinesterase reactivators. MFPCh also acts directly on the acetylcholine receptors. However, despite its high toxicity, methylfluorophosphonylcholine is a relatively unstable compound and degrades rapidly in storage, so it was not deemed suitable to be weaponised for military use.